In today’s dynamic world, the relationship between university degrees, the job market, and career development is undergoing significant transformation. As higher education becomes more accessible, the once-assured value of a university degree in the job market is now being questioned. This article aims to shed light on the current situation and explore possible solutions.
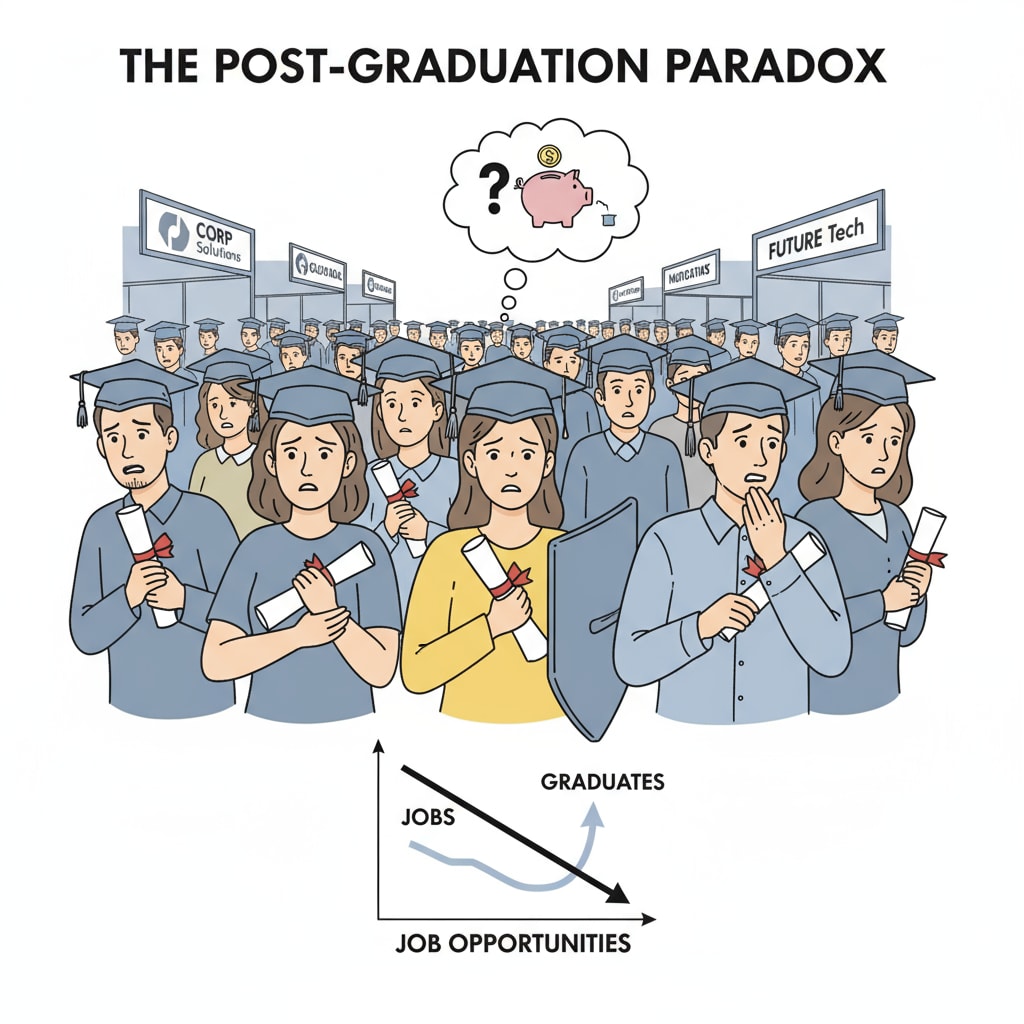
The Changing Landscape of University Degrees
The past few decades have witnessed a remarkable expansion of higher education. More people than ever are enrolling in universities, leading to a significant increase in the number of degree holders. According to National Center for Education Statistics, the number of bachelor’s degrees conferred in the United States has been steadily rising. However, this growth has also led to what some refer to as “degree inflation.”
Degree inflation means that as the supply of degree holders increases, the relative value of a university degree in the job market may decline. Employers are now inundated with a large pool of candidates with similar qualifications, making it more challenging for graduates to stand out.
The Disconnect Between Degrees and Career Development
One of the most significant issues is the growing gap between what students learn in university and the skills required in the job market. Many university curricula are designed to provide a broad-based education, focusing on theoretical knowledge rather than practical skills. For example, a computer science graduate may have a deep understanding of algorithms and programming languages but lack hands-on experience in developing real-world applications.
