For non-medical professionals, particularly educators and K-12 students, finding accessible and engaging resources to explore cardiology can be a challenge. However, online courses tailored to non-specialists have emerged as an effective way to introduce complex medical topics, such as heart health and cardiovascular systems, in a simplified yet accurate manner. These resources bridge the gap between foundational knowledge and advanced medical insights, paving the way for interdisciplinary learning and future scientific pursuits.
Why Introduce Medical Education in K-12 Classrooms?
Medical education is often viewed as a domain exclusive to professionals in healthcare. However, introducing basic medical concepts at the K-12 level can foster early interest in science, improve health literacy, and inspire future careers in STEM fields. Topics like cardiology, which focus on the heart and its functions, are particularly relevant as cardiovascular health has become a global priority. Educating students about how the heart works, common diseases like heart attacks, and preventive measures can not only spark curiosity but also empower them to make informed lifestyle choices.
Moreover, integrating these topics into general science curricula aligns with the growing emphasis on interdisciplinary education. Non-medical professionals, such as teachers, can use online courses to equip themselves with accurate knowledge and engaging teaching strategies. This approach ensures that students receive credible information in an age of misinformation.
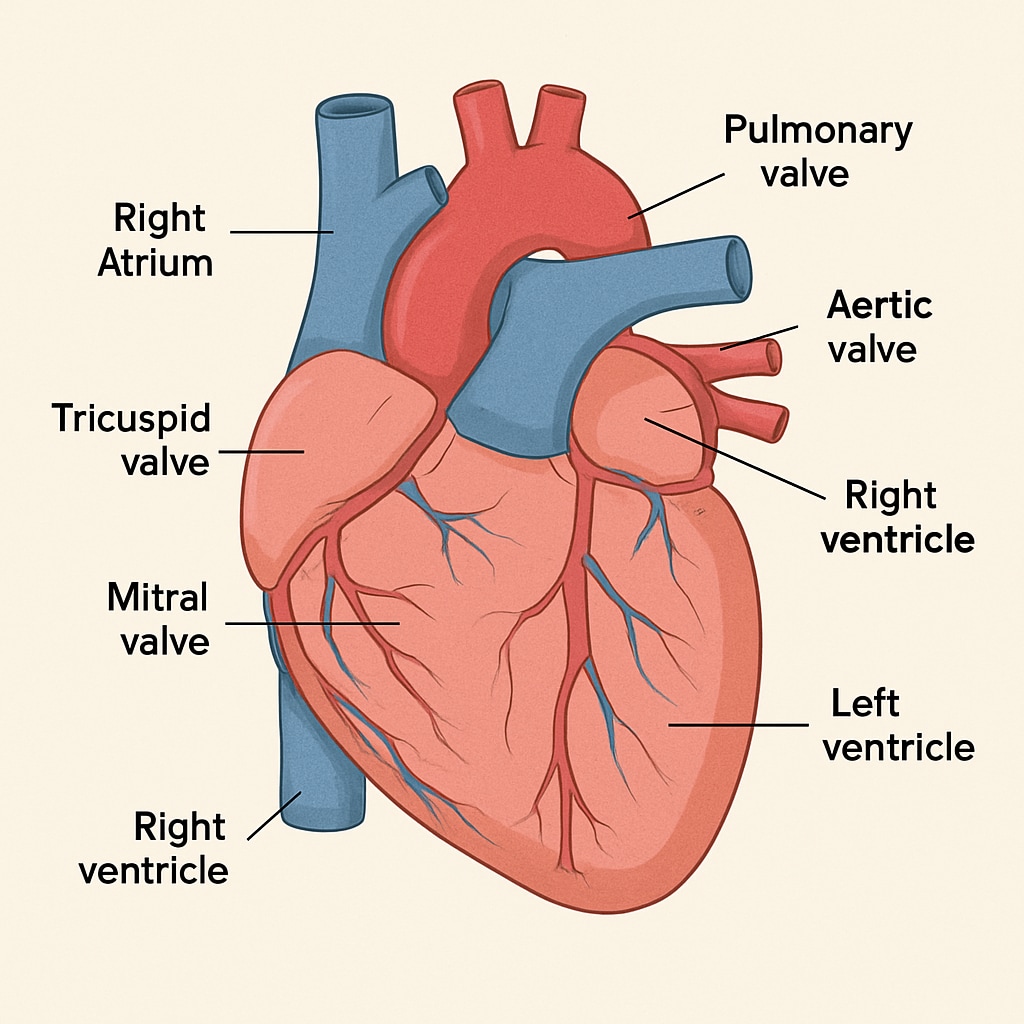
Features of Effective Online Courses for Non-Medical Professionals
Online courses designed for non-medical audiences must balance simplicity and accuracy. Here are some key features to look for:
- Clear Explanations: Courses should use straightforward language, avoiding medical jargon where possible. Visual aids, such as diagrams and animations, can help illustrate complex concepts.
- Interactive Content: Interactive quizzes, videos, and case studies make learning more engaging and memorable for users of all ages.
- Expert Involvement: Courses developed by medical professionals ensure the accuracy and relevance of the material.
- Accessibility: Resources should be affordable or free, ensuring they are available to a broad audience, including schools with limited budgets.
One example of an effective resource is the Khan Academy’s Health and Medicine section, which offers free, beginner-friendly lessons on various medical topics, including cardiology. Another is the edX platform, which provides more in-depth courses for those seeking advanced knowledge.
