The implementation of the New Education Policy (NEP) in India, an important education policy, has been a topic of great interest. Three years after its roll – out, it’s crucial to assess its actual implementation status and the resulting effects.
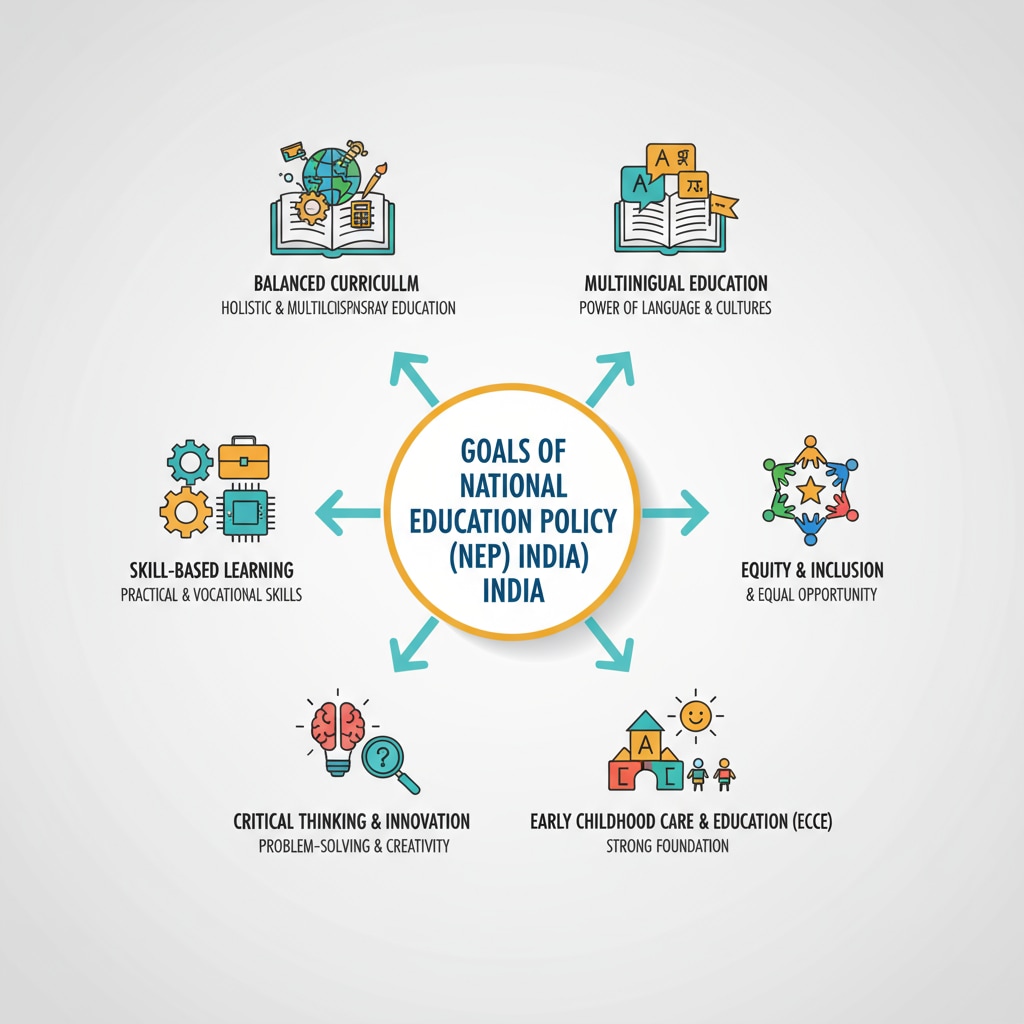
The Goals of NEP
The NEP in India was designed with lofty goals. Its aim was to revolutionize the education system, making it more holistic, flexible, and in tune with the 21st – century requirements. For example, it sought to promote multilingualism, critical thinking, and a more skill – based learning approach. According to Wikipedia’s entry on the New Education Policy 2020 (India), the policy envisioned a comprehensive overhaul of the curriculum to meet the diverse needs of students.
Implementation in K12 Education
In the K12 education segment, the implementation has been a mixed bag. On one hand, there have been efforts to introduce new teaching methods. Some schools have started incorporating project – based learning, which is in line with the NEP’s emphasis on practical skills. However, on the other hand, many schools are struggling to adapt. For instance, a lack of trained teachers in the new methodologies has been a significant hurdle. As reported by Britannica’s article on education in India, the existing teacher training infrastructure needs to be upgraded to support the new policy.
