With the wide application of AI technology in the education field, the phenomenon of students using AI to generate content for homework has become increasingly common. The question of whether manually entered AI-rewritten content can evade AI detection tools has sparked a lively debate. Let’s delve into this complex issue.

The Rise of AI in K12 Education
In recent years, AI has made significant inroads into K12 education. It offers various benefits, such as personalized learning experiences and quick access to information. However, it has also given rise to a new challenge – students relying on AI to complete their assignments. For example, some students use AI writing tools to rewrite existing content, and then manually input it in the hopes of bypassing detection. Artificial intelligence in education on Wikipedia
The原理 of AI Detection Tools
AI detection tools operate on several principles. They analyze factors like language patterns, vocabulary usage, and the logical flow of the text. These tools are designed to recognize the hallmarks of AI-generated content, such as overly perfect grammar, repetitive sentence structures, and lack of unique perspectives. For instance, many detection tools compare the submitted text with a vast database of known AI-generated and human-written texts. Artificial intelligence on Britannica
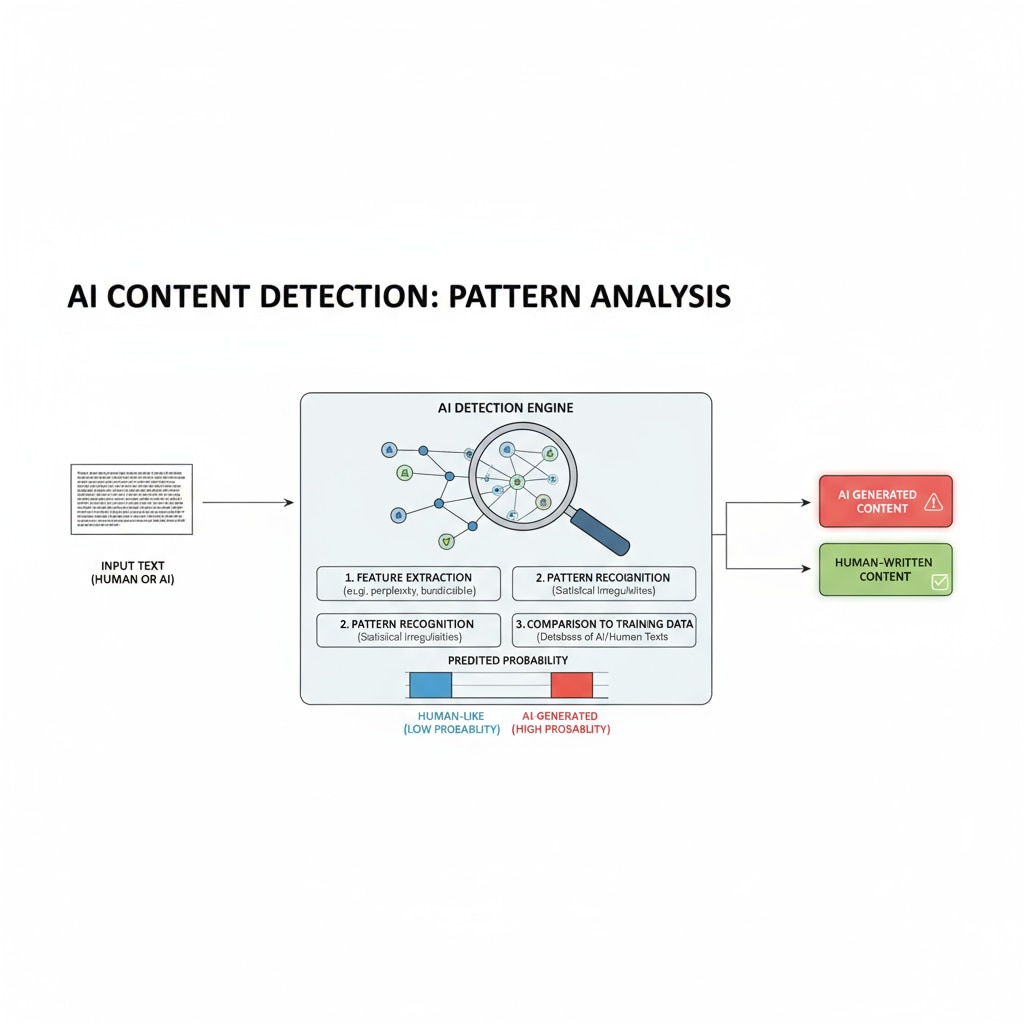
Despite their sophistication, these tools have limitations. The language used by students can be highly diverse, and some advanced AI rewriting techniques can produce content that closely mimics human writing. This makes it difficult for detection tools to accurately identify all cases of AI-generated content, especially when it is manually entered.
Can Manual Input Truly Evade Detection?
Manually entering AI-rewritten content might seem like a foolproof way to avoid detection, but it’s not that simple. While it can bypass some basic detection methods that rely solely on digital footprints, advanced detection tools can still pick up on telltale signs. For example, if the rewritten content still retains certain AI-generated language patterns, even after manual input, it may be flagged. Additionally, educators can use their own judgment by assessing the overall quality and coherence of the work in relation to the student’s usual performance.
Readability guidance: In this article, we’ve explored the complex relationship between AI detection tools, manual input, and rewritten content in K12 education. By understanding the principles of detection and its limitations, educators can better address the issue of AI-generated content in the classroom.