Exploring Cardiology: A Gateway to Lifelong Learning
Cardiology, the study of the heart and its functions, is an excellent entry point for K-12 students and educators interested in medical science. Topics like the anatomy of the heart, blood circulation, and common heart diseases are relatable and impactful. For example, understanding how lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise influence heart health can resonate with students on a personal level.
Additionally, cardiology serves as a foundation for exploring related fields, such as biology, chemistry, and even technology. For instance, students can learn about how medical devices like pacemakers work, combining biology with engineering concepts. By delving into cardiology, students not only gain scientific knowledge but also develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
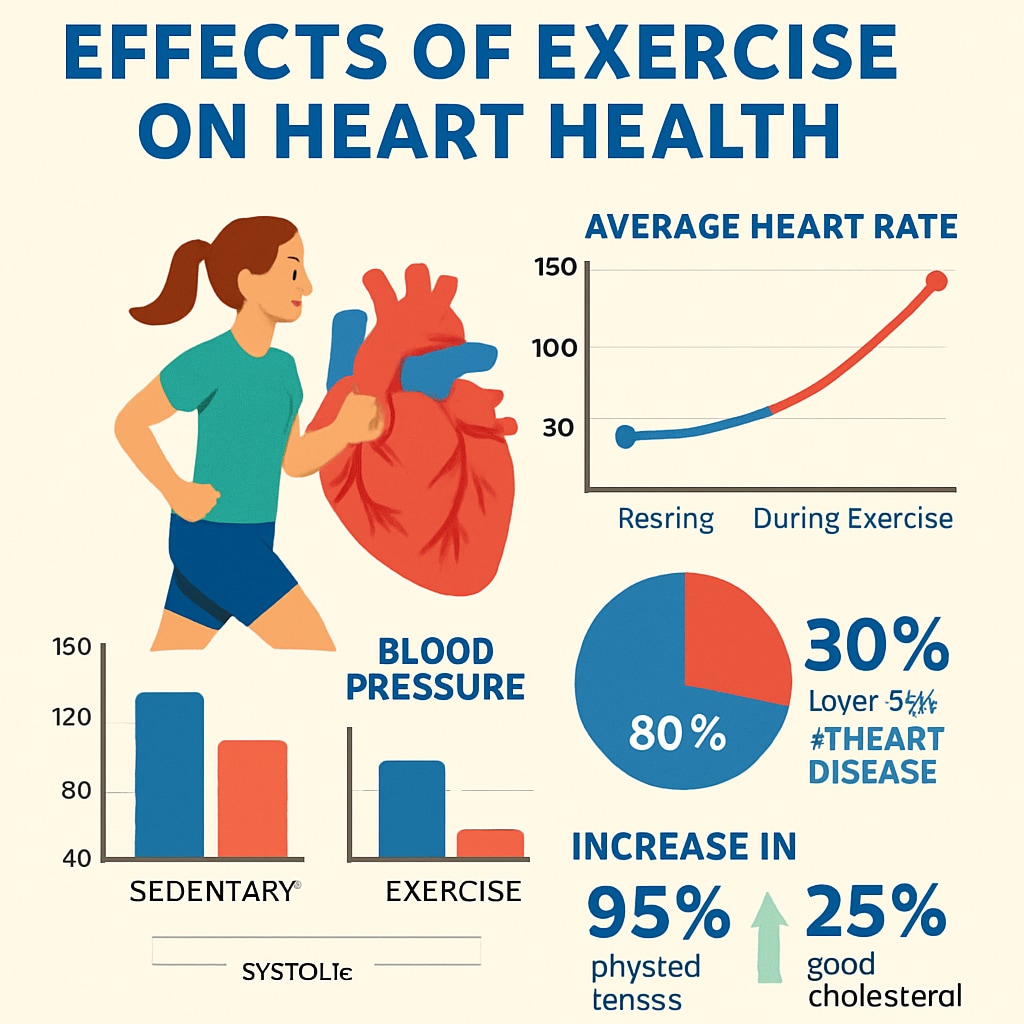
Challenges and Solutions in Bringing Medical Education to K-12
Despite its benefits, introducing medical education in K-12 settings comes with challenges:
- Lack of Expertise: Many educators may feel unqualified to teach medical topics. Online courses can serve as training tools, enabling teachers to confidently integrate these subjects into their lessons.
- Resource Limitations: Not all schools have access to advanced teaching materials. Free or low-cost online platforms can help bridge this gap.
- Student Engagement: Medical topics can seem intimidating or abstract to younger students. Using hands-on activities, such as building heart models or conducting simple experiments, can make learning more interactive and enjoyable.
Furthermore, collaboration between educators, medical professionals, and curriculum developers is essential to creating effective educational programs. By leveraging the expertise of each group, schools can offer well-rounded and impactful medical education.
Conclusion: Building a Future of Informed Learners
Integrating medical education into K-12 classrooms, with a focus on cardiology, provides an opportunity to inspire curiosity, improve health literacy, and prepare students for interdisciplinary learning. Through accessible online courses, non-medical professionals can acquire the knowledge and skills needed to bring these topics to life in the classroom. By doing so, we can cultivate a generation of informed learners who are better equipped to navigate the complexities of health and science in the modern world.
As the demand for STEM education grows, resources like online courses become invaluable tools for bridging the gap between professional medical knowledge and everyday understanding. Whether you’re an educator, student, or simply curious about the subject, exploring cardiology online is a step toward lifelong learning and better health awareness.


