AI detectors, plagiarism identification, academic integrity, and false positives have become hot-button issues as schools increasingly adopt automated tools to verify student work. According to a 2023 Stanford study, 12% of original student essays get flagged as AI-generated by popular detection systems. This alarming error rate exposes fundamental flaws in current technology that demand immediate attention from educators and policymakers alike.
The Hidden Dangers of Overreliance on AI Detectors
Most AI detection tools analyze three key characteristics:
- Text perplexity (vocabulary complexity)
- Burstiness (sentence length variation)
- Semantic patterns (word choice sequences)
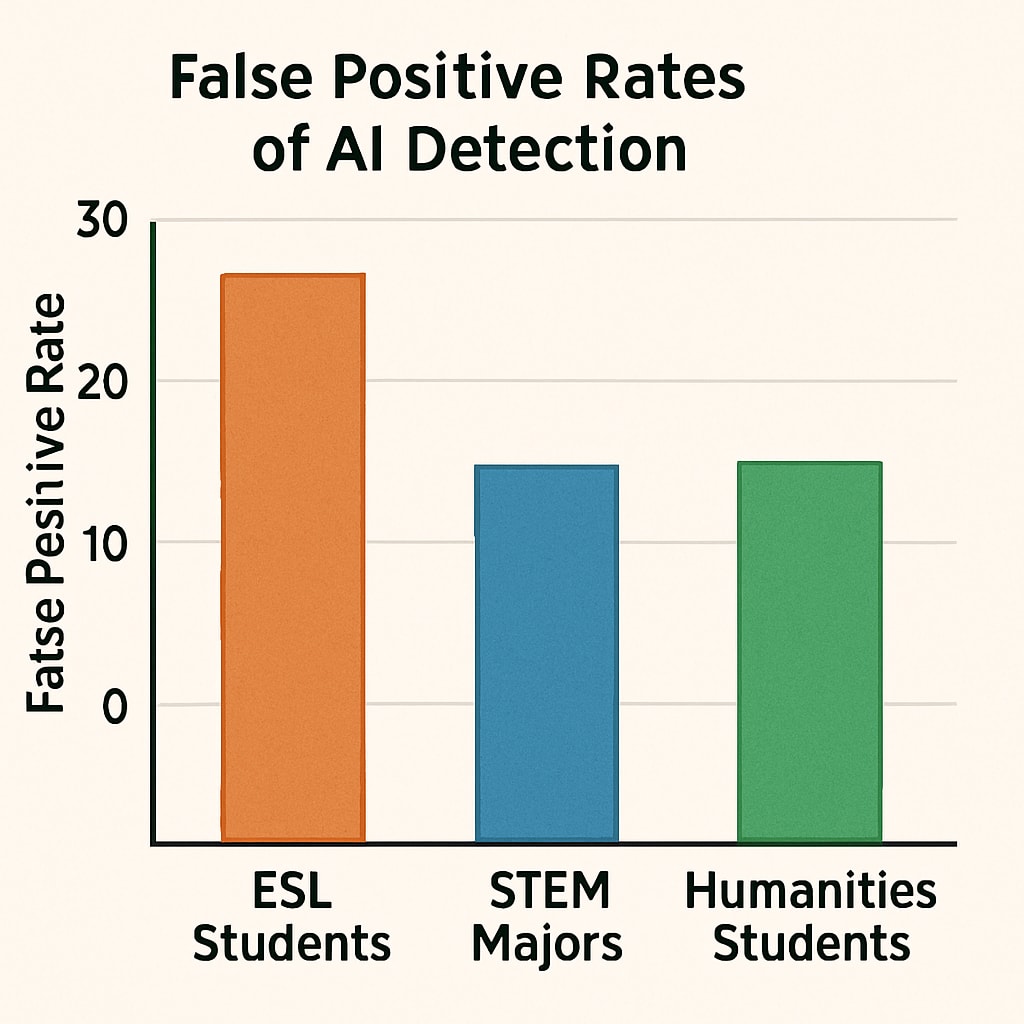
However, as noted in Wikipedia’s AI in Education entry, these metrics frequently misclassify non-native English speakers’ work and highly structured academic writing. For example, a MIT case study found that advanced STEM students receive 3x more false positives than humanities peers due to technical writing styles.
Protecting Students From False Accusations
Five evidence-based strategies can help schools balance technological assistance with human judgment:
- Implement multi-layered verification: Combine AI tools with teacher evaluations and writing process reviews
- Educate about detection limitations: Teach students how algorithms work and their known biases
- Document drafting history: Use platforms like Google Docs that track revision timelines
- Establish appeal protocols: Create clear procedures for contesting AI detection results
- Promote authentic assessment: Design assignments that require personal reflection and in-class drafting
The Encyclopedia Britannica’s academic integrity guidelines emphasize that prevention always outperforms punishment in building ethical scholarship.
Building Trust in the Digital Classroom
Rather than treating AI detectors as infallible truth machines, educators should view them as imperfect tools requiring human oversight. When Massachusetts implemented mandatory detection software training for teachers, false accusation rates dropped by 62% within one academic year. This demonstrates how professional development can mitigate technology’s shortcomings while preserving student-teacher trust.
Key takeaways:
- Current AI writing detectors have unacceptably high false positive rates
- Marginalized student groups face disproportionate risks of misclassification
- Combining technology with human judgment creates more equitable systems
- Transparent policies protect both academic standards and student rights


