As education evolves to meet modern challenges, the debate over U.S. high school curriculum reform has intensified. The proposed focus on curriculum streamlining, STEM education, and overall balance aims to equip students with the skills needed for the future. By reducing the emphasis on humanities courses, schools hope to create more room for disciplines in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). However, this shift raises critical questions about preserving a comprehensive educational experience while preparing students for an increasingly tech-driven world.
Why STEM Education is Taking Center Stage
STEM education has become a cornerstone of global competitiveness. Countries worldwide are investing heavily in STEM to address workforce shortages in technology and science-based industries. In the U.S., high school students often struggle to meet the rigorous demands of STEM subjects due to limited exposure and insufficient resources. Reforming the curriculum to emphasize STEM can help bridge this gap, ensuring that students are better prepared for college and careers in these fields.
- Workforce Demand: STEM careers are projected to grow much faster than non-STEM occupations, according to U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
- Global Trends: Nations like China and Germany have already prioritized STEM education, yielding significant advancements in technology and engineering.
- Technological Integration: Schools need to adapt to innovations like artificial intelligence and robotics, which heavily rely on STEM foundations.

The Role of Curriculum Streamlining in Educational Reform
To accommodate the growing emphasis on STEM, many educators are advocating for curriculum streamlining. This involves reducing redundancy in humanities courses while maintaining foundational knowledge in subjects like history, literature, and social studies. By trimming excessive coursework, schools can allocate more time to STEM-focused programs without sacrificing interdisciplinary learning.
However, critics argue that humanities foster critical thinking, creativity, and empathy—skills that complement STEM expertise. For example, a scientist who understands ethical considerations may develop more socially responsible innovations. Therefore, curriculum reform must strike a balance, ensuring that humanities are not neglected but optimized for efficiency.
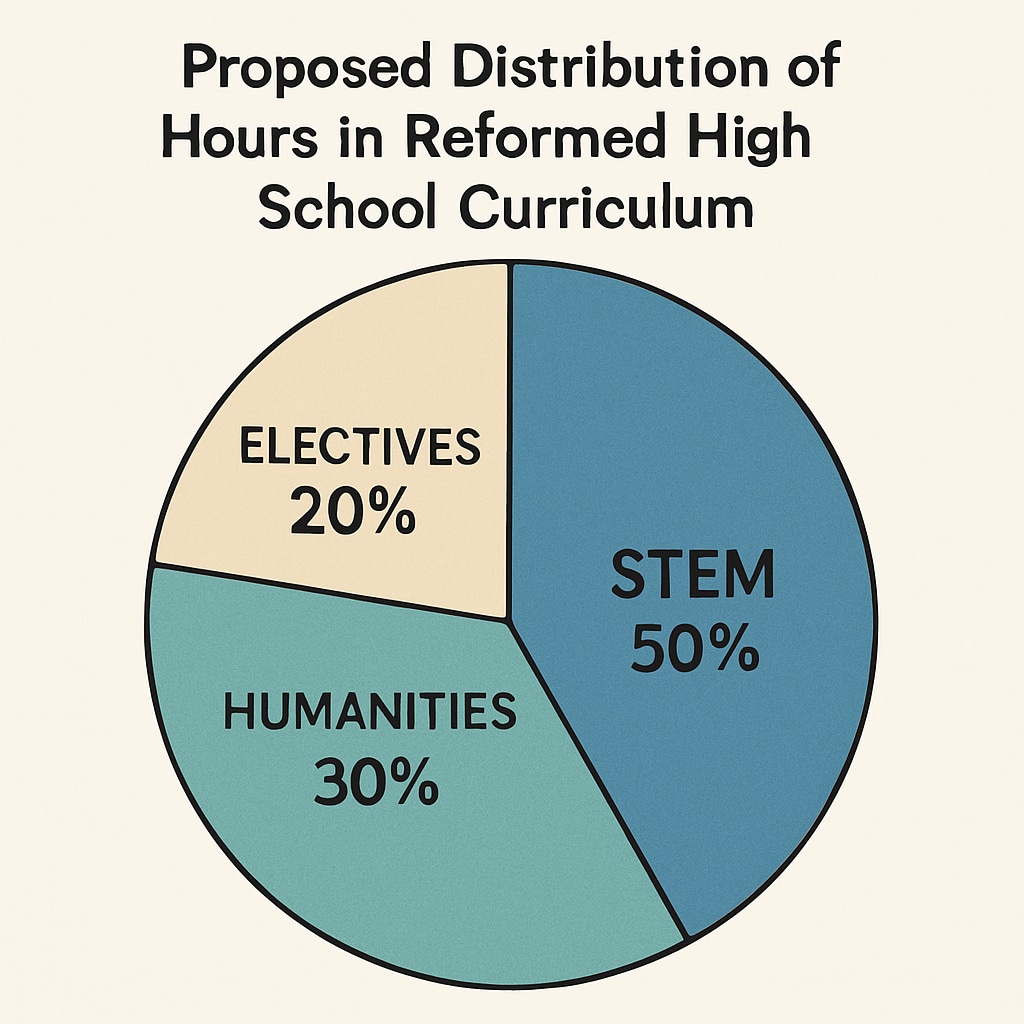
Challenges and Opportunities in High School Curriculum Reform
Implementing these reforms presents unique challenges. Schools must overcome budget constraints, train educators in STEM methodologies, and address the diverse needs of students. Additionally, curriculum changes often face resistance from stakeholders who fear the loss of educational depth. Despite these hurdles, opportunities abound:
- Enhanced Teacher Training: Professional development programs can equip educators with tools to integrate STEM into classrooms effectively.
- Interdisciplinary Learning: Combining STEM with humanities creates a richer educational experience, blending technical skills with creativity.
- Flexible Scheduling: Schools can adopt modular systems to allow students to explore both STEM and humanities in depth.
As a result, reforming high school curricula is not just an academic endeavor but a cultural shift, reshaping how future generations perceive and interact with the world.
Looking Ahead: Balancing STEM and Humanities
The ultimate goal of high school curriculum reform should be to prepare students for a complex, interconnected future. While STEM education is crucial for economic and technological progress, humanities remain vital for fostering well-rounded individuals. Policymakers, educators, and communities must collaborate to design curricula that balance these priorities. For example, integrating STEM principles into humanities classes—such as using data analysis in history projects—can create synergies between the two fields.
In conclusion, streamlining U.S. high school curricula to emphasize STEM while retaining humanities is a delicate but necessary undertaking. By striking the right balance, schools can produce students who are both technically skilled and socially conscious, ready to tackle the challenges of tomorrow.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs, clear transitions, and strategic use of lists improve comprehension. Overlap between STEM and humanities concepts provides a nuanced perspective, fostering balanced discourse.


