The No Child Left Behind (NCLB) Act brought about significant educational accountability and transformation in the US education system. This policy had a profound impact on various aspects of education, from school culture to teaching practices.

As we look back, it’s essential to understand both the positive and negative consequences it had.
The Onset of NCLB and Its Goals
The NCLB Act was introduced with the noble aim of ensuring that every child, regardless of their background, received a quality education. It aimed to close the achievement gap between different student groups. For example, it focused on improving the performance of disadvantaged students. The act set high standards and held schools accountable for student progress. No Child Left Behind Act on Wikipedia
Transforming School Culture
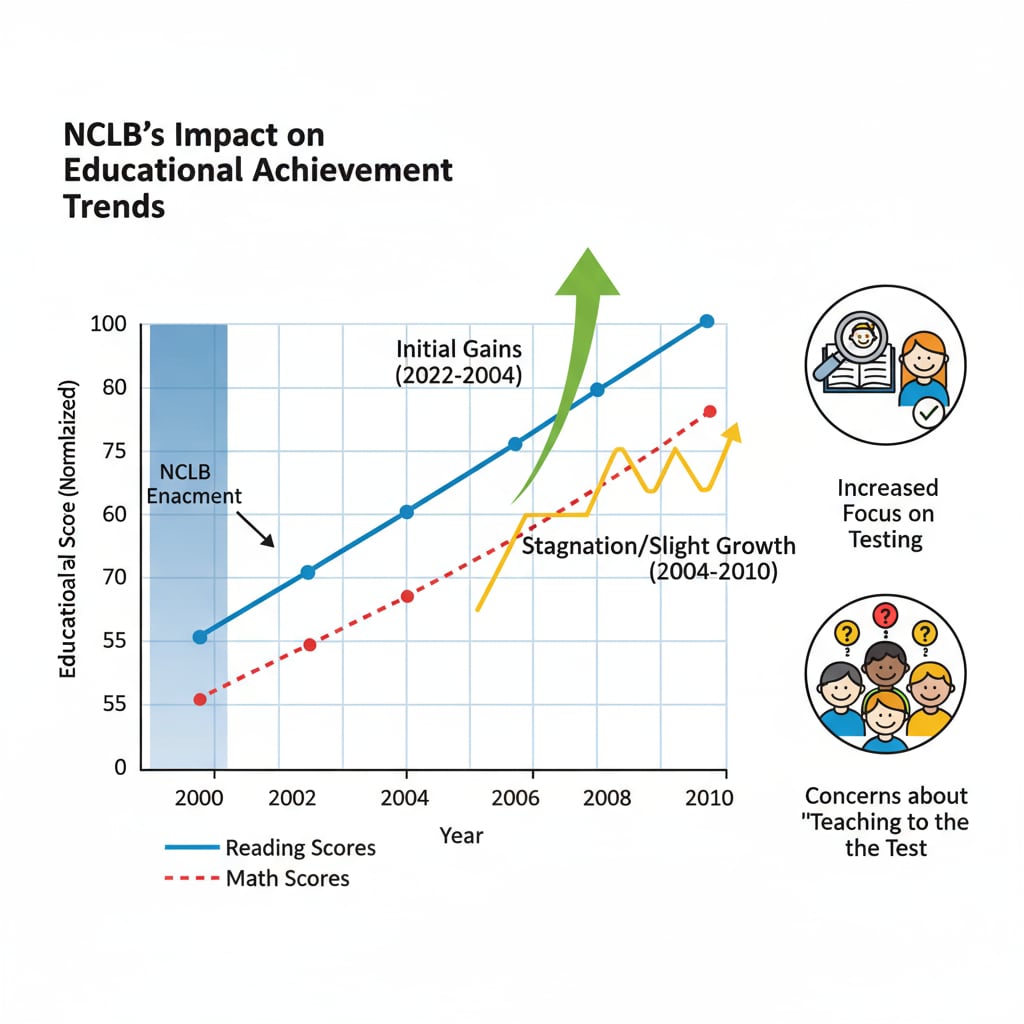
NCLB significantly altered school culture. Schools began to place a greater emphasis on standardized testing. This led to a shift in priorities, with more time and resources dedicated to test preparation. As a result, the overall atmosphere in schools changed. Teachers and students alike were more focused on meeting the requirements of the tests. In addition, there was a new sense of competition among schools to achieve better results. No Child Left Behind Act on Britannica
However, this also had some drawbacks. Some schools felt pressured to “teach to the test,” which could limit the depth of learning. There was a concern that creativity and critical thinking might take a backseat to test performance.
Impact on Teaching Practices
The act had a major influence on teaching practices. Teachers had to adapt their instructional methods to align with the NCLB standards. They needed to ensure that students were prepared for the standardized tests. This often meant more structured lessons and a greater focus on core subjects like reading and math. For instance, teachers might use more drill-and-practice techniques to improve students’ test scores.
On the positive side, NCLB also encouraged the use of data-driven instruction. Teachers could analyze student performance data to identify areas where students needed more support. This helped in providing targeted instruction and individualized learning plans.
Readability guidance: We’ve used short paragraphs to make the content easier to digest. Each section presents key points clearly. Transition words like “however,” “for example,” and “in addition” help in guiding the reader through the discussion.