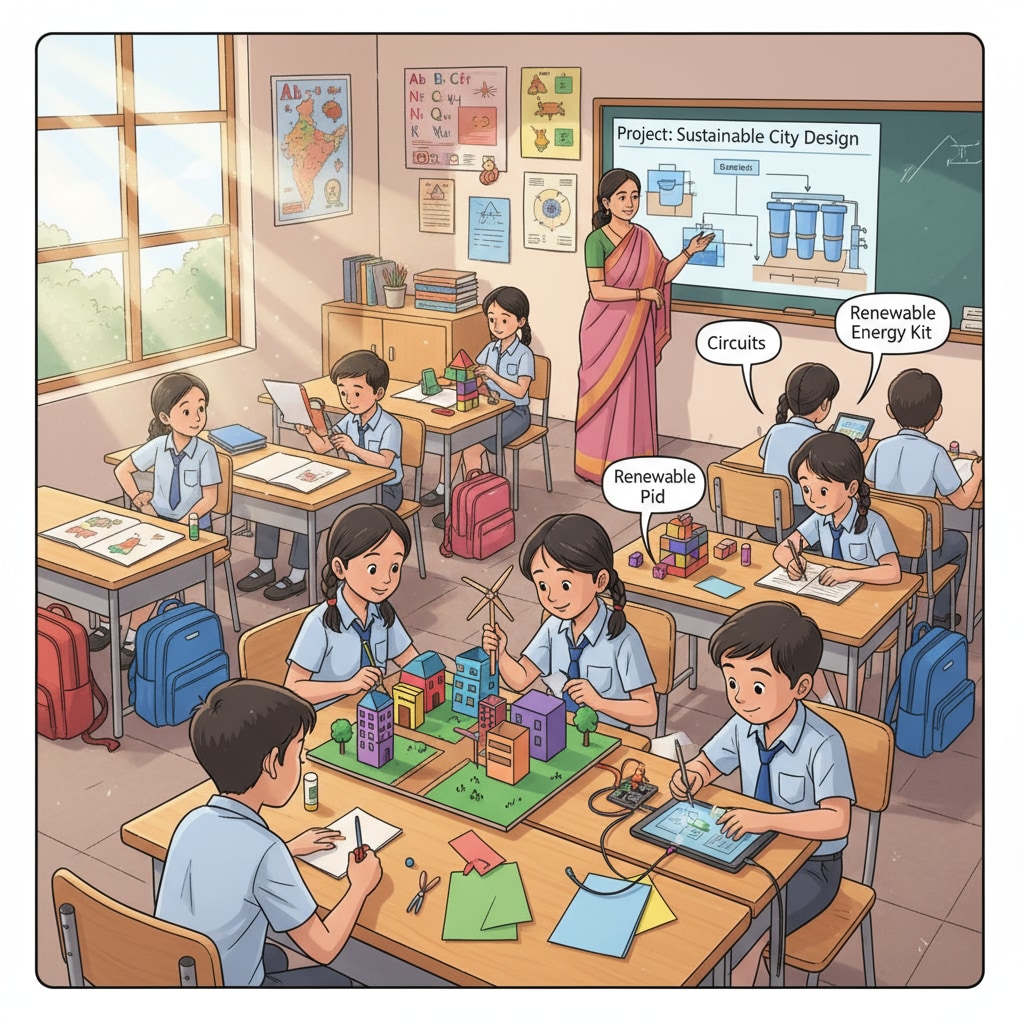

Another aspect is the curriculum reform. The NEP proposed a more integrated curriculum, but in reality, the transition has been slow. Many schools are still following the old curriculum frameworks due to a lack of clear guidelines and resources for implementing the new one.
Readability guidance: The implementation of NEP in K12 education has both positive and negative aspects. We have used short paragraphs to clearly present these different aspects. Transition words like ‘however’ and ‘on the other hand’ have been used to show the contrast. A list could be made here: Positive aspects – introduction of new teaching methods; Negative aspects – lack of trained teachers, slow curriculum reform.
Impact on Students
The impact on students is gradually becoming visible. Some students in schools that have successfully implemented NEP initiatives are showing improved creativity and problem – solving skills. They are more engaged in the learning process as the new methods make learning more interactive. However, for a large number of students, especially those in rural areas or underprivileged schools, the benefits are yet to be fully realized. The lack of proper infrastructure and resources in these schools is preventing the effective implementation of the policy.
The Gap Between Ideal and Reality
There is a significant gap between the ideal envisioned by the NEP and the current educational reality in India. The policy’s ambitious goals require substantial investment, both in terms of financial resources and human capital. The slow pace of teacher training, lack of updated infrastructure, and resistance to change from some traditional educational institutions are all contributing to this gap.
Readability guidance: We have used short paragraphs to quickly convey the main points. Transition words like ‘however’ help in showing the difference between the impact on different groups of students. A list could summarize the reasons for the gap: lack of investment, slow teacher training, and resistance to change.
Future Improvement Directions
To bridge the gap, several steps need to be taken. First, there should be a focused effort on teacher training. This includes providing in – service training programs that are specifically designed to train teachers in the new NEP – compliant teaching methods. Second, more resources should be allocated to improve school infrastructure, especially in rural and underprivileged areas. Third, there needs to be better communication and awareness campaigns to ensure that all stakeholders, including parents, understand the benefits of the NEP and support its implementation.
In conclusion, the implementation of the New Education Policy (NEP) in India has shown both progress and challenges. While the policy has the potential to transform the education system, it will require sustained efforts and targeted interventions to overcome the existing hurdles and achieve its intended goals.


