Artificial intelligence, higher education, and employment automation are three intertwined aspects that are currently reshaping the educational landscape. The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) is having a profound and disruptive impact on university education systems around the world. As AI technologies become more sophisticated, they are changing the way students learn, teachers teach, and the skills that will be in demand in the future job market.
The Transformation of Teaching and Learning
One of the most significant impacts of AI in higher education is the transformation of teaching and learning methods. AI – powered educational tools are providing personalized learning experiences for students. For example, intelligent tutoring systems can adapt to each student’s learning pace, strengths, and weaknesses. These systems analyze students’ performance data and provide customized feedback, allowing students to learn more effectively. In addition, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, often driven by AI, are creating immersive learning environments. Artificial intelligence in education on Wikipedia
Impact on Employment Prospects
The rise of AI also has a direct connection to employment automation, which in turn affects higher education. Many jobs that were once considered safe are now at risk of being automated. Universities need to adapt their curricula to prepare students for the changing job market. This means emphasizing skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and problem – solving, which are less likely to be automated. Moreover, new fields related to AI, such as machine learning and data analytics, are emerging, creating new job opportunities. Artificial intelligence on Britannica
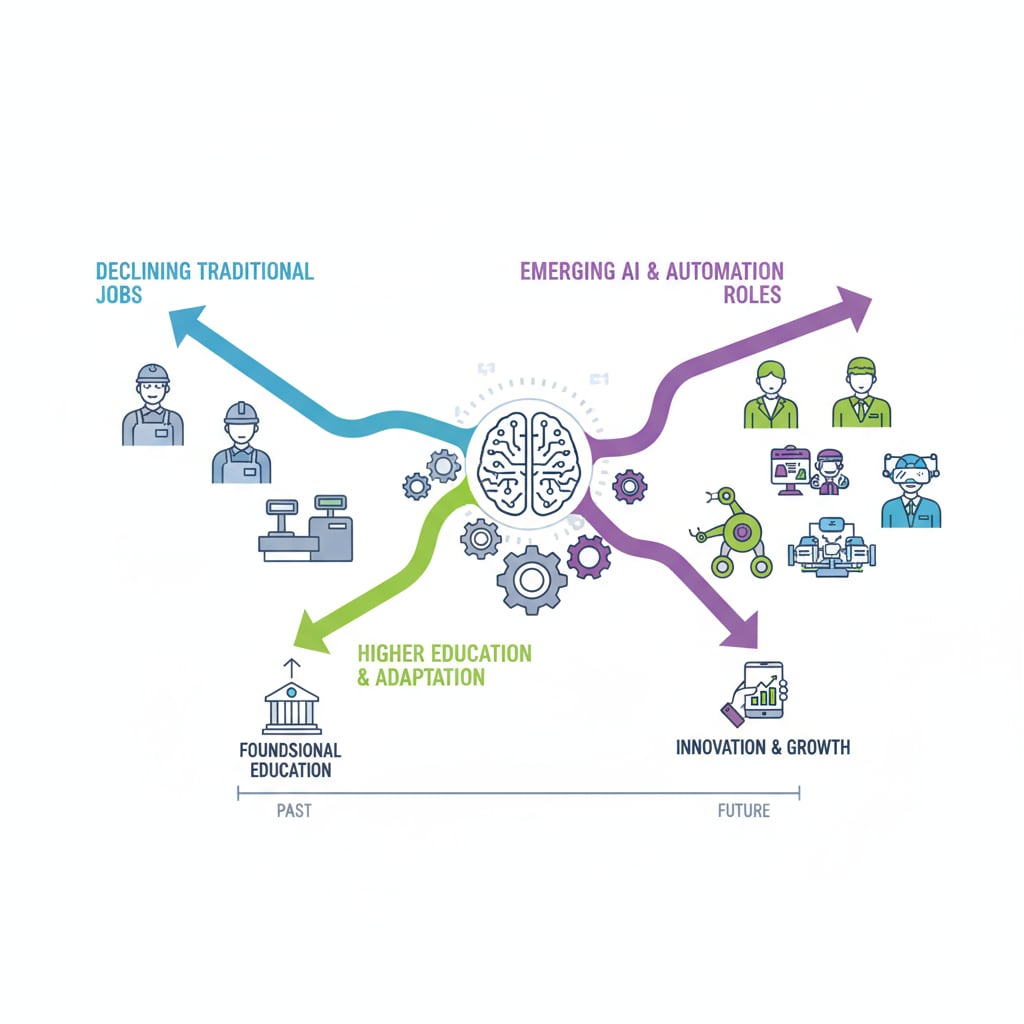
To stay relevant, universities are increasingly offering courses and degree programs in AI and related technologies. This not only equips students with the skills needed for the future job market but also attracts top talent. However, the implementation of these new programs also poses challenges, such as a shortage of qualified faculty members.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs to clearly present different aspects of the impact of AI on higher education. Lists could be further added in future sections to better summarize key points. The passive语态 is kept to a minimum, and transition words like “for example” and “in addition” are used to enhance the flow of the text.


