RPN calculators, also known as Reverse Polish Notation calculators, are transforming the way students engage with mathematical calculations. Unlike traditional calculators that rely on infix notation (e.g., 3 + 4), RPN calculators use a postfix method, requiring operands to precede operators. This unique approach offers a range of advantages, including improved calculation efficiency, reduced errors, and the development of logical thinking skills. As a result, they are poised to reshape K-12 mathematics education and encourage a more intuitive approach to problem-solving.
What is Reverse Polish Notation and How Does It Work?
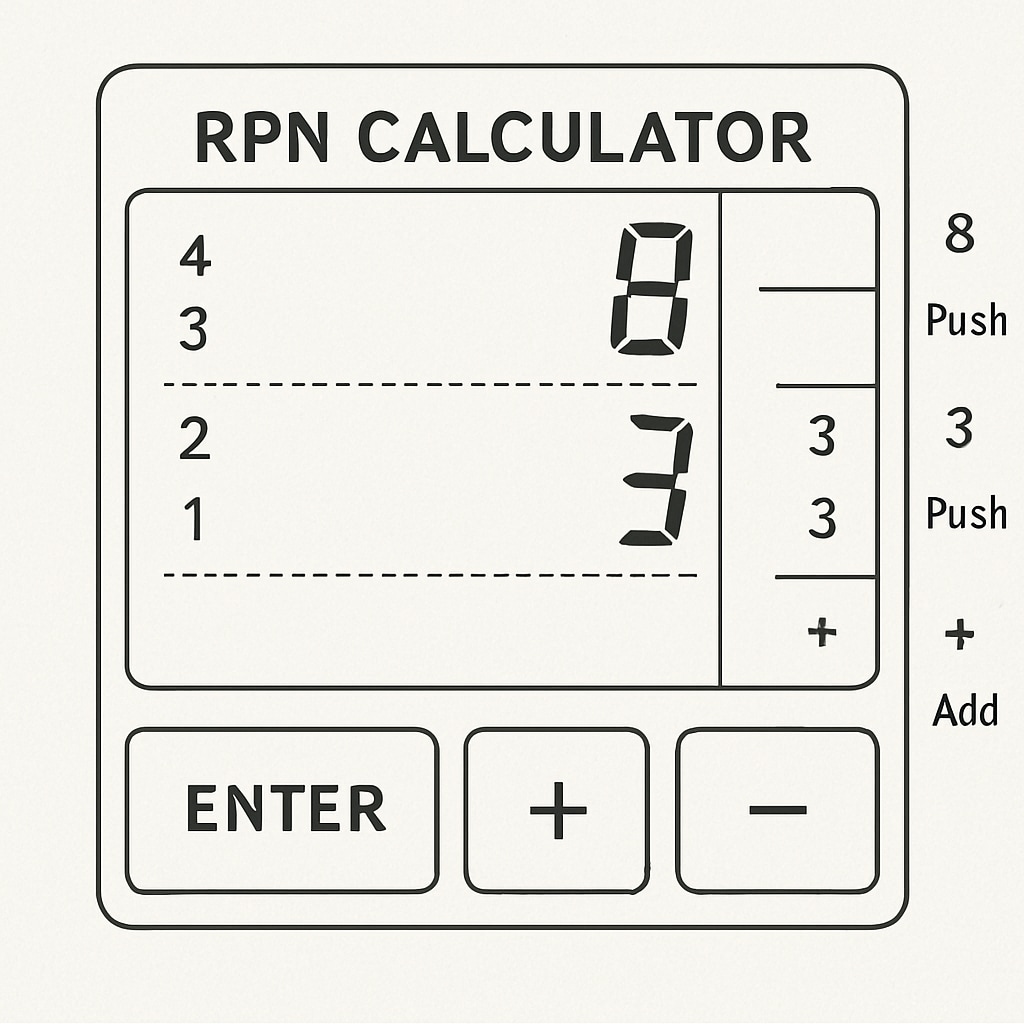
Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) is a mathematical notation in which operators follow their operands. For example, instead of writing “3 + 4,” you would write “3 4 +.” This eliminates the need for parentheses to indicate order of operations, as the sequence of the notation inherently dictates the calculation process. RPN calculators follow this principle, making them highly efficient tools for performing complex computations.
One of the key strengths of RPN is its minimalistic approach. By removing the need for parentheses and reducing the number of keystrokes, calculations are faster and less prone to user error. This design is especially beneficial in educational settings, where students can focus on understanding the logic behind the operations rather than the mechanics of inputting them.
The Advantages of RPN Calculators in K-12 Education
RPN calculators offer several distinct advantages that make them ideal for K-12 math education:
- Enhanced Efficiency: The elimination of parentheses and the direct input of operations streamline the calculation process, saving time and reducing complexity.
- Error Reduction: RPN’s step-by-step approach minimizes the risk of input errors, as students are less likely to misplace parentheses or lose track of operation sequences.
- Improved Logical Thinking: By requiring students to think in terms of operand and operator sequences, RPN calculators foster a deeper understanding of mathematical operations and their relationships.
Educators have noted that students using RPN calculators develop a stronger grasp of problem-solving techniques. This is because the need to enter calculations sequentially aligns with the logical thought processes required in mathematics.

Challenges and Solutions for Introducing RPN in Schools
While the benefits of RPN calculators are clear, their adoption in K-12 education does face some challenges. The primary hurdle is the learning curve associated with understanding reverse Polish notation. Most students and teachers are accustomed to infix notation, and transitioning to RPN requires initial effort.
However, these challenges can be mitigated through thoughtful implementation strategies:
- Comprehensive Training: Providing workshops and tutorials for both teachers and students can ease the transition and build confidence in using RPN calculators.
- Integrating Gradually: Introducing RPN alongside traditional methods allows students to compare and understand the advantages of the system over time.
- Custom Educational Materials: Developing curriculum-aligned resources that incorporate RPN concepts can help students see its practical applications.
As educators and policymakers invest in these strategies, the long-term benefits of RPN calculators in fostering mathematical intuition are likely to outweigh the initial difficulties.
The Future of Mathematics Education with RPN Calculators
RPN calculators represent more than just a tool for performing computations; they embody a shift toward more logical and efficient methods of teaching mathematics. By prioritizing understanding over rote memorization, reverse Polish notation aligns perfectly with modern educational goals.
Moreover, as STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) fields continue to grow, the ability to think critically and solve problems efficiently will become increasingly valuable. Tools like RPN calculators can equip students with the foundational skills needed to excel in these areas.
In conclusion, RPN calculators are not just a niche tool for advanced users—they are a powerful resource for transforming K-12 mathematics education. By enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and fostering logical thinking, these devices have the potential to revolutionize how students approach mathematical problem-solving. The next step is for educators to embrace this innovation and integrate it into their classrooms, ensuring that students are prepared for the challenges of the future.
Readability guidance: The article uses concise paragraphs, specific examples, and structured lists to ensure clarity. Transitions like “however,” “for example,” and “as a result” enhance flow, while passive voice and overly long sentences are minimized.


