Teaching artificial intelligence foundations, educational projects, and computing resource constraints effectively requires creative solutions when hardware access is limited. For undergraduate programs facing budget restrictions, we propose a framework combining theoretical depth with hands-on micro-projects that run efficiently on standard laptops. This approach ensures students grasp core AI concepts while working within practical limitations.
Layered Learning Architecture for Resource-Efficient AI Education
By structuring the curriculum in progressive layers, educators can maximize learning outcomes without demanding high-end hardware:
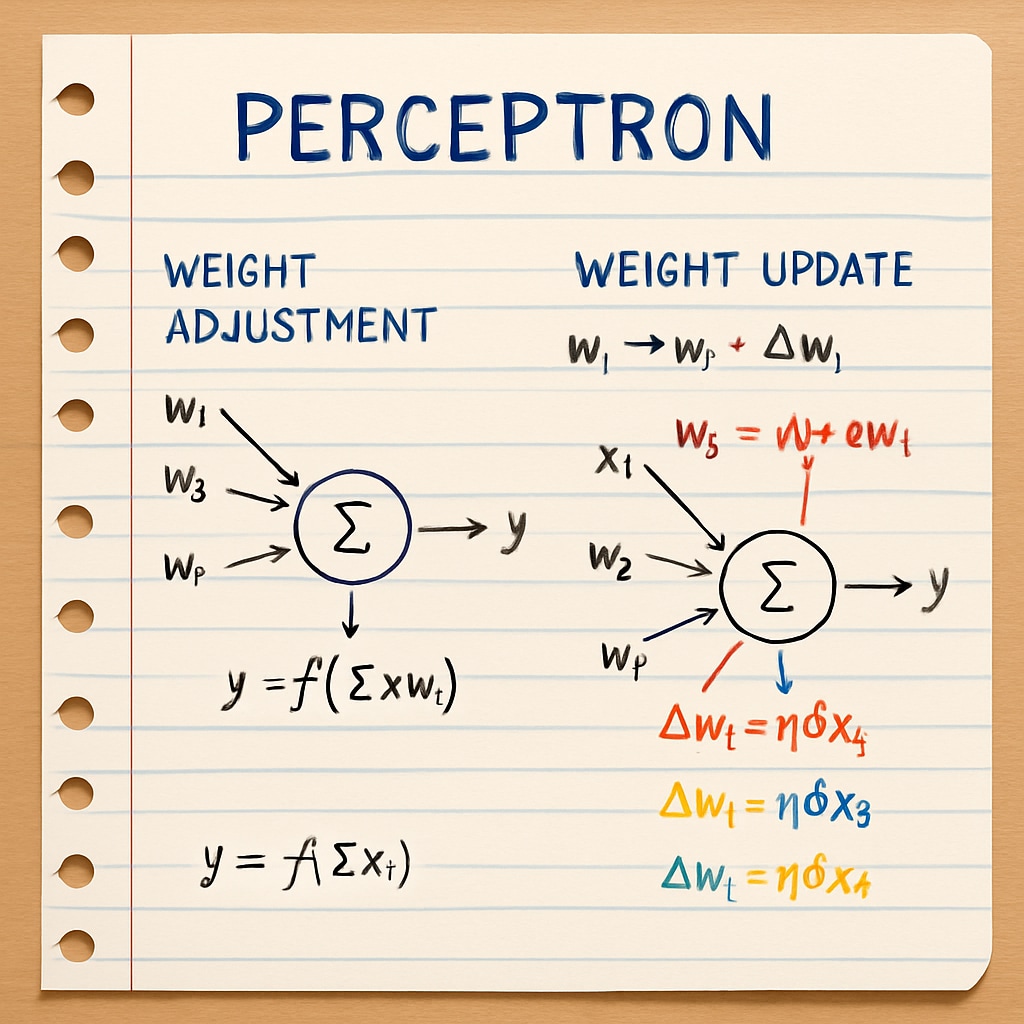
- Conceptual layer: Foundational theories taught through visualizations and analogies (e.g., explaining neural networks using perceptron models)
- Simulation layer: Browser-based tools like TensorFlow.js for lightweight model experimentation
- Micro-implementation layer: Focused coding exercises with optimized datasets (under 1MB)

Five Impactful Micro-Projects for Limited Resources
These carefully designed projects deliver meaningful learning experiences while minimizing computational demands:
- Paper-based perceptron trainer: Students manually adjust weights to classify simple patterns
- Tiny CNN for MNIST: A minimalist convolutional neural network using downsampled 14×14 images
- Rule-based chatbot: Building dialog systems with decision trees instead of LLMs
- Genetic algorithm art: Evolving simple shapes with basic genetic algorithms
- Feature importance Olympics: Competition to extract insights from small datasets using basic statistics
Assessment Innovations for Low-Resource Environments
Traditional AI coursework often relies on computational benchmarks that require substantial resources. Instead, consider:
- Algorithm design challenges evaluated on conceptual elegance
- Model explanation competitions (students justify decisions without training)
- Peer-reviewed project proposals focusing on resource efficiency
Implementation tip: Use cloud-based IDEs during class hours for occasional resource-intensive demonstrations, while maintaining 90% of coursework as locally executable activities.


