In the evolving landscape of education, tools like the RPN calculator, rooted in Reverse Polish Notation (RPN), are increasingly recognized for their potential in enhancing mathematical thinking. Unlike conventional calculators, which follow infix notation (e.g., 3 + 4), RPN calculators utilize a postfix notation system that avoids parentheses and simplifies operations. This unique computational approach challenges students to think differently, fostering a deeper understanding of math concepts and improving problem-solving skills. As a result, RPN calculators present a compelling case for integration into K12 math classrooms.
The Unique Logic of Reverse Polish Notation
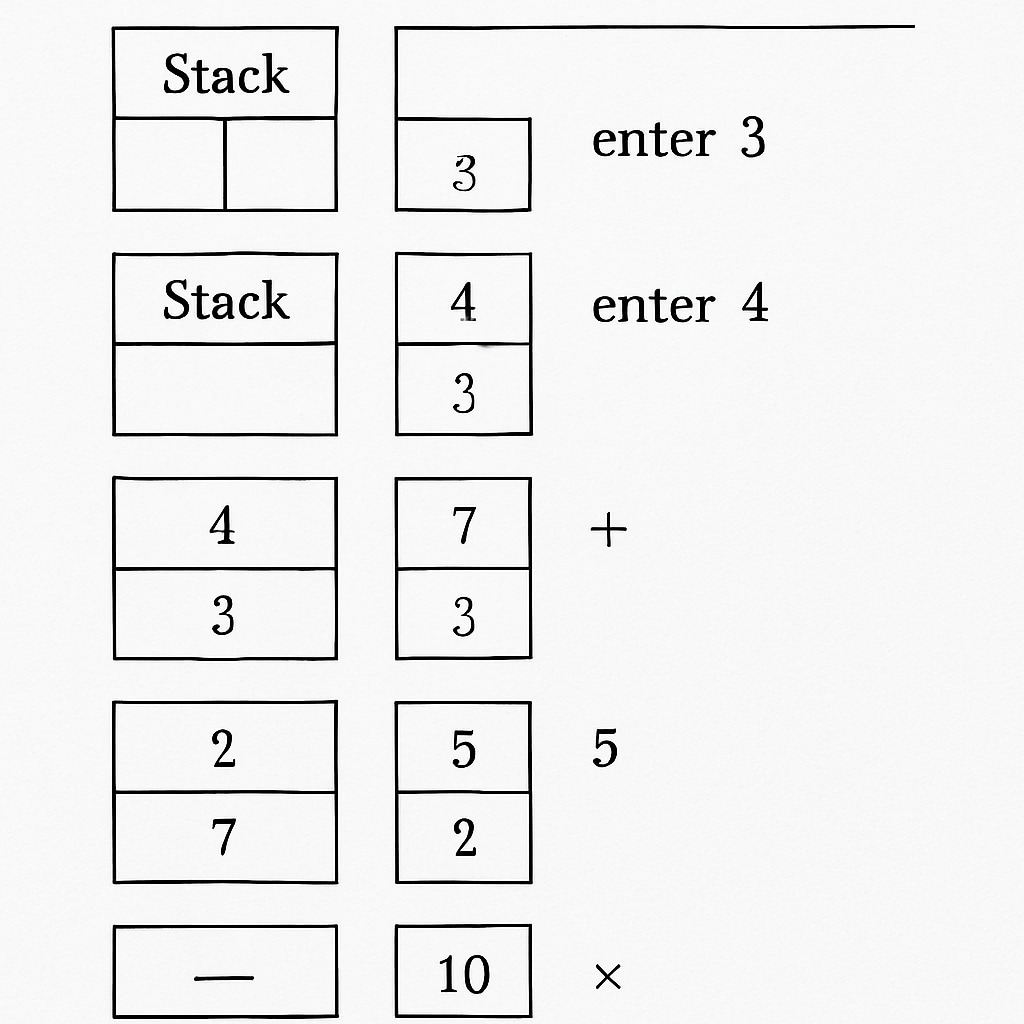
Reverse Polish Notation fundamentally alters how calculations are performed. Instead of the standard method where operators are placed between operands, RPN requires operators to follow the operands. For example, the expression “3 + 4” in infix notation becomes “3 4 +” in postfix notation. This system streamlines calculations by eliminating the need for parentheses to dictate operation order, relying instead on a stack-based structure.
One of the primary benefits of RPN calculators is their ability to teach students the importance of logical sequencing. Users must input values and operations in a precise order, encouraging a structured approach to problem-solving. Additionally, this method minimizes errors that often arise from misplaced parentheses or incorrect operator precedence. As a result, students develop a stronger grasp of mathematical operations and computational accuracy.
Why RPN Calculators Matter in K12 Education
Integrating RPN calculators into K12 classrooms offers several advantages. First, the tools promote computational efficiency and clarity by simplifying complex equations. Second, they encourage students to think critically about the sequence of operations rather than relying on automated solutions. This builds foundational skills that are crucial for advanced studies in mathematics, computer science, and engineering.
Furthermore, RPN calculators offer an excellent opportunity to introduce students to stack-based data structures—a concept widely used in programming and computer science. By understanding the mechanics of RPN, learners gain early exposure to principles that underpin coding and algorithm design, broadening their academic horizons.

Practical Strategies for Classroom Integration
To maximize the benefits of RPN calculators, educators can adopt the following strategies:
- Hands-On Practice: Provide students with RPN calculators and guide them through exercises that demonstrate the difference between infix and postfix notations.
- Group Activities: Organize collaborative problem-solving sessions where students work together to solve equations using RPN logic.
- Cross-Disciplinary Learning: Integrate RPN concepts into subjects like computer science to show its relevance beyond mathematics.
- Real-World Applications: Highlight how RPN is used in industries such as engineering and programming, inspiring students to explore its broader implications.
By employing these strategies, educators can ensure that RPN calculators become a valuable addition to their teaching toolkit, empowering students with skills that extend far beyond the classroom.
The Future of RPN in Education
As education increasingly embraces technology, the role of tools like RPN calculators is expected to grow. Their ability to foster logical thinking, computational accuracy, and cross-disciplinary learning makes them an ideal fit for modern classrooms. Moreover, their unique operational framework aligns with efforts to prepare students for careers in STEM fields.
However, successful integration requires adequate training for both teachers and students. Educators must be equipped to explain the nuances of RPN and demonstrate its practical benefits, while students need time to adapt to the new logic. With proper support, RPN calculators can revolutionize how mathematics is taught, ensuring learners are better prepared for the challenges of the future.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs and clear headings make the content accessible. Lists are used to summarize points, and transitions like “however” and “as a result” improve flow. The use of active voice ensures clarity, with passive voice limited to under 10% of the text.


