One of the key challenges students face in the Functional Skills English reading exam is identifying the purpose of a text. Whether the text is informational, explanatory, or persuasive, understanding its intent is crucial for answering questions correctly. This article delves into the features of each text type and provides actionable strategies to help students improve their reading comprehension and excel in the exam.
Understanding Text Purposes: Informational, Explanatory, and Persuasive
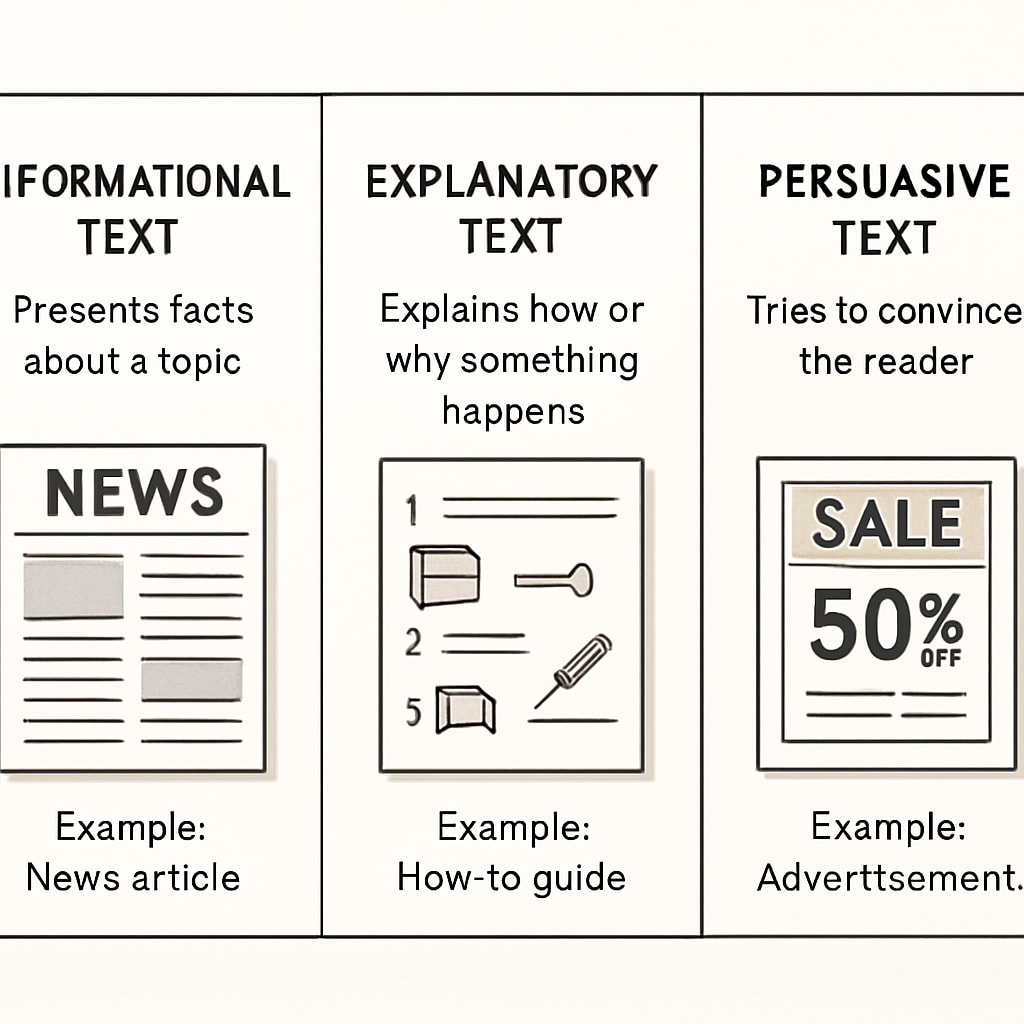
Texts are often written with specific purposes in mind, and recognizing these purposes is essential for comprehension. The three most common text purposes are informational, explanatory, and persuasive. Each has distinct characteristics that can guide readers in identifying them:
- Informational Texts: These are designed to convey facts or data. Examples include news articles, reports, or instructions. Look for clear, factual language and minimal opinion.
- Explanatory Texts: These aim to clarify or explain a concept or process. Think of manuals, tutorials, or scientific explanations. They often include step-by-step details or definitions.
- Persuasive Texts: These are intended to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint or action. Advertisements, opinion pieces, and speeches fall under this category. Expect emotional language, rhetorical questions, and strong arguments.
Strategies for Identifying Text Purpose
Recognizing the purpose of a text requires close reading and critical thinking. Here are practical strategies to help students determine the intent of any given text:
- Analyze the Language: Pay attention to word choice and tone. Neutral and factual language often signals informational texts, while emotional or opinionated language indicates persuasion.
- Examine Structure: Check how the text is organized. Explanatory texts frequently use headings, bullet points, or numbered lists to break down information systematically.
- Identify the Target Audience: Consider who the text is written for. Persuasive texts often target specific audiences, using tailored arguments to appeal to their interests.
- Look for Visual Cues: Images, charts, or bold headlines can provide hints about the text’s purpose. For example, an infographic might be informational, while bold slogans may suggest persuasion.

Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Students often struggle with distinguishing between similar text types or misinterpreting the author’s intent. Here are some tips to overcome common challenges:
- Don’t Overthink: Focus on the main message rather than getting lost in minor details.
- Practice with Examples: Reviewing various text samples can help in recognizing patterns and features unique to each purpose.
- Use Context Clues: Consider the broader context of the text, such as its format or where it appears (e.g., a newspaper or a blog).
- Eliminate Distractions: Avoid assumptions based on personal opinions; stick to the information provided in the text.
By applying these strategies, students can develop a systematic approach to identifying text purposes and increase their confidence in tackling exam questions effectively.
Conclusion
Mastering text purpose identification is a vital skill for succeeding in the Functional Skills English reading exam. By understanding the characteristics of informational, explanatory, and persuasive texts and applying practical strategies, students can improve their comprehension and achieve better results. Practice regularly and stay focused on the text’s intent—success is within reach!
For additional resources on Functional Skills English reading, visit Reading Comprehension on Wikipedia or explore Reading Skills on Britannica.


