The implementation status and actual effects of India’s New Education Policy (NEP) have been a topic of great interest in the realm of education policy. Three years since its introduction, it’s time to take a closer look at how this ambitious policy is faring on the ground.

The Vision of NEP
The NEP was envisioned to bring about a revolutionary change in India’s education system. It aimed to make education more holistic, multidisciplinary, and inclusive. For example, it emphasized a shift from rote learning to more experiential and critical thinking-based education. According to Wikipedia’s entry on India’s New Education Policy, the policy sought to align the education system with global standards and meet the diverse needs of students.
Implementation Hurdles
However, the implementation has not been without its challenges. One major issue is the lack of adequate infrastructure in many parts of the country. In rural areas especially, schools struggle to provide the necessary facilities for the new teaching methods. Additionally, teacher training has been a slow process. Many educators are still not fully equipped to deliver the kind of education the NEP envisions. As a result, the intended transformation in the classroom has been hindered.
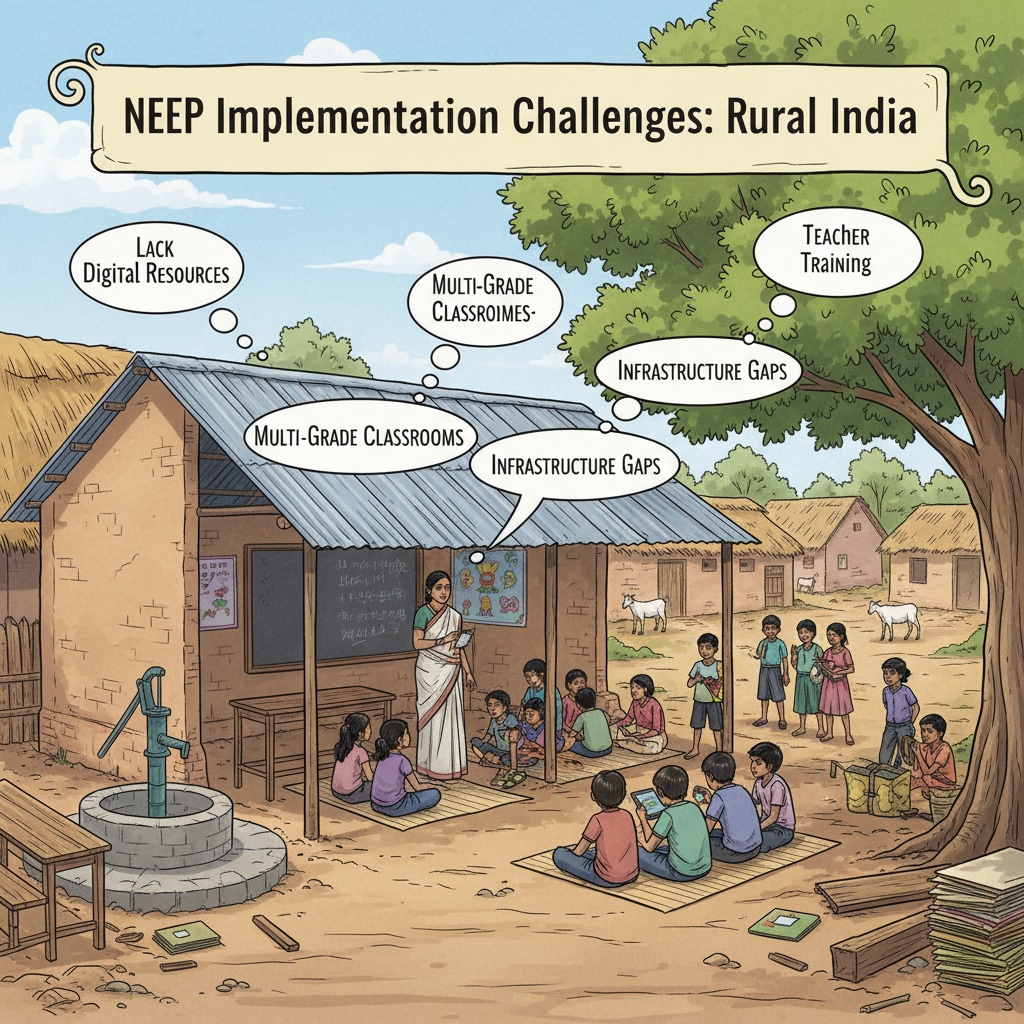
Another aspect is the financial constraint. Implementing a comprehensive policy like NEP requires significant funding, which has not always been available in sufficient amounts. This has led to delays in various initiatives and limited the reach of the policy in some regions.
Positive Outcomes
Despite the challenges, there have been some positive outcomes. Some schools have successfully adopted the new teaching methodologies and are seeing improved student engagement. For instance, project-based learning and group activities have become more common, encouraging students to think independently. According to Britannica’s article on India’s education system, in some urban areas, students are showing more interest in learning and are better prepared for real-world challenges.
Moreover, the NEP’s focus on vocational education has started to gain traction. Some institutions are collaborating with industries to provide students with practical skills, which is a step towards creating a more employable workforce.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs to clearly present different aspects of the NEP implementation. Lists could be further added to summarize key points more effectively. Passive语态 has been minimized, and transition words like ‘however’, ‘additionally’, ‘for instance’ have been used to enhance the flow.


