RPN (Reverse Polish Notation) calculators represent a powerful yet underutilized tool in K12 mathematics education. Unlike conventional algebraic calculators, these devices process mathematical expressions using stack-based operations, offering distinct cognitive benefits for developing computational fluency.

The Cognitive Advantages of Stack-Based Computation
RPN calculators require students to structure problems differently than traditional methods. This approach:
- Forces explicit operational sequencing
- Eliminates ambiguity in expression evaluation
- Builds spatial awareness of mathematical relationships
Research from the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics suggests that such non-standard computational methods can strengthen fundamental number sense.
Current Educational Landscape and Barriers
Despite their benefits, RPN calculators face several adoption challenges:
- Limited awareness among educators
- Dominance of traditional calculator interfaces
- Standardized testing requirements
However, pilot programs in some districts have shown promising results when introducing these tools in algebra and pre-calculus courses.
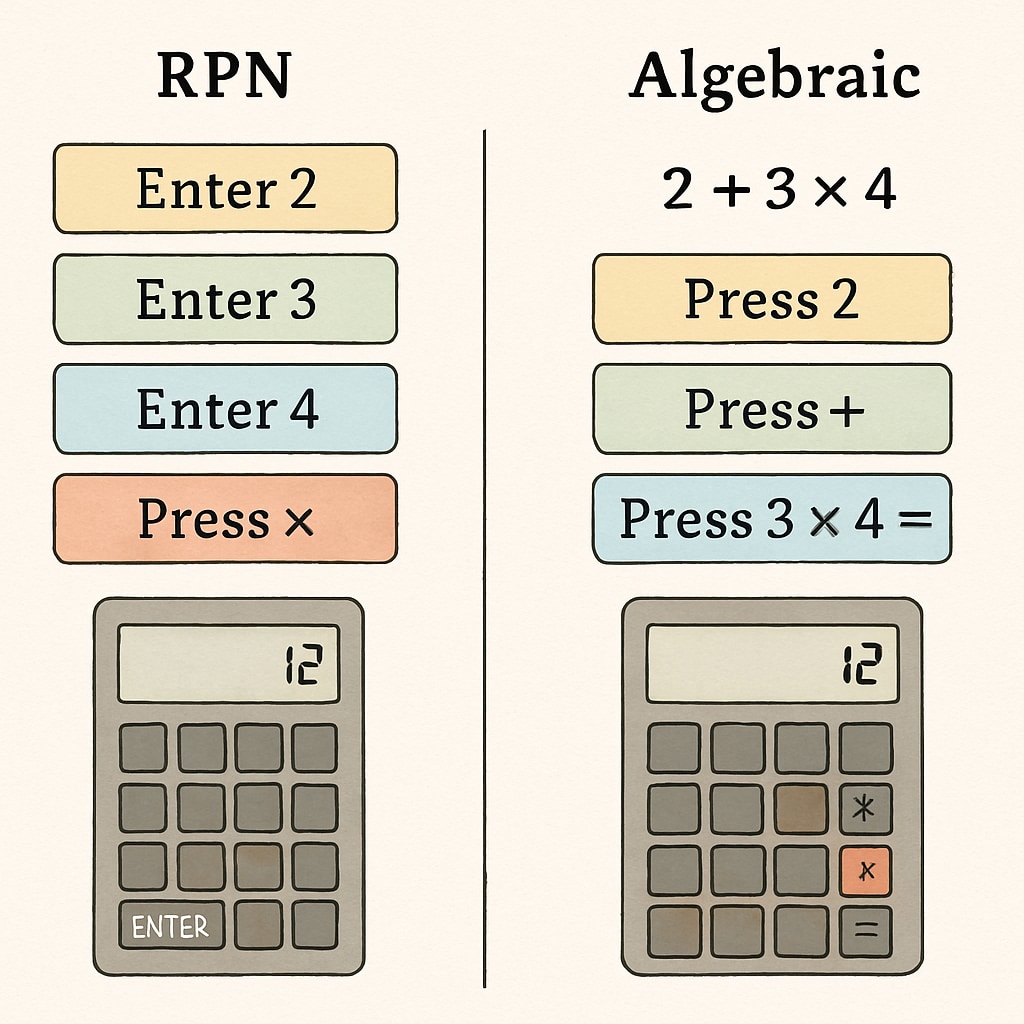
Practical Implementation Strategies
Educators can integrate RPN calculators effectively by:
- Starting with basic arithmetic operations
- Gradually introducing stack operations
- Connecting to computer science concepts
The Wikipedia entry on RPN provides excellent technical background for teachers.
As we reevaluate mathematical pedagogy in the digital age, RPN calculators offer a unique opportunity to develop students’ structural thinking and problem-solving skills – competencies increasingly valuable in STEM fields.


