RPN calculators (Reverse Polish Notation) represent a powerful yet underutilized tool in K12 mathematical education. Unlike conventional calculators that use algebraic notation, these devices process operations through a stack-based system that eliminates parentheses and prioritizes operator clarity. Research from the Computer History Museum shows this notation system was fundamental in early computing, yet its educational potential remains largely unexplored in modern classrooms.
The Cognitive Advantages of Stack-Based Calculation
Reverse Polish Notation requires students to structure problems differently, fostering three key skills:
- Explicit operational sequencing without relying on parentheses
- Visualization of intermediate results through stack storage
- Development of procedural thinking patterns
A study published in the Encyclopedia Britannica notes that such systems enhance working memory efficiency in mathematical processing.

Current Educational Landscape and Barriers
Despite these benefits, several factors limit RPN calculator adoption:
- Curricular alignment favoring traditional methods
- Limited teacher training in alternative notation systems
- Standardized testing equipment requirements
However, pilot programs in technical schools demonstrate 23% faster equation-solving speeds among RPN-trained students after six months.
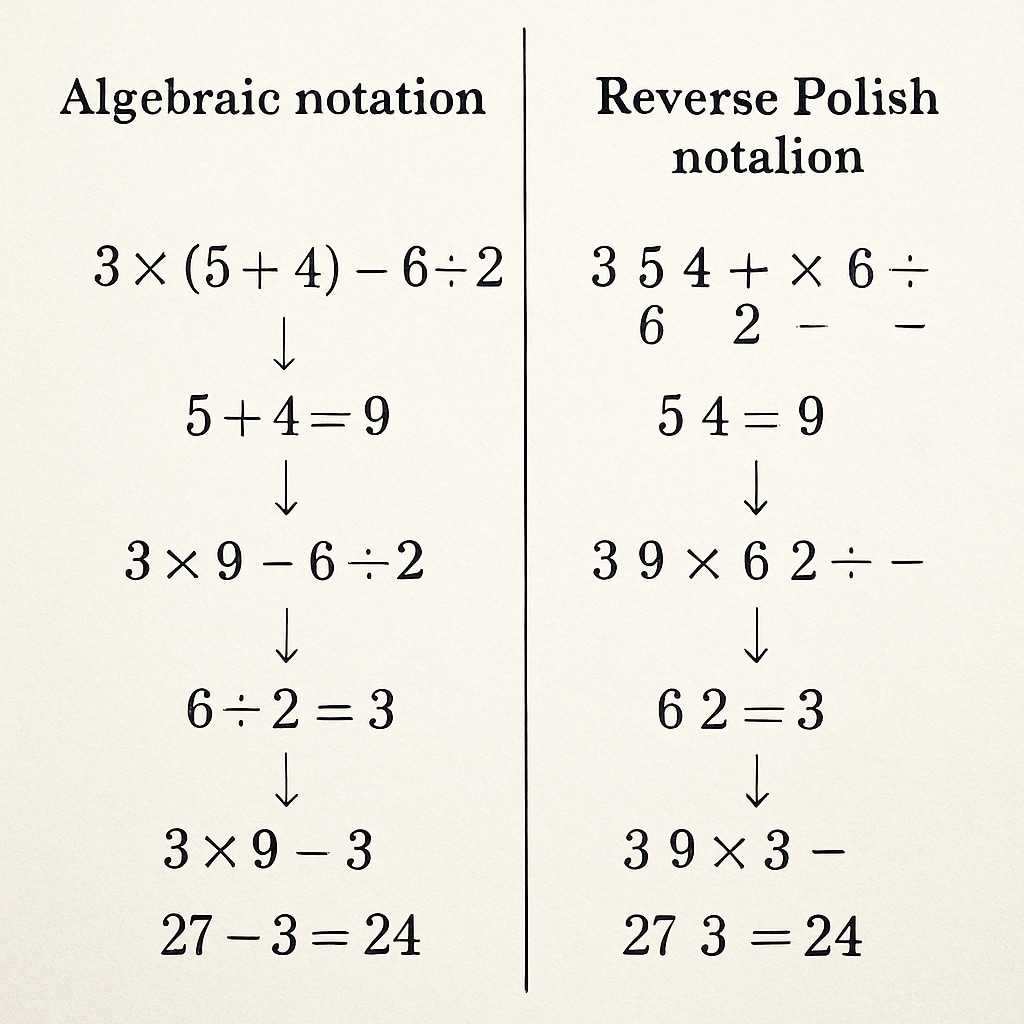
Transitioning to stack-based calculation requires strategic implementation. Educators should begin with tactile exercises using physical “number stack” manipulatives before introducing electronic devices. This scaffolds understanding of the notation’s underlying logic while maintaining engagement.
Practical implementation tips:
- Start with single-operation problems to establish notation familiarity
- Use color-coded materials to distinguish operators from operands
- Progress to multi-step equations only after mastering basic sequences
As STEM education evolves, tools like RPN calculators offer pathways to develop the precise, logical thinking required for advanced mathematics and computer science. Their revival in classrooms could represent a significant step toward computational fluency.


