In an era where technology and innovation are reshaping industries, the importance of engineering design thinking cannot be overstated. For parents and educators aiming to prepare students for future success, fostering engineering design thinking during the K12 education phase is crucial. This article delves into the significance of early exposure to design principles, the role of K12 education in shaping career trajectories, and practical strategies for nurturing these skills.
The Importance of Engineering Design Thinking in K12 Education
Engineering design thinking is a problem-solving process that combines creativity, critical thinking, and technical knowledge. Introducing this mindset during the K12 years prepares students to tackle real-world challenges, equipping them with skills that are highly valuable in fields like engineering, architecture, and technology. According to Britannica, engineering is fundamentally about applying scientific principles to design solutions for practical problems, and this approach can be cultivated early through hands-on learning experiences.
Moreover, fostering these skills during the formative years helps students identify their interests and strengths, which is beneficial when choosing a career path or pursuing advanced degrees like a master’s in design engineering. By developing a mindset that values experimentation and resilience, students not only excel academically but also grow into innovative professionals who can adapt to an ever-changing workforce.
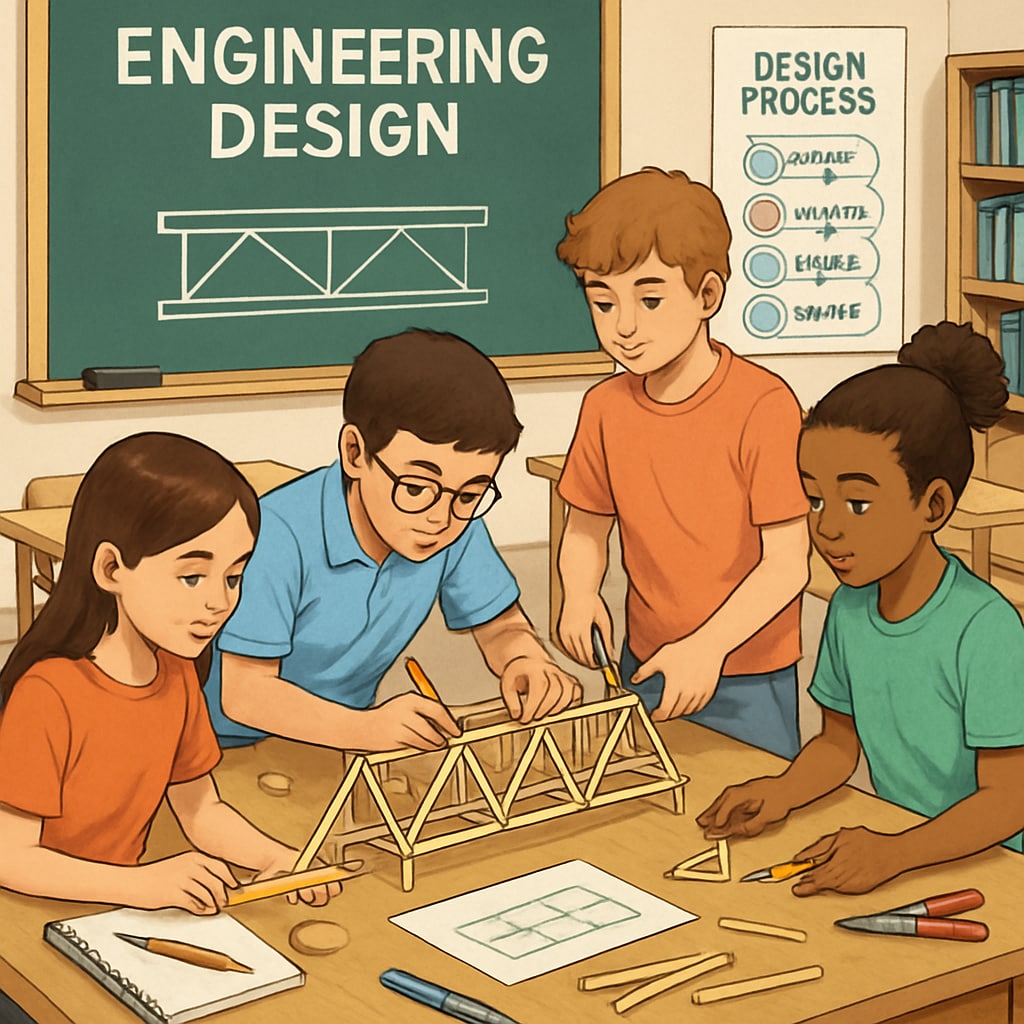
Strategies to Incorporate Engineering Design Thinking into K12 Education
To effectively nurture engineering design thinking, schools and parents can adopt the following strategies:
- Project-Based Learning: Encourage students to engage in projects that require them to identify problems, brainstorm solutions, and create prototypes. For example, building a functional model of a wind turbine can teach both design principles and environmental awareness.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Facilitate group activities that mimic real-world engineering scenarios, emphasizing teamwork and communication.
- STEM Integration: Combine science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) subjects to provide interdisciplinary learning experiences. This approach mirrors the multifaceted challenges engineers face in their careers.
- Mentorship and Role Models: Connect students with professionals in the engineering field to inspire them and provide practical insights into career opportunities.
Incorporating these strategies not only makes learning more engaging but also aligns with the essential competencies required for higher education and professional success.

Preparing for Advanced Studies and Career Development
One of the ultimate goals of fostering engineering design thinking is to pave the way for students to pursue advanced degrees, such as a master’s in design engineering. These specialized programs often require a strong foundation in problem-solving, creativity, and technical skills—all of which can be developed during the K12 years.
When choosing an advanced degree, students should consider how their undergraduate education and K12 experiences align with their career aspirations. For instance, a student with exposure to design projects in high school may be more inclined to pursue fields like mechanical engineering or industrial design. As noted by Wikipedia, engineering encompasses a broad spectrum of disciplines, allowing students to tailor their education to their interests and the demands of the job market.
In addition, early exposure to engineering principles can help students make informed decisions about their academic paths. Parents and educators play a pivotal role in guiding students toward opportunities that align with their strengths and interests, ensuring they are well-prepared for both graduate studies and professional growth.
Conclusion: Building the Foundation for Future Innovators
Engineering design thinking is more than just a skill—it is a mindset that empowers students to approach problems with creativity and confidence. By incorporating hands-on projects, fostering collaboration, and providing early exposure to STEM principles, K12 education can lay the groundwork for lifelong learning and career success.
As the demand for innovative problem-solvers continues to grow, equipping students with engineering design thinking will not only enhance their educational experiences but also prepare them to excel in a competitive and ever-evolving job market. Whether pursuing a master’s in design engineering or thriving in a related field, the skills cultivated during K12 education can make all the difference.
Readability guidance: This article uses short paragraphs, active voice, and transition words to ensure clarity. Lists are used to summarize strategies, and external links provide additional context for readers seeking deeper insights.


