In functional English reading tests, understanding the purpose of a text is essential for effective comprehension. Functional English reading skills focus on real-life contexts such as interpreting instructions, analyzing informational texts, or understanding persuasive content. This article will guide K12 students and educators on identifying text purpose types accurately, improving reading comprehension, and mastering functional English reading techniques.
Understanding the Three Main Text Purpose Types
Functional English reading tests primarily evaluate the ability to identify three types of text purposes: informational, instructional, and persuasive. Each type has distinct characteristics that students must learn to recognize.
- Informational Texts: These texts aim to provide facts, data, or explanations. Examples include news articles, scientific reports, and brochures. Key indicators include neutral tone, evidence-based content, and structured formatting.
- Instructional Texts: Designed to guide the reader on performing a task, instructional texts are prevalent in recipes, manuals, and step-by-step guides. Look for numbered steps, imperative verbs, and clear sequential organization.
- Persuasive Texts: These texts seek to convince or influence the reader’s opinion. Advertisements, opinion pieces, and promotional materials often fall into this category. Pay attention to emotive language, rhetorical questions, and calls to action.

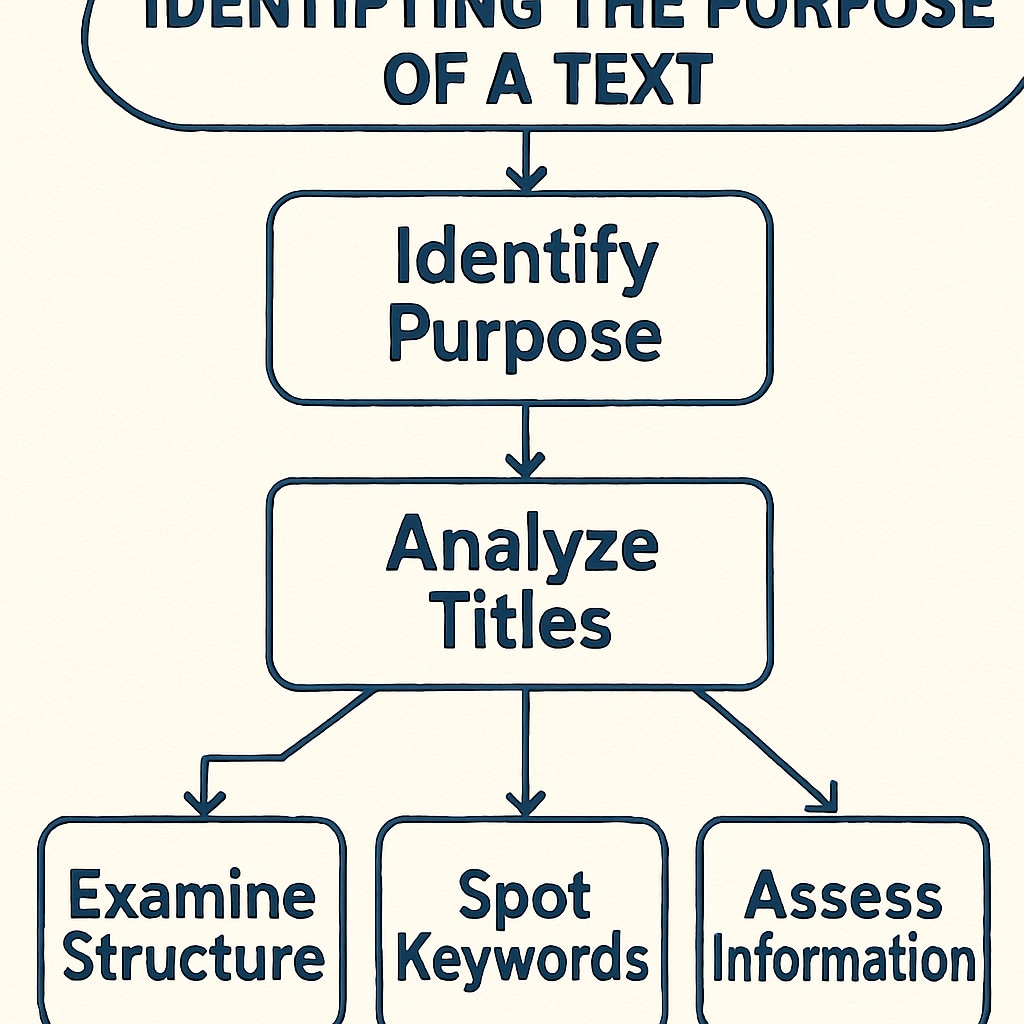
Practical Strategies for Identifying Text Purpose
Recognizing a text’s purpose can be challenging, especially when the content mixes multiple purposes. Here are practical strategies to simplify the identification process:
- Analyze the Title: Titles often provide clues about the text’s intent. For instance, a title like “How to Bake a Cake” suggests an instructional text.
- Examine the Structure: Informational texts usually include sections, headings, and bullet points, while instructional texts often feature lists or steps. Persuasive texts may use paragraphs with emotive language and arguments.
- Identify the Audience: Understanding who the text is targeting can help determine its purpose. For example, advertisements often address consumers directly.
- Spot Key Words and Phrases: Look for imperative verbs in instructional texts, factual statements in informational texts, and persuasive language in opinion pieces.
Applying Text Purpose Identification in Tests
During exams, time management and efficient reading are crucial. Below are tips to enhance performance:
- Skim and Scan: Quickly skim the text to grasp its structure and key elements before diving into details.
- Highlight Clues: Use a highlighter or underline words that suggest the text’s purpose, such as “instructions,” “facts,” or persuasive phrases.
- Answer Contextually: When answering questions, refer back to the text to ensure your response aligns with its intended purpose.
These strategies not only help in exams but also improve overall functional reading skills, making students more adept at understanding texts in real-world scenarios.
Conclusion: Mastering Functional English Reading
Identifying the purpose of a text is a foundational skill in functional English reading. By understanding the characteristics of informational, instructional, and persuasive texts, students can enhance their comprehension and excel in reading tests. Implementing the strategies outlined above will make the process more intuitive and efficient, empowering K12 learners to approach functional English with confidence.
For further reading on text structure and purpose, visit Text Structure on Wikipedia or explore Reading Comprehension on Britannica.


