Choosing among STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) majors like computer science, biomedical engineering, and medicine represents one of the most critical professional selection decisions high school graduates face. This crossroads often triggers anxiety as students weigh personal interests against academic demands and career prospects.
Decoding the STEM Landscape
The STEM umbrella covers diverse disciplines, each with unique characteristics:
- Computer Science: Focuses on programming, algorithms, and system design (Computer science on Wikipedia)
- Biomedical Engineering: Combines biology with engineering principles to develop medical solutions
- Medicine: Requires extensive clinical training and biological sciences mastery
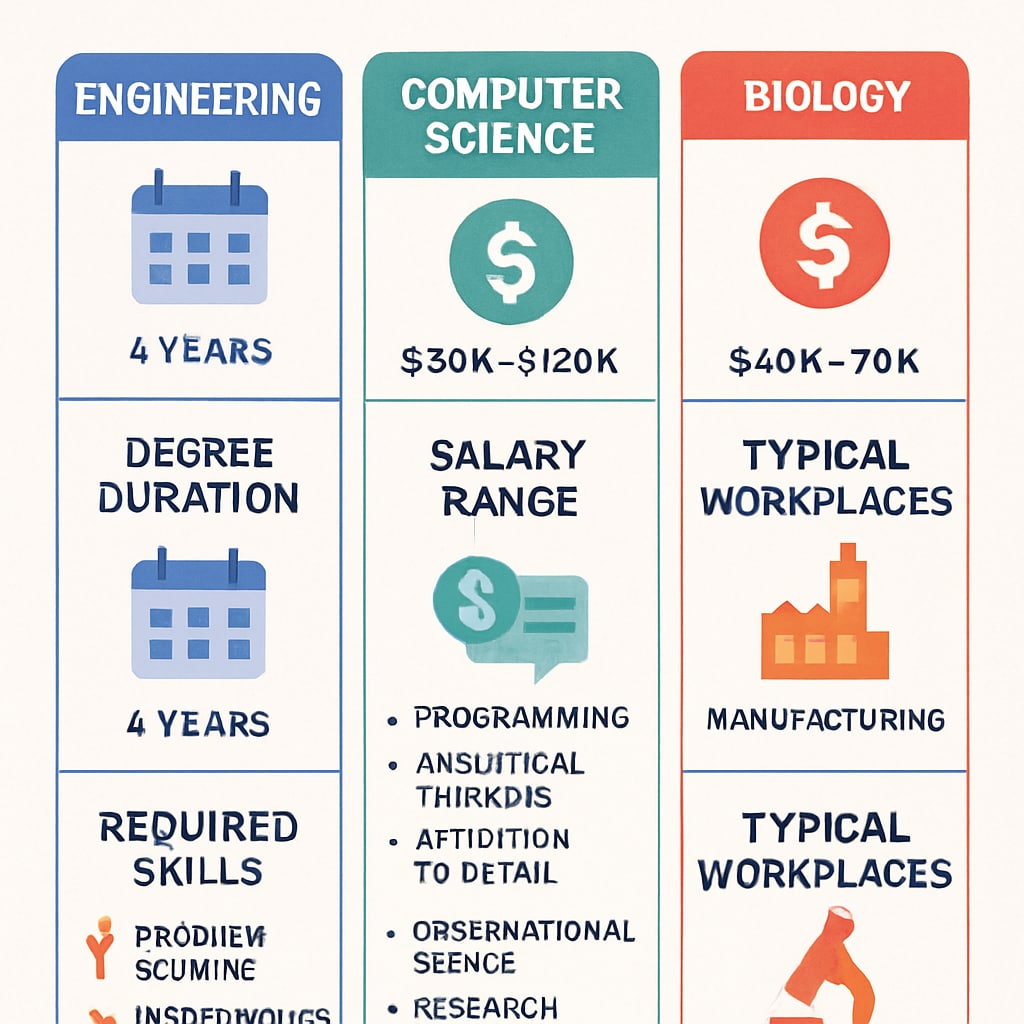
Career Pathways and Industry Demand
Each field offers distinct trajectories:
- Tech Sector: Computer science graduates enjoy high demand in software development and AI (Bureau of Labor Statistics data)
- Healthcare Innovation: Biomedical engineers work in medical device development and research
- Clinical Practice: Medical professionals follow structured residency programs
Key considerations include program duration, required competencies, and projected job growth. For example, while computer science offers relatively quick entry into the workforce, medicine requires nearly a decade of training before full practice.
Transitioning between these fields becomes increasingly difficult after undergraduate studies. Therefore, students should carefully evaluate their aptitude for mathematics, biological sciences, and hands-on problem-solving before committing.


