In the realm of K12 education, research, evaluation, and educational social inequality are intertwined concepts that play a crucial role in shaping the future of education. Research in K12 education refers to the systematic investigation of educational phenomena, aiming to generate knowledge, understand teaching and learning processes, and identify effective practices. Evaluation, on the other hand, is the process of assessing the value, effectiveness, or worth of educational programs, policies, or practices. Educational social inequality, unfortunately, persists in many educational systems, manifesting in differences in access to quality education, educational resources, and educational outcomes among different social groups.

The Professional Definitions of Research and Evaluation in K12 Education
Research in K12 education encompasses various methods, including quantitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to test hypotheses and draw general conclusions. For example, a researcher might conduct a large-scale survey to determine the impact of a new teaching method on student achievement. Qualitative research, on the other hand, focuses on understanding the experiences, perspectives, and meanings of individuals through methods such as interviews, observations, and case studies. This type of research can provide in-depth insights into the factors influencing student learning. Educational research on Wikipedia
Evaluation in K12 education typically involves the use of multiple criteria to assess the effectiveness of educational initiatives. These criteria may include student learning outcomes, teacher performance, program implementation, and cost-effectiveness. Formative evaluation is conducted during the development or implementation of an educational program to provide feedback and make improvements. Summative evaluation, on the other hand, is carried out at the end of a program to determine its overall effectiveness. Evaluation in education on Britannica
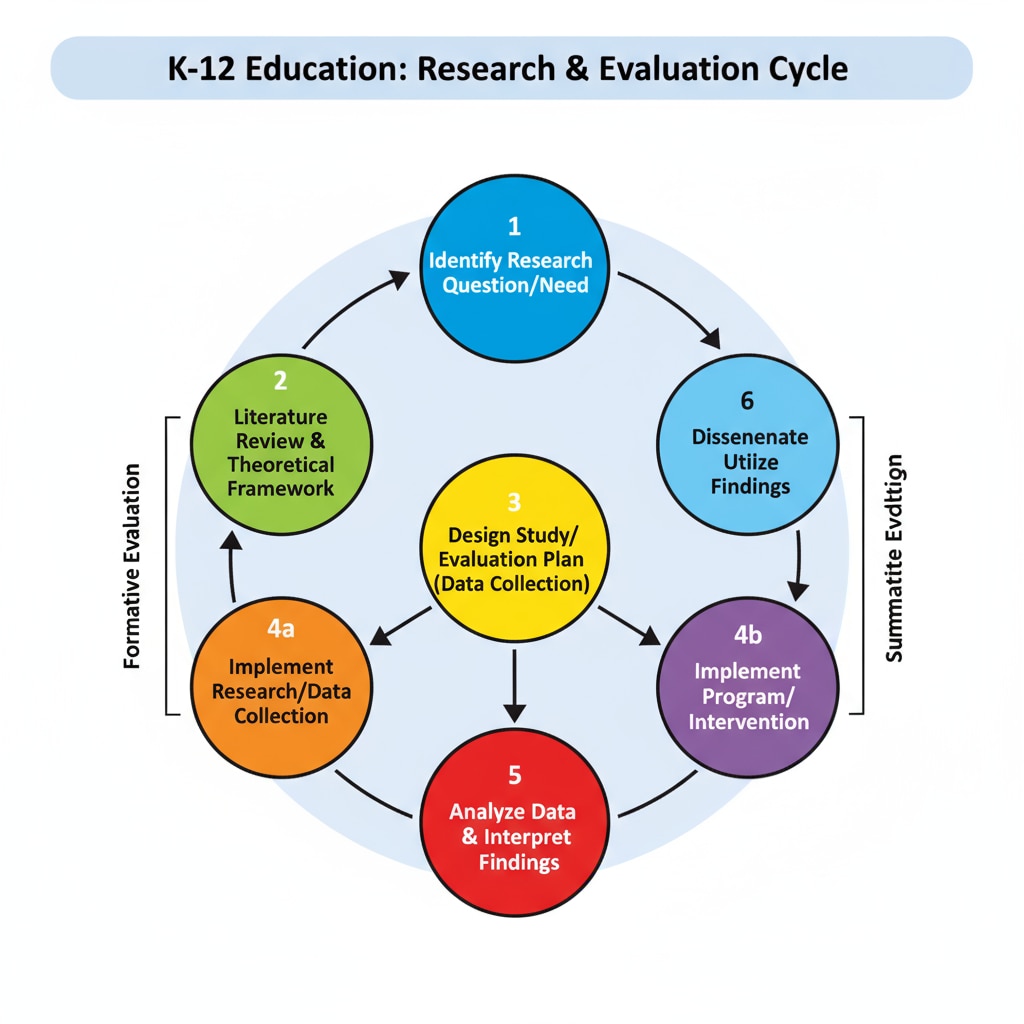
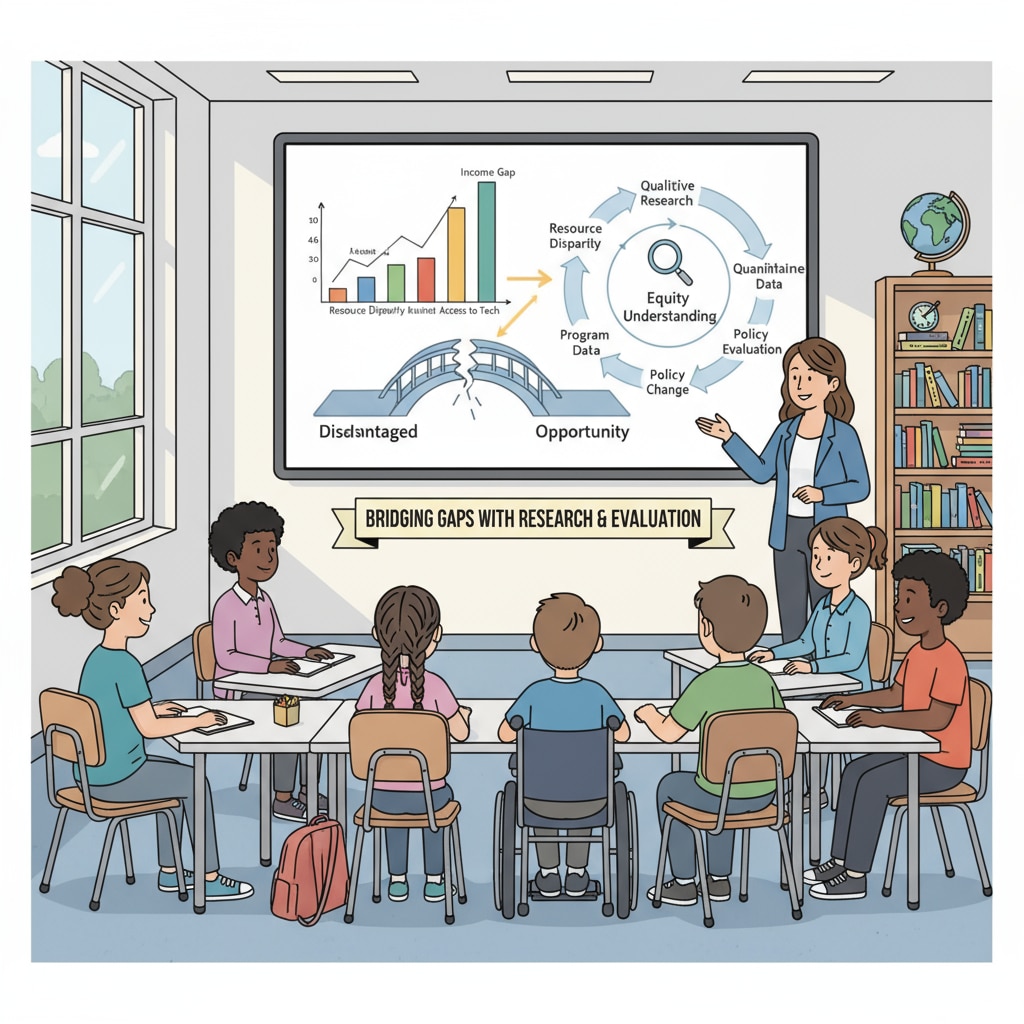
