Girls’ education in STEM has long been a topic marked by significant gender differences. Despite the growing importance of STEM fields in today’s world, girls often face various barriers that hinder their full participation. Understanding these gender differences and implementing effective teaching methods is crucial for creating a more inclusive and equitable learning environment.

The Gender Gap in STEM Education
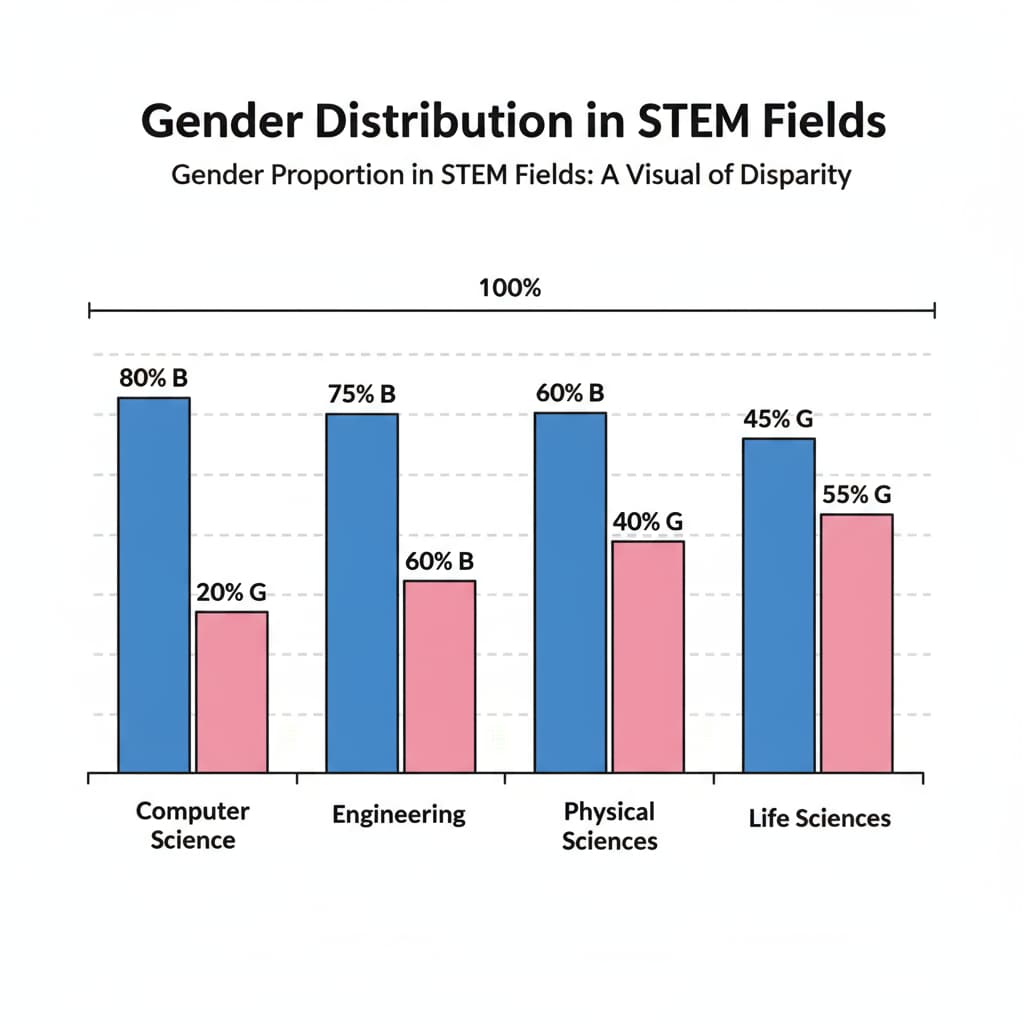
The underrepresentation of girls in STEM subjects is a well-documented issue. For example, fewer girls choose to study advanced mathematics, physics, or computer science compared to boys. This gap can be traced back to several factors. Social stereotypes play a major role. From a young age, girls are often steered towards more “feminine” fields, while STEM is commonly associated with masculinity. According to Wikipedia’s page on Gender Inequality in Education, these stereotypes can influence girls’ self-perception and career aspirations.
Root Causes of Gender Differences
In addition to social stereotypes, the lack of female role models in STEM can also have a negative impact on girls’ interest. When girls do not see women excelling in these fields, they may be less likely to pursue STEM careers themselves. Moreover, the teaching environment and curriculum can sometimes be unfriendly to girls. Traditional teaching methods that rely heavily on rote learning may not engage girls as effectively as more interactive and project-based approaches. As stated on Britannica’s education page, adapting teaching methods to better suit different learning styles is essential.
Another contributing factor is the lack of early exposure to STEM concepts. Many girls miss out on hands-on experiences in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics during their formative years. This early exposure is crucial for sparking interest and building confidence in these subjects.
Readability guidance: Here we have clearly presented the main factors contributing to the gender gap in STEM education, using short paragraphs for better readability. Each factor is introduced with a transition word like “moreover” or “another” to make the flow smooth.
Effective Teaching Strategies
- Integrate real-world examples: By connecting STEM concepts to everyday life, girls can better understand the relevance and practical applications of these subjects. For instance, using examples of how technology is used in fashion or how engineering principles are applied in building sustainable homes.
- Encourage group work: Group projects allow girls to collaborate, share ideas, and learn from their peers. This can boost their confidence and teamwork skills, which are valuable in STEM fields.
- Provide mentorship: Pairing girls with female STEM professionals can give them role models and insights into the real-world experiences of women in these fields.
Creating an Inclusive Learning Environment
Educators should strive to create a classroom environment that is inclusive and welcoming to all students. This includes using gender-neutral language, avoiding gender-biased teaching materials, and promoting equal participation. Teachers can also organize STEM-related extracurricular activities, such as science clubs or robotics competitions, to engage girls outside of the regular curriculum.
In conclusion, addressing the gender differences in girls’ education in STEM requires a multi-faceted approach. By understanding the root causes, implementing effective teaching strategies, and creating an inclusive learning environment, we can inspire more girls to pursue STEM careers and bridge the gender gap in these important fields.

Readability guidance: In this section, we have used bullet points to clearly list the teaching strategies, making it easier for readers to scan and understand. Short paragraphs are also used to maintain readability, and transition words like “in conclusion” help to summarize the overall message.