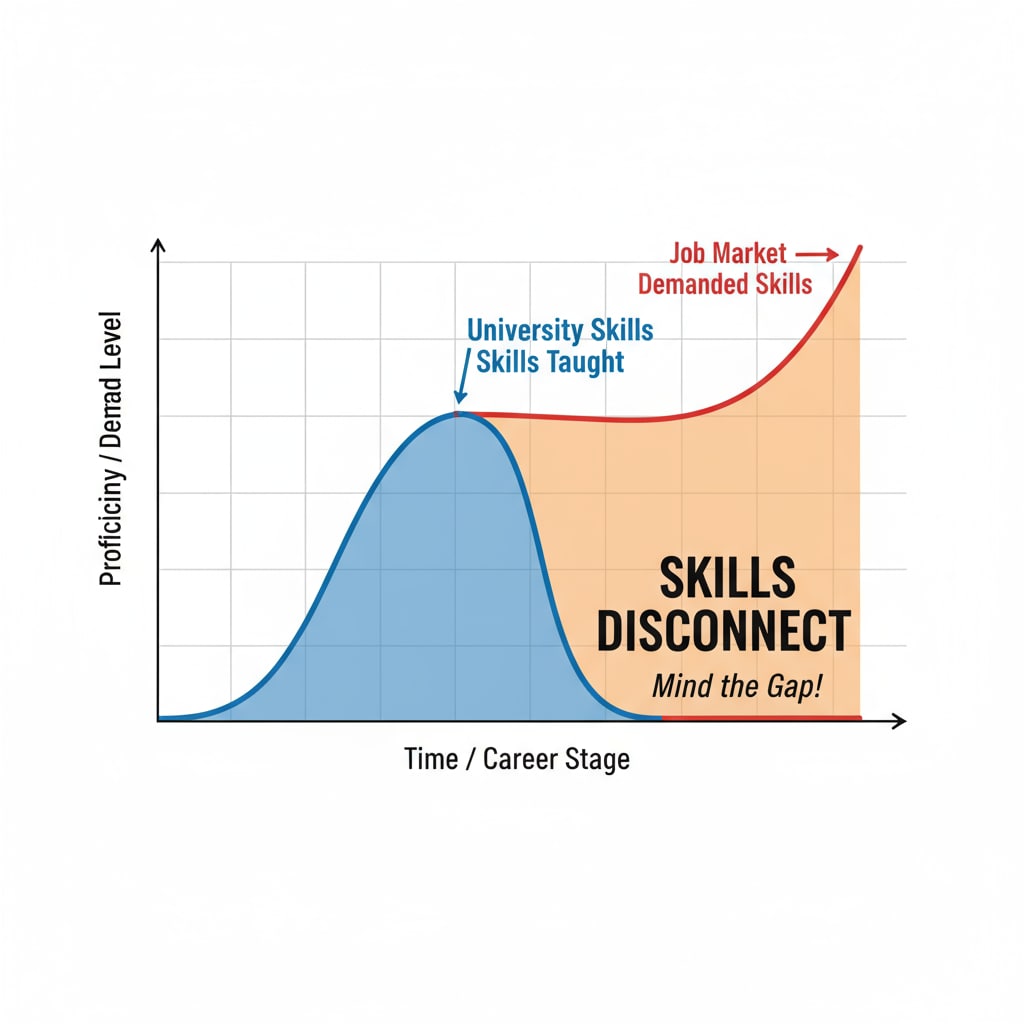
This disconnect can lead to difficulties in career development. Graduates may find it hard to secure jobs that align with their expectations, and even when they do, they may struggle to adapt to the workplace environment. As a result, many end up in jobs that do not fully utilize their degree knowledge, wasting years of education and potential.
Another aspect is the changing nature of jobs. The rapid pace of technological advancement and globalization has led to the emergence of new job roles and the obsolescence of some traditional ones. University degrees that were once highly sought-after may no longer be relevant in the current job market. For instance, jobs in certain industries like print media have declined significantly, leaving many journalism graduates with limited career options.
Readability guidance: As we’ve seen, the landscape of university degrees in the job market is complex. The growth in higher education has both positive and negative implications. The disconnect between degrees and career needs is a pressing issue that requires attention. In the following sections, we’ll explore how K12 education can play a role in addressing these challenges.
The Role of K12 Education in Responding to the Trend
K12 education has a crucial role to play in preparing students for the changing job market. Instead of solely focusing on academic achievements, it should also emphasize the development of practical skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. For example, introducing more project-based learning and internships in high school can give students a taste of the real working world.
Moreover, K12 education should also keep pace with the evolving job market trends. By incorporating courses on emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and digital marketing, students can be better equipped to pursue relevant careers in the future. This way, when they enter university, they have a clearer understanding of their career goals and can choose degree programs that align with the job market demands.
In conclusion, the value of university degrees in the job market is no longer as straightforward as it once was. The era of “high学历等于高薪就业” (a high degree equals high-paying employment) is fading. While a university degree still holds some value, it is essential to recognize the challenges and take proactive steps to bridge the gap between education and career development. K12 education, in particular, can play a significant role in shaping the future workforce and ensuring that students are well-prepared for the dynamic job market.


