Choosing the right degree in design engineering can significantly influence one’s career trajectory. With options ranging from bachelor’s programs to specialized master’s degrees such as MEng (Master of Engineering) and MSc (Master of Science), students face critical decisions that shape their employment prospects. This article delves into the distinctions between these degrees, offering insights into how they align with career goals and market demands.
Understanding the Basics of Design Engineering Degrees
Design engineering is a dynamic field that combines technical expertise with creativity to develop innovative solutions. At the undergraduate level, students typically pursue a Bachelor of Science (BSc) or Bachelor of Engineering (BEng) degree. These programs provide foundational knowledge in areas such as product design, materials science, and engineering principles.
At the graduate level, MEng and MSc programs offer advanced training tailored to specific career paths. While both degrees are valuable, their focus and outcomes differ significantly. For example, the MEng is often more practice-oriented, emphasizing hands-on projects and industry collaboration, whereas the MSc leans towards theoretical research and academic exploration.
MEng vs. MSc: Which Path Should You Choose?
The choice between an MEng and an MSc depends on your career aspirations. Below are some key differences:
- MEng (Master of Engineering): Ideal for students aiming for industry roles. It emphasizes practical skills, internships, and real-world applications, making graduates highly employable. Common career options include design engineer, product development specialist, and systems engineer.
- MSc (Master of Science): Best suited for those interested in research, academia, or specialized technical roles. MSc programs focus on scientific research, advanced analytics, and theoretical concepts, often leading to roles in R&D or further academic pursuits.
For example, a student aiming to work with cutting-edge technologies in aerospace may benefit from an MSc, while someone interested in designing consumer electronics may find the MEng more valuable. Both degrees, however, are highly regarded in the industry.
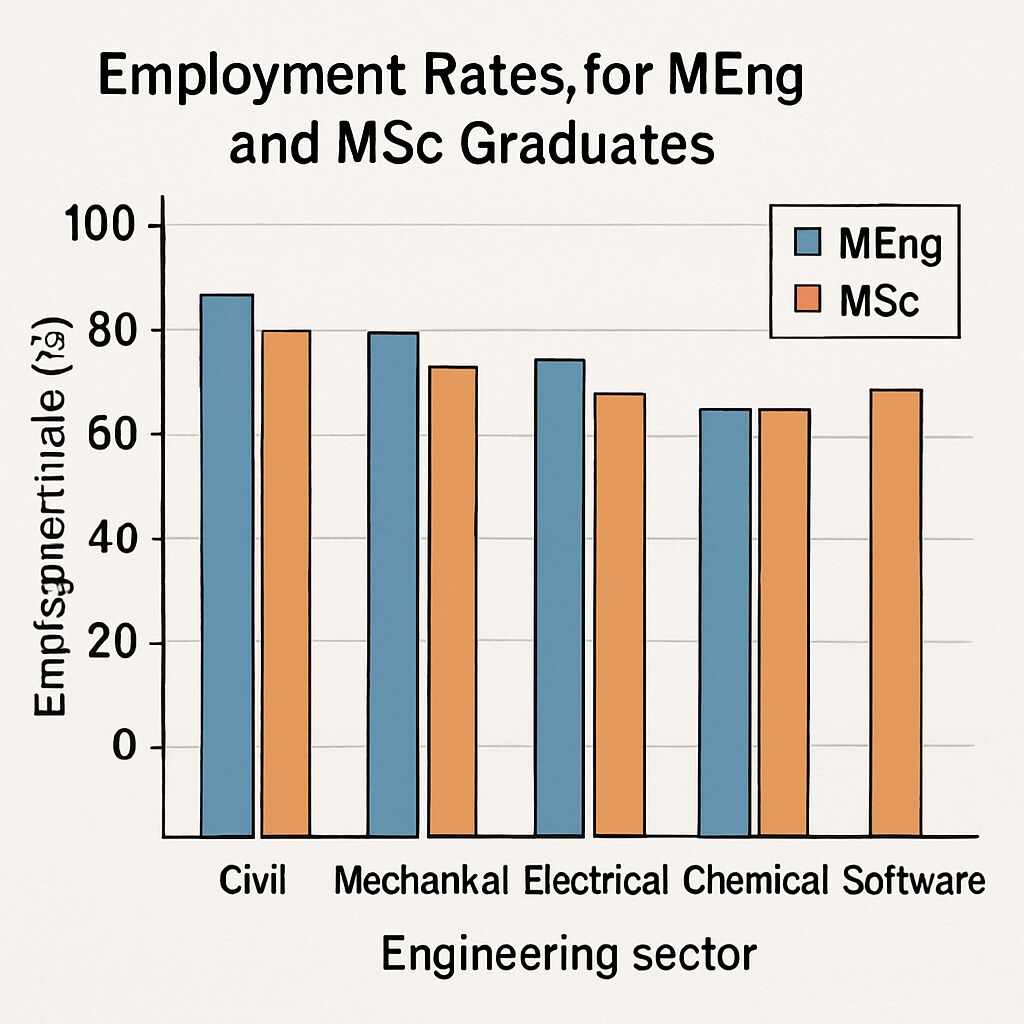
How Design Engineering Degrees Affect Employment Prospects
Employers often seek graduates with the skills and knowledge to tackle complex problems. According to data from engineering career studies, master’s degree holders generally earn higher starting salaries and have access to more senior roles than bachelor’s degree holders. This is especially true in industries such as automotive, renewable energy, and technology.
Additionally, the global demand for design engineers is growing. A report by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics highlights a steady increase in engineering job opportunities, particularly for those with advanced qualifications. Similarly, EngineeringUK notes that engineering graduates are among the most employable professionals worldwide.
Making an Informed Decision
When choosing a degree, students should consider the following factors:
- Career Goals: Determine whether you aim for industry, research, or academia.
- Program Structure: Evaluate the curriculum, internships, and project opportunities.
- Geographic Location: Some regions may prioritize certain degrees over others based on industry needs.
- Financial Considerations: Weigh tuition costs against potential salary benefits.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on aligning your education with your aspirations. Both MEng and MSc programs can serve as stepping stones to fulfilling and lucrative careers.
Conclusion: A degree in design engineering is more than just an educational credential; it is an investment in your future. By understanding the nuances between MEng and MSc programs, students can make informed decisions that maximize their career potential. Whether you envision yourself innovating in the industry or advancing scientific knowledge, there is a path in design engineering tailored for you.


