Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) calculators, often overlooked in modern classrooms, offer a unique approach to mathematical computation that emphasizes logic and simplicity. Unlike traditional calculators, which rely on infix notation and the use of parentheses to define operational precedence, RPN calculators streamline the process by using postfix notation. This eliminates the need for parentheses, allowing students to focus more on the sequence of operations and the underlying mathematical concepts. Despite their potential to improve input efficiency and encourage critical thinking, RPN calculators remain largely absent from K12 math education. This article explores their practical benefits and argues for their inclusion in modern curricula.
What Makes RPN Calculators Unique?
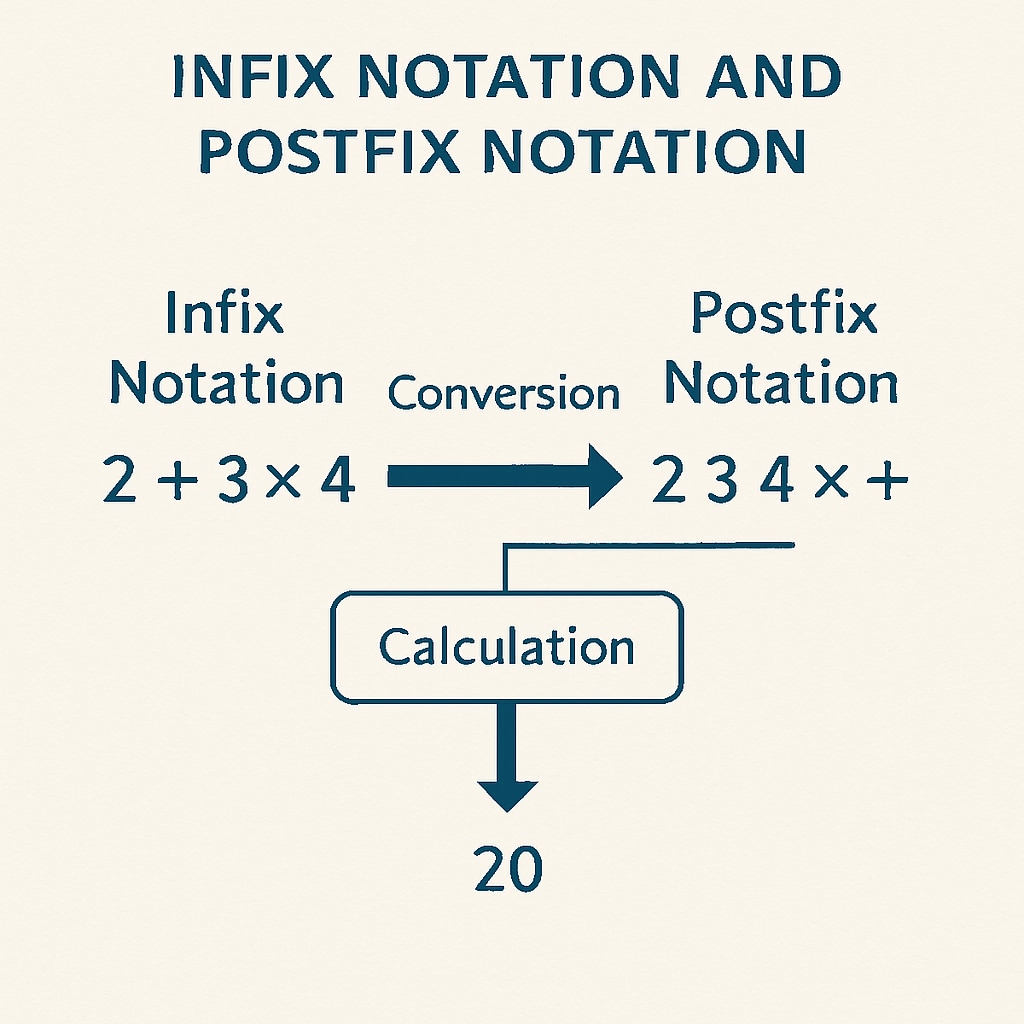
The defining feature of RPN calculators is their use of postfix notation, also known as Reverse Polish Notation. In this system, operators follow their operands, simplifying the computational process by removing the need for parentheses. For example, instead of writing “3 + (4 × 5)”, an RPN calculator would input this as “3 4 5 × +”. This approach ensures that operations are performed in the correct order without requiring additional rules or syntax.
One major advantage of this system is input efficiency. By reducing the need for parentheses and operator precedence rules, users can enter calculations faster and with fewer errors. Additionally, the logical structure of RPN calculations encourages students to think critically about the sequence of operations, fostering a deeper understanding of mathematical principles.
The Educational Value of RPN Calculators
RPN calculators have significant potential in K12 education, particularly in teaching problem-solving and logical reasoning. By focusing on the order of operations, students develop a more intuitive understanding of mathematical processes. This contrasts with traditional calculators, which often allow students to bypass critical thinking by relying on built-in operator precedence and automated results.
Moreover, RPN calculators help minimize common mistakes associated with parentheses and operator precedence. These errors are especially prevalent among younger students who are still mastering algebraic concepts. By eliminating these challenges, RPN calculators allow students to concentrate on the core mathematical problems rather than struggling with syntax.
For educators, introducing RPN calculators could also complement lessons on programming logic, as postfix notation is frequently used in computer science. This interdisciplinary approach can prepare students for advanced studies in both mathematics and technology fields.

Challenges and Solutions for Integrating RPN Calculators in K12 Math
Despite their benefits, RPN calculators face several barriers to adoption in K12 education. One major challenge is the unfamiliarity of both students and teachers with postfix notation. Traditional infix notation has been the standard for decades, and transitioning to a new system may require additional training and resources.
Another issue is the limited availability of RPN calculators compared to standard models. While some manufacturers, such as Hewlett-Packard, continue to produce RPN devices, their market share remains small. Schools may need to invest in specialized equipment or software to implement RPN calculators in classrooms.
To address these challenges, educators could start by incorporating RPN calculators alongside traditional models rather than replacing them entirely. This dual approach allows students to explore the benefits of RPN while retaining familiarity with standard tools. Additionally, online simulators and apps can provide accessible and cost-effective alternatives to physical calculators. Educator training programs and workshops can also help teachers become comfortable with RPN concepts and teaching methods.
Conclusion: The Case for RPN Calculators in Modern Education
Incorporating RPN calculators into K12 math education offers a unique opportunity to enhance input efficiency and promote logical thinking. By simplifying mathematical computations and reducing common errors, these tools can help students develop a deeper understanding of core concepts. While there are challenges to their adoption, strategic implementation and teacher training can overcome these obstacles, paving the way for a more innovative and effective approach to mathematics education.
As education continues to evolve in the digital age, tools like RPN calculators have the potential to bridge the gap between traditional learning methods and modern technological advancements. Their inclusion in K12 curricula could not only improve computational efficiency but also prepare students for future studies in mathematics and computer science.
Readability guidance: This article uses short paragraphs, clear transitions, and lists to enhance readability. It balances technical details with accessible language, ensuring that both educators and general readers can understand the benefits of RPN calculators.


