American geometry education, high school geometry courses, and geometry learning apps play crucial roles in shaping students’ mathematical understanding in the United States. The American high school geometry education system is a complex yet fascinating area to explore. It encompasses a wide range of aspects, from the curriculum framework to the various learning resources available.
The Structure of American High School Geometry Curriculum
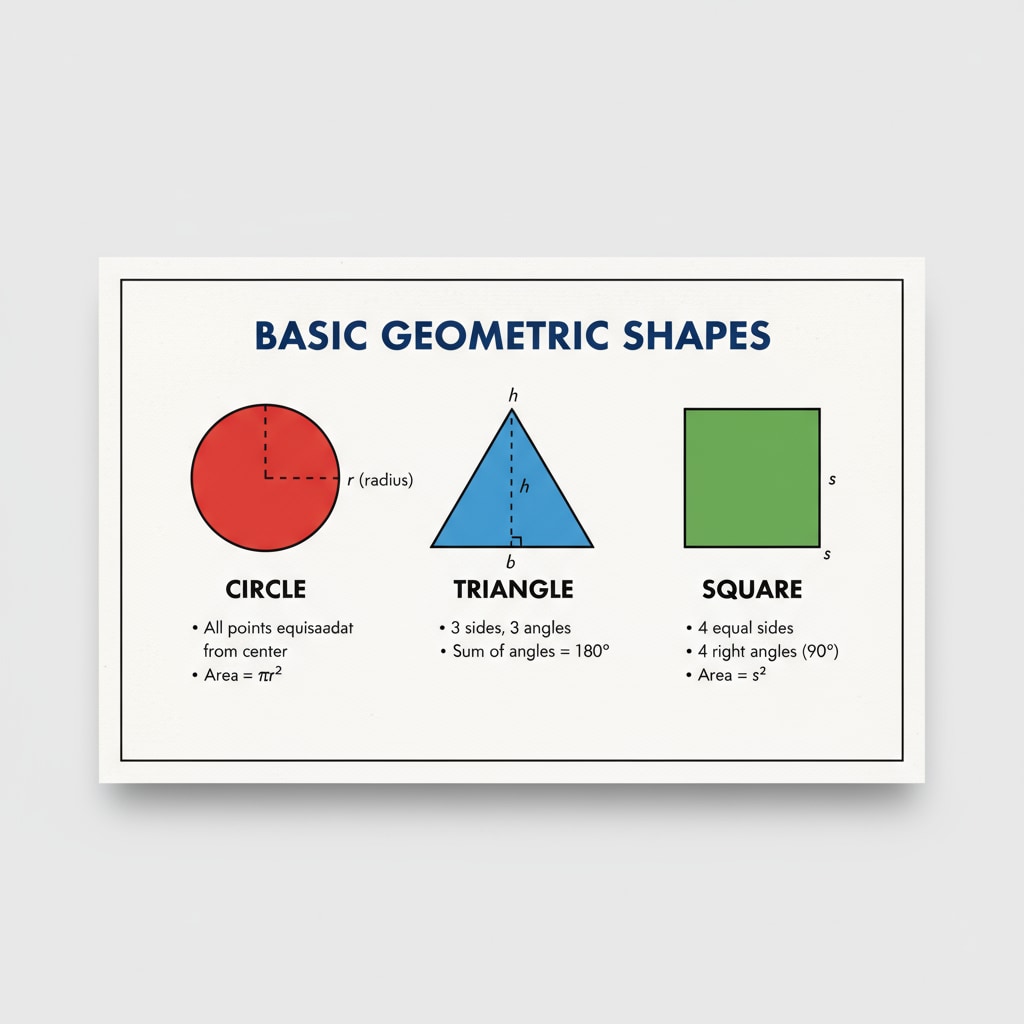
The American high school geometry curriculum is designed to build students’ logical thinking and spatial reasoning skills. It typically starts with basic geometric concepts such as points, lines, and planes. For example, students learn about the properties of different types of angles and how to measure them. As they progress, they move on to more complex topics like congruence and similarity of geometric figures. According to Wikipedia’s page on Geometry education in the United States, the curriculum also includes three-dimensional geometry, where students study shapes like cubes, spheres, and pyramids. This structured approach helps students gradually develop a solid foundation in geometry.
Teaching Resources in American High School Geometry
In addition to textbooks, American high school geometry educators have access to a variety of teaching resources. Online platforms offer interactive lessons, videos, and simulations. For instance, some websites provide virtual manipulatives that allow students to explore geometric concepts in a hands-on way. These resources enhance the learning experience and make geometry more engaging. Teachers also use real-world examples to illustrate geometric principles. As a result, students can better understand how geometry applies to everyday life. Britannica’s entry on Geometry mentions the importance of practical applications in making geometry accessible to students.
The use of geometry learning apps has also become increasingly popular. These apps offer features like step-by-step problem-solving guides and personalized learning paths. They are convenient for students to use both in and out of the classroom, providing additional support for their learning.
Readability guidance: The paragraphs above are short and to the point. The use of examples and external links adds credibility. Transition words like “for example”, “as a result”, and “in addition” are used to enhance the flow. Each H2 has a related list of key points to summarize the main ideas.


