The rapid adoption of AI检测器,学术诚信,false positive systems in education has created unprecedented challenges for verifying student work authenticity. According to a 2023 Nature study, 38% of AI-generated content gets misclassified as human-written, while 15% of original student work faces false accusations.
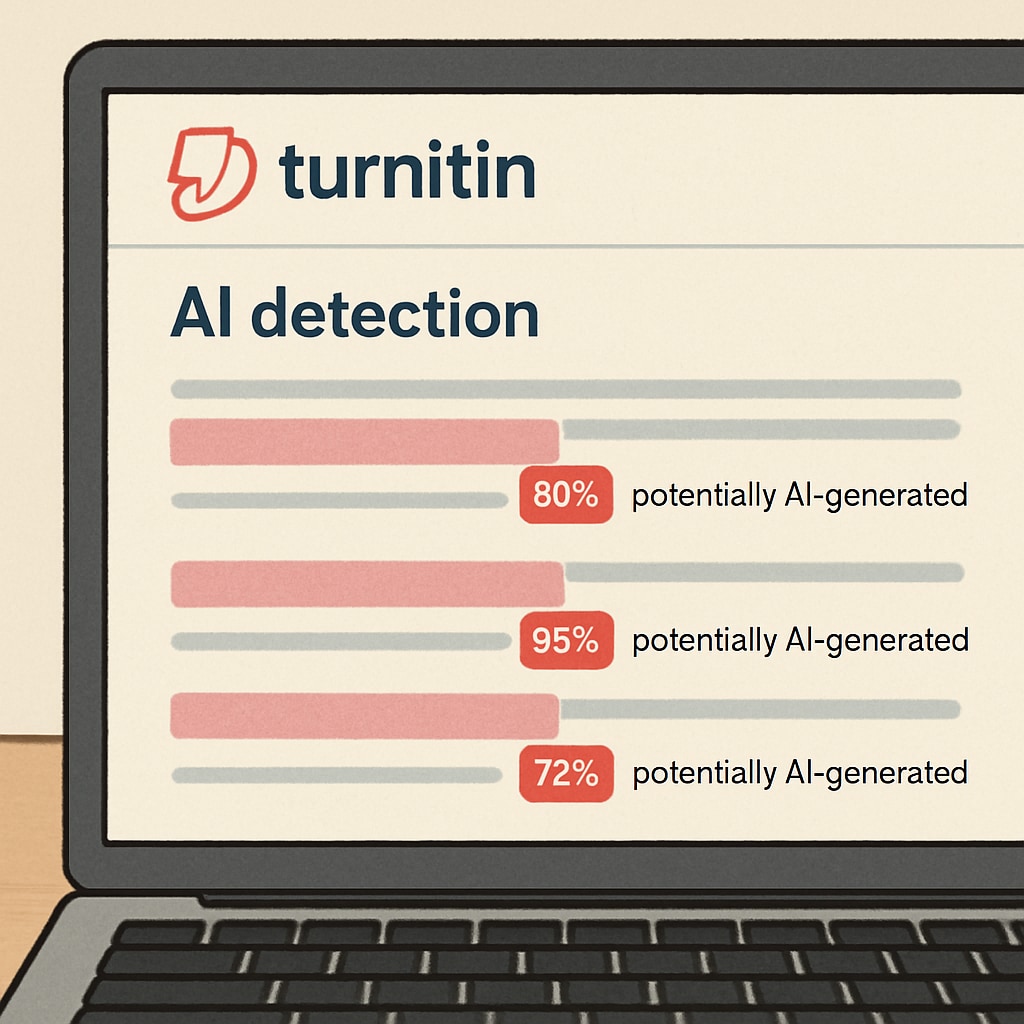
The Accuracy Crisis in AI Detection Tools
Current generation detectors face three fundamental limitations:
- Bias toward complex writing: Systems often flag sophisticated vocabulary as AI-generated, penalizing high-performing students
- Training data gaps: Most tools train on outdated GPT-3 content while students use newer models like GPT-4
- Cultural blind spots: Non-native English speakers face 27% higher false positive rates according to recent research
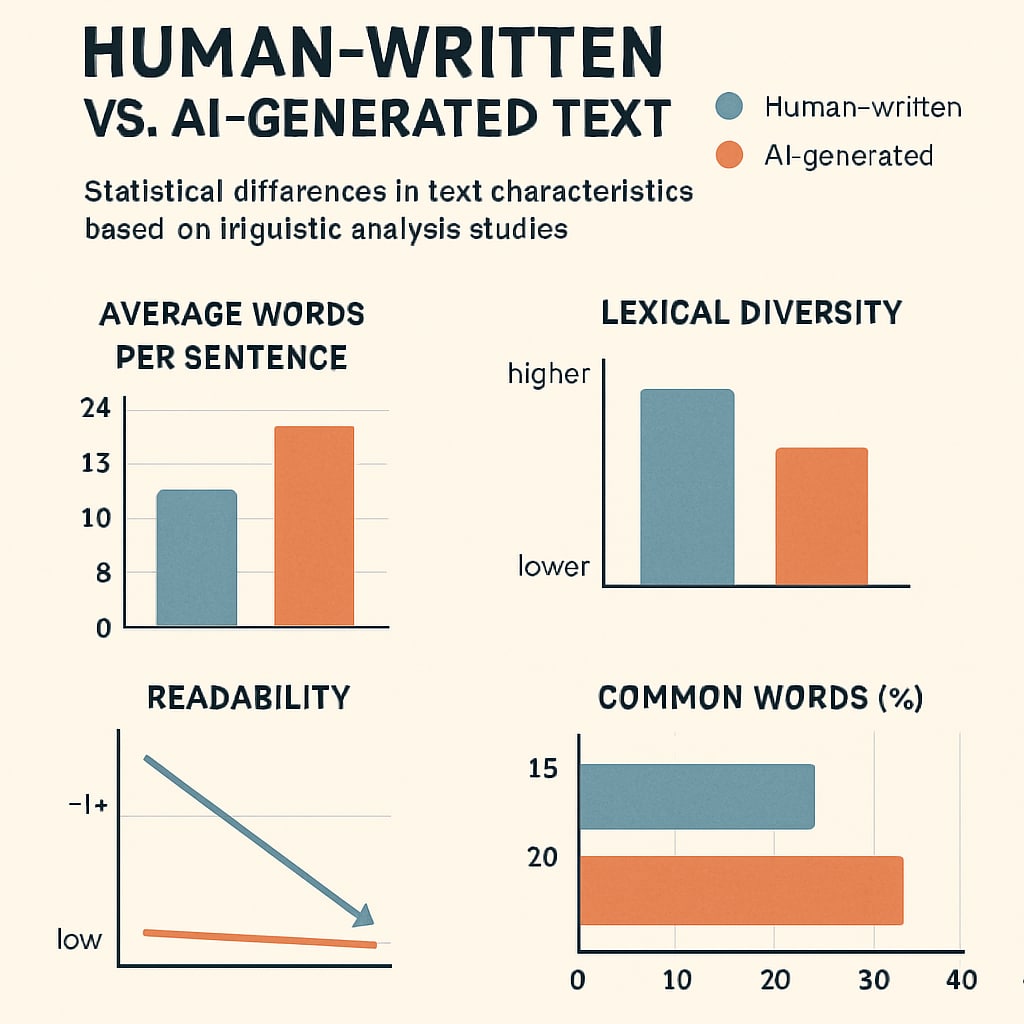
Consequences of Faulty Academic Integrity Alerts
When institutions over-rely on imperfect detection systems:
- Students experience unnecessary stress during appeals processes
- Educator-student trust erodes when false accusations occur
- Grading delays create administrative bottlenecks
Stanford’s 2024 policy brief recommends treating AI detector results as “advisory rather than definitive” due to their 62-78% accuracy range.
Balancing Technology and Ethics
Progressive institutions are implementing hybrid solutions:
- Multi-stage verification: Combining AI checks with oral assessments
- Transparency policies: Disclosing detection margins of error to students
- AI literacy programs: Teaching ethical usage rather than blanket prohibition
As MIT’s EdTech Lab director notes, “The goal shouldn’t be perfect detection, but creating learning environments where AI complements rather than replaces critical thinking.”


