Robotics education is rapidly transforming how K12 students engage with STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). While traditional approaches often focus on either overly basic concepts or highly specialized skills, a new method has emerged to bridge this gap: project-based robotics education for beginners. This comprehensive, hands-on approach introduces students to the fundamentals of robotics while encouraging creativity, problem-solving, and innovation. By providing a one-stop learning experience, this curriculum ensures that every learner, regardless of prior knowledge, can grasp core concepts and apply them in real-world scenarios.
Why Project-Based Learning is the Future of Robotics Education
Project-based learning (PBL) is an educational strategy where students acquire knowledge and skills by working on meaningful projects that solve real-world problems. In robotics education, PBL means guiding students through the process of designing, building, and programming robots that perform specific tasks.
Unlike traditional lecture-based methods, PBL emphasizes active learning. It allows students to experiment, test ideas, and learn from their mistakes. This method is particularly effective for beginners because:
- It builds foundational skills: Students learn the basics of robotics, such as mechanics, electronics, and coding, in a structured yet engaging way.
- It fosters creativity: By designing their own projects, students think outside the box and develop innovative solutions.
- It boosts confidence: Successfully completing a project gives students a sense of achievement, motivating them to tackle more complex challenges.
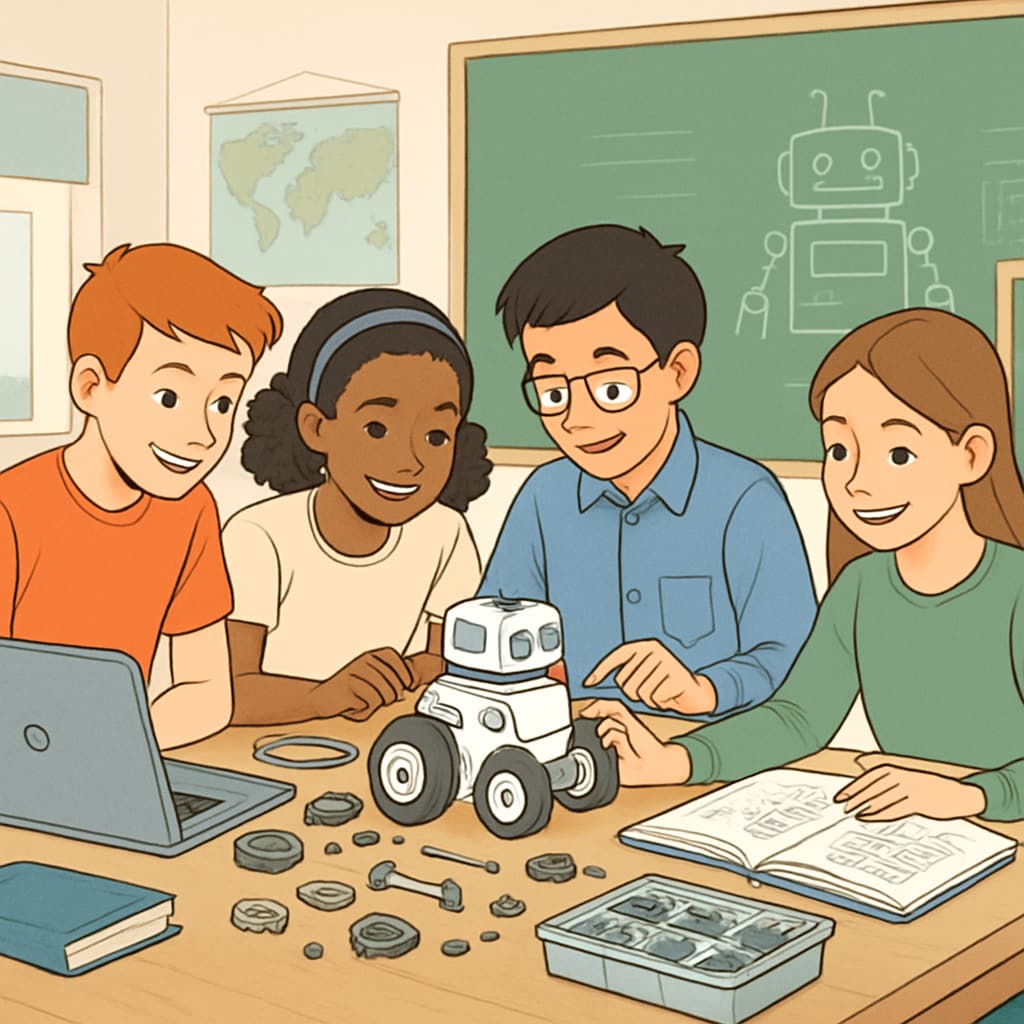
How a One-Stop Robotics Curriculum Serves K12 Beginners
Many existing robotics courses face a common issue: they are either too simplistic, focusing on basic concepts without application, or too advanced, making it hard for beginners to keep up. A one-stop robotics curriculum addresses this problem by providing a seamless learning pathway from theory to practice. Here’s how:
- Comprehensive Modules: The curriculum is divided into modules that cover mechanics, electronics, programming, and integration. Each module builds on the previous one.
- Guided Projects: Beginners are led through step-by-step projects, such as building a line-following robot or a robotic arm, which gradually increase in complexity.
- Real-World Applications: Students learn how robotics can solve real-world problems, such as automating processes or aiding in disaster response.
For example, students might start with a simple task like programming an LED light to blink, then progress to controlling motors, sensors, and eventually building a robot that navigates a maze. This gradual progression ensures that no student feels overwhelmed, while still challenging them to grow.
Bridging the Gap Between Beginners and Advanced Learners
One of the unique benefits of a project-based robotics curriculum is its ability to cater to a diverse range of learners. Beginner students often struggle to transition into more advanced robotics topics because of a lack of practical experience. By incorporating hands-on projects from the start, this curriculum provides a strong foundation that prepares students for future challenges.
Moreover, this approach encourages collaboration. Students often work in teams, sharing ideas and learning from each other. This not only enhances their technical skills but also teaches essential soft skills like communication, teamwork, and time management. These skills are invaluable, both in academic settings and in future careers.
The Role of Robotics Education in Fostering Innovation
Robotics education does more than teach technical skills—it inspires students to think critically and imagine possibilities beyond the classroom. For K12 students, this is particularly important as they begin exploring their passions and potential career paths. Through project-based learning, students are exposed to challenges that require innovative thinking, such as designing robots to assist people with disabilities or developing automated systems for environmental monitoring.
By blending creativity with technical knowledge, robotics education equips students with the tools they need to become problem-solvers and innovators. This aligns with the growing demand for STEM professionals in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and technology.
As a result, students who participate in project-based robotics programs are not only more likely to pursue STEM careers but also better prepared to succeed in them. By starting with a beginner-friendly curriculum, they gain the skills and confidence needed to tackle advanced robotics concepts and real-world challenges.
In conclusion, project-based robotics education for K12 beginners is an effective way to bridge gaps in traditional teaching methods. By offering a one-stop learning experience, these programs ensure that every student, regardless of background, can master the fundamentals of robotics while developing critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration skills. This approach not only prepares students for academic success but also positions them as future innovators in a rapidly evolving world.
For more on robotics education, check out resources like Educational Robotics on Wikipedia or Robotics on Britannica.


