The similarity between violin sounds and human crying often leads to interesting misunderstandings. One day, as the soft strains of a violin filled the air, a passerby stopped in their tracks, thinking someone nearby was crying. This incident highlights the strong emotional connection that can be forged between the two, and it’s a topic worthy of deeper exploration.
The Acoustic Resemblance
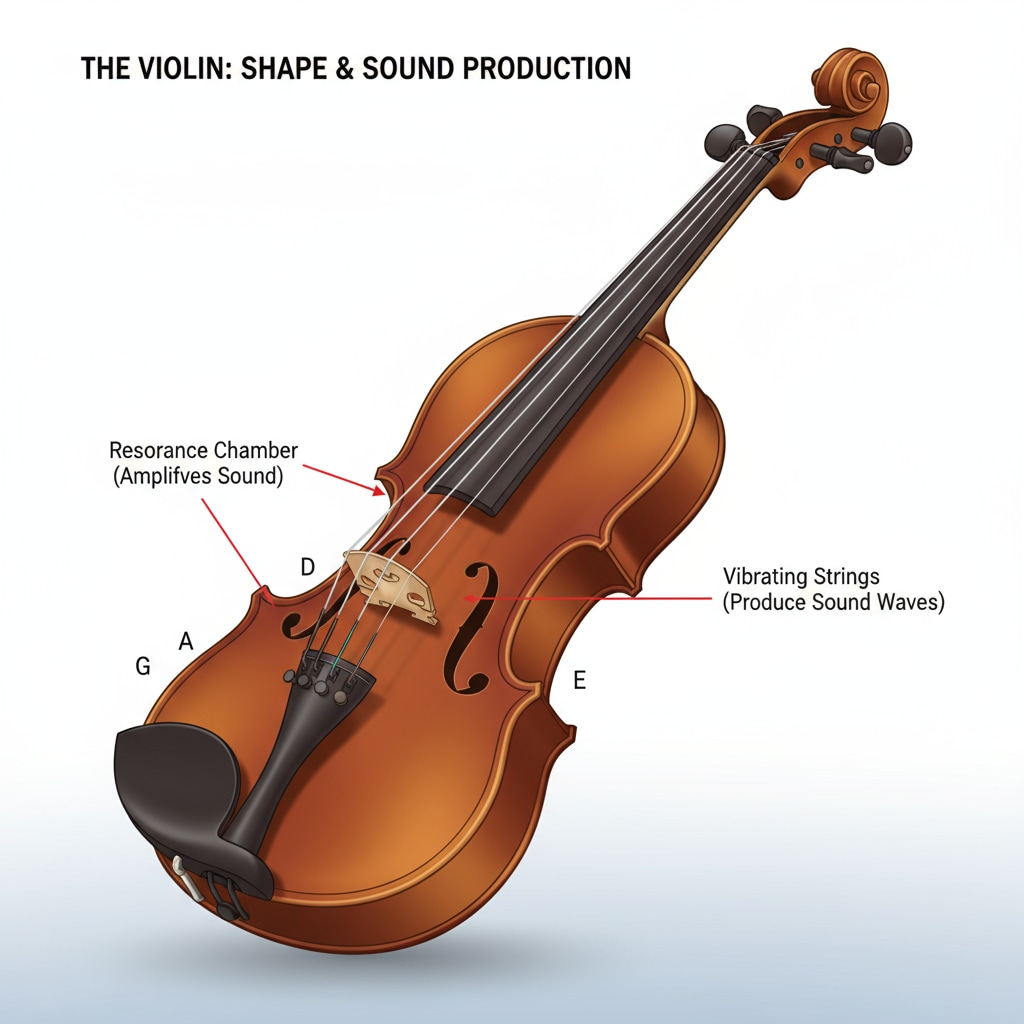
The similarity in sound between a violin and crying is not a mere coincidence. Violin tones can mimic the pitch fluctuations and timbre of a human cry. For example, the way a violinist can draw out a long, mournful note, similar to the wail of someone in distress. According to Wikipedia’s entry on the violin, the instrument’s unique construction allows for a wide range of expressive sounds, some of which closely resemble the human voice in moments of intense emotion. This acoustic similarity forms the basis for the frequent misinterpretations.
Emotional Connotations
Both violin music and crying carry deep emotional connotations. When we hear a violin playing a sad melody, it can evoke the same feelings of sorrow and empathy as the sound of someone crying. This emotional resonance is what makes the misinterpretation possible. As stated on Britannica’s page on music, music has the power to tap into our innermost emotions, and the violin, with its rich and expressive tones, is particularly effective at doing so. The shared emotional territory between the two creates a bridge that can lead to confusion.
These similarities between the violin and crying have significant implications for K12 music education. Educators can use this connection to help students better understand the emotional power of music. By exploring how the violin can imitate human cries, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the expressive capabilities of the instrument and music in general. This can enhance their musical perception and emotional intelligence.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs and lists are used to summarize key points. Each H2 section provides a list of related ideas. The proportion of passive voice and long sentences is controlled. Transition words like ‘however’, ‘therefore’, ‘in addition’, ‘for example’, and ‘as a result’ are scattered throughout the text.