The Role of Research and Evaluation in Addressing Educational Social Inequality
Research can help identify the root causes of educational social inequality. By studying factors such as socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, and gender, researchers can gain insights into why some students face more barriers to learning than others. This knowledge can then be used to develop targeted interventions and policies to reduce inequality. For example, research might show that students from low-income families often lack access to educational resources outside of school, leading to lower academic achievement. Based on this finding, policymakers can implement programs to provide these students with access to tutoring, books, and technology.
Evaluation plays a crucial role in ensuring that educational interventions and policies are effective in addressing inequality. By evaluating the impact of these initiatives on different social groups, educators and policymakers can determine whether they are achieving their intended goals. If an evaluation reveals that a particular program is not benefiting all students equally, adjustments can be made to improve its effectiveness. This iterative process of research, evaluation, and improvement is essential for driving educational change and reducing social inequality.
In conclusion, research and evaluation are essential tools for addressing educational social inequality in K12 education. By understanding their professional definitions and how they interact, educators and policymakers can use them to develop and implement effective strategies to promote educational equality. Through ongoing research and evaluation, we can work towards a more just and equitable education system for all students. Readability guidance: The key points have been presented in short paragraphs. The content under each H2 includes a list-like structure to enhance clarity. The proportion of passive voice and long sentences has been controlled, and transition words have been used throughout the text to improve flow.


