When considering BTEC, Computer Science, university applications, and apprenticeships, students face a critical decision in their educational journey. This comprehensive guide examines how these qualifications differ and which might better suit individual career aspirations.

Understanding the Qualification Structures
The BTEC Level 3 in Computer Science emphasizes practical skills through continuous assessment, while A-levels focus on theoretical knowledge examined through final tests. Key differences include:
- BTEC: 100% coursework-based with real-world projects (according to Pearson’s official BTEC guidelines)
- A-level: 70-80% exam-weighted with some coursework components
- BTEC offers specialization in areas like cybersecurity or software development
- A-level provides broader mathematical and theoretical foundations
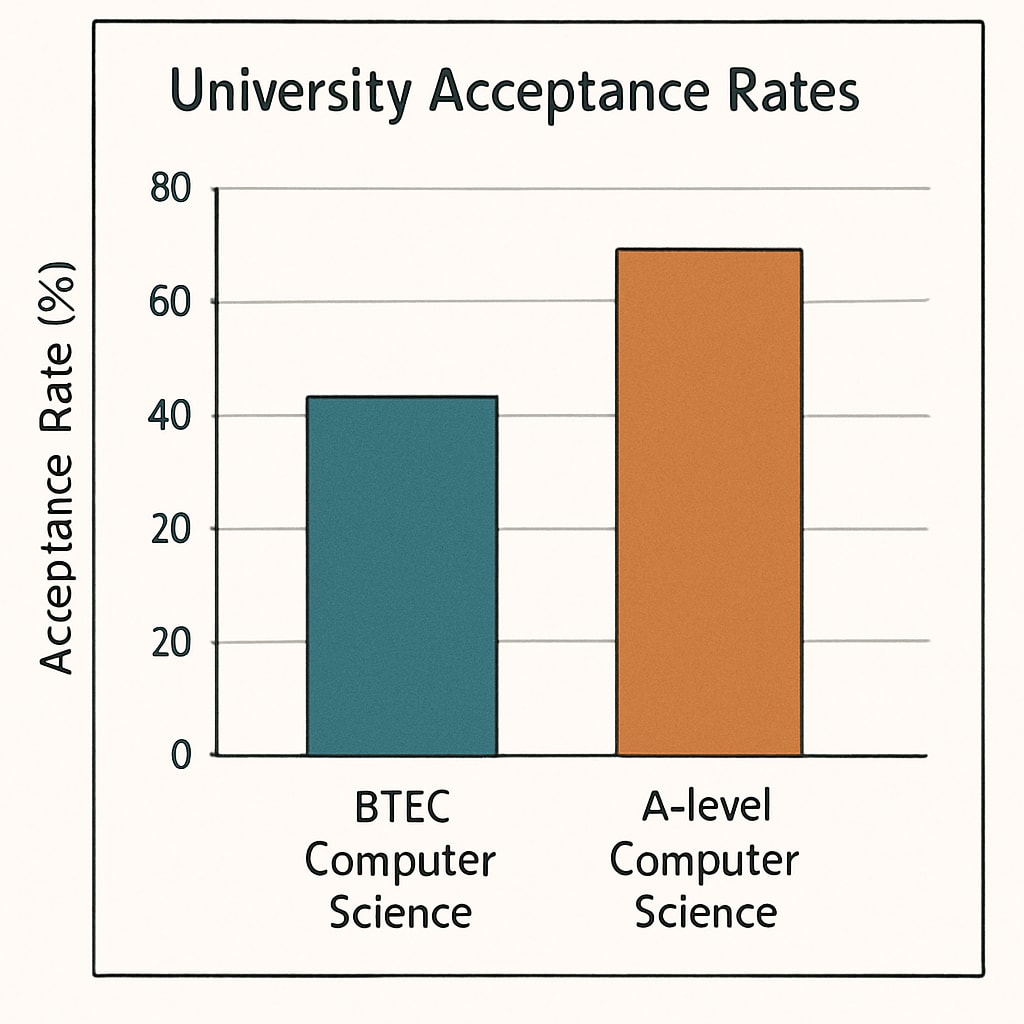
University Admission Considerations
Russell Group universities traditionally favored A-levels, but recent policy changes show increasing acceptance of BTEC qualifications. Important factors:
- Top-tier universities may require specific A-level subjects alongside BTEC
- BTEC students often demonstrate stronger practical skills for computer science degrees
- A-level Mathematics remains crucial for theoretical computer science programs
Career Pathways and Apprenticeship Opportunities
The vocational nature of BTEC qualifications provides distinct advantages for certain career trajectories:
- BTEC graduates typically transition faster into technical roles
- A-level students may have stronger theoretical foundations for research careers
- Many tech apprenticeships specifically request BTEC qualifications
- Industry certifications (e.g., Cisco, Microsoft) align well with BTEC coursework
Enhancing Your Application Profile
Regardless of qualification choice, students should consider these competitive boosters:
- Participating in coding competitions (e.g., Google Code Jam)
- Developing a portfolio of personal projects on GitHub
- Completing industry-relevant MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses)
- Securing work experience in tech-related environments
Readability guidance: The article maintains clear structure with bullet points for key comparisons. Transition words like “regardless,” “typically,” and “may” appear throughout to ensure smooth flow between ideas.


