In today’s job market, humanities degrees often face significant employment dilemmas, and the process of skill transformation has become crucial. Humanities graduates find themselves at a crossroads, grappling with the practical value challenges in a job market increasingly dominated by STEM fields.

For instance, according to Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for STEM-related jobs has been steadily rising, while some traditional humanities positions have seen a decline.
The Challenges Faced by Humanities Graduates
One of the primary challenges is the perception gap. Many employers believe that humanities degrees lack the practical skills directly applicable to the modern workplace. As a result, humanities graduates may find it difficult to secure positions in highly competitive industries. For example, in the technology sector, which is booming, skills like programming and data analysis are highly sought after, leaving humanities graduates with fewer obvious entry points. Additionally, the salary disparity between humanities and STEM graduates can be a demotivating factor. Research from National Center for Education Statistics shows a significant difference in starting salaries, further highlighting the employment dilemmas faced by humanities graduates.
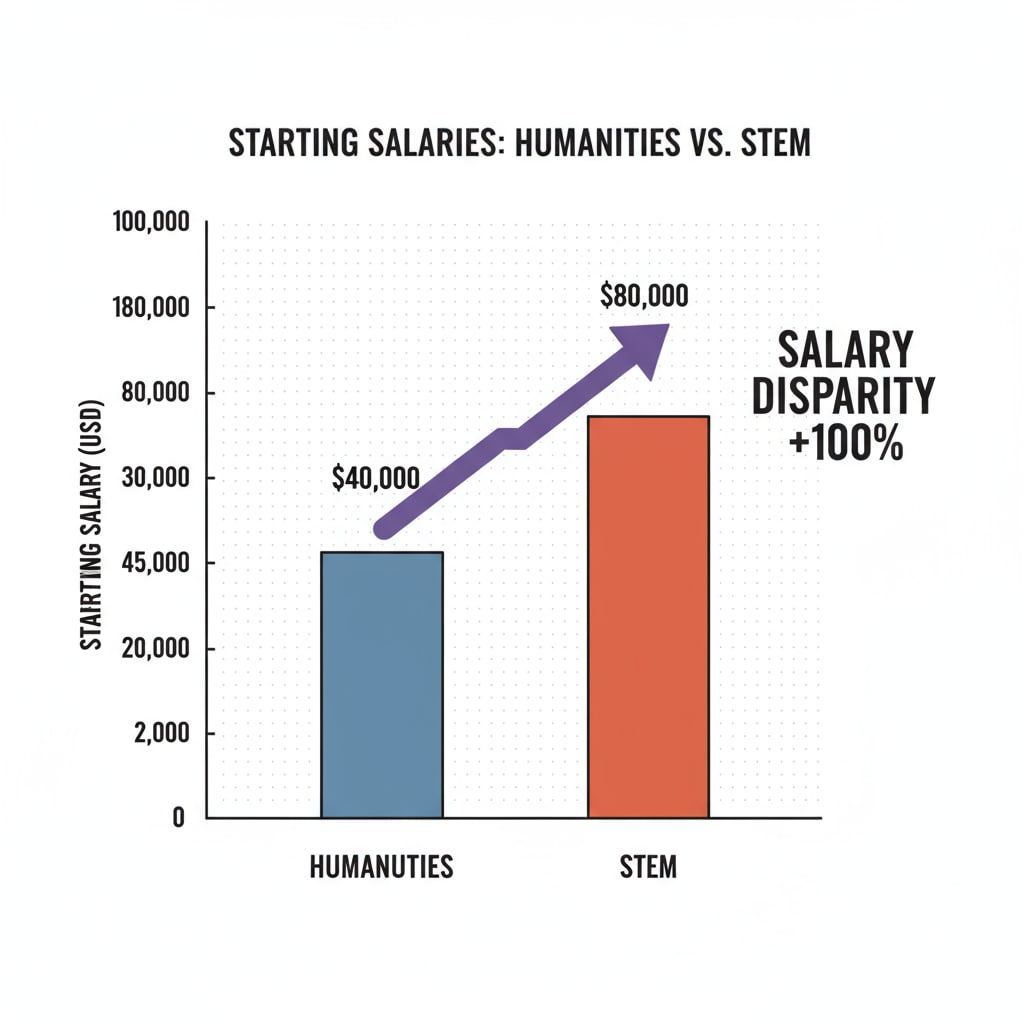
Reasons Behind the Predicament
The root cause lies in the disconnect between the skills taught in humanities education and the requirements of the job market. Humanities education often emphasizes critical thinking, communication, and cultural understanding, but these skills are not always easily translatable into tangible job skills. Moreover, the lack of career guidance in humanities programs can leave students ill-prepared for the job search process. They may not know how to effectively showcase their skills and knowledge in a way that appeals to employers. Another factor is the rapid pace of technological change. The job market is evolving at an unprecedented rate, and humanities education has struggled to keep up, leaving graduates facing an uphill battle in the employment landscape.
K12 Education Reform: A Path Forward
To address these issues, K12 education needs to undergo significant reform. Firstly, integrating more practical elements into the humanities curriculum can help students better understand how their studies relate to real-world jobs. For example, project-based learning that involves solving real problems can enhance their problem-solving and teamwork skills. Secondly, providing career exploration opportunities from an early age can help students make more informed decisions about their future. This could include internships, job shadowing, and guest lectures from professionals in various fields. Finally, promoting interdisciplinary learning can break down the barriers between humanities and STEM subjects. By combining skills from different areas, students can develop a more well-rounded skill set that is highly valued in the job market.
In conclusion, while humanities degrees currently face employment dilemmas, through effective skill transformation and K12 education reform, they can regain their relevance and value in the job market. Humanities graduates possess unique qualities that, when combined with practical skills, can open doors to a wide range of rewarding careers. It’s time to bridge the gap and empower the next generation of humanities students to thrive in the modern workplace.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs and lists are used to summarize key points. Each H2 section provides a list as much as possible. The proportion of passive voice and long sentences is controlled, and transitional words are scattered throughout the text.


