Gravity, time warping, and relativity are fascinating yet complex concepts in the realm of physics. In K12 science education, making these ideas understandable and engaging for students can be a challenging but rewarding task. Einstein’s theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of space and time, especially the concept that gravity can affect the passage of time. This article will explore how to bring these concepts into the K12 science classroom.
The Concept of Gravity and Time Warping
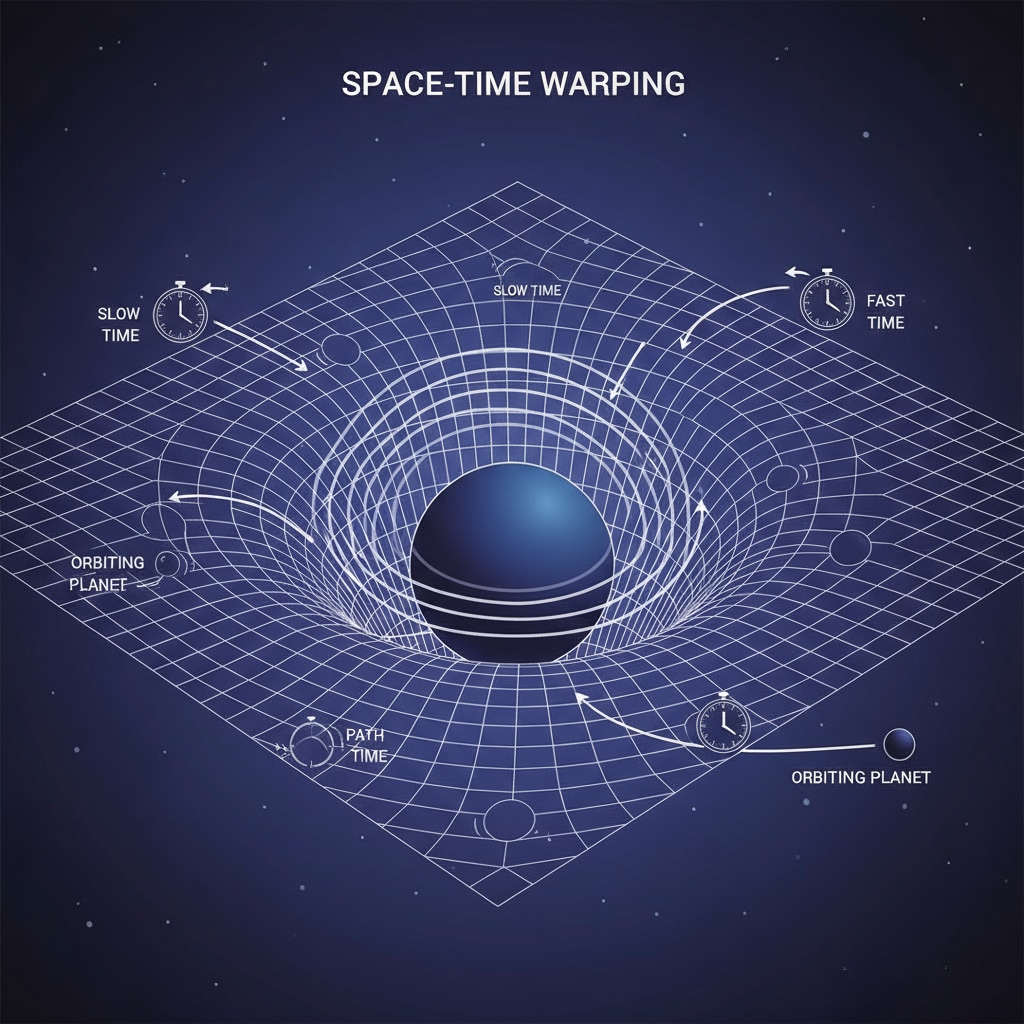
Gravity, as we know, is the force that pulls objects towards each other. According to Einstein’s general theory of relativity, gravity is not just a force but a curvature of space-time. Massive objects like planets and stars cause this curvature. This curvature, in turn, affects the passage of time. Time actually passes more slowly in stronger gravitational fields. For example, time on Earth runs a tiny bit slower than in deep space. General Relativity on Wikipedia
Teaching Strategies in K12 Science
To teach these concepts in K12 science classes, we can start with simple analogies. For instance, compare the curvature of space-time to a trampoline. Place a heavy ball in the middle of the trampoline, and it will create a depression. Smaller balls rolling on the trampoline will be affected by this depression, just like objects in space are affected by the curvature of space-time. In addition, we can use videos and animations to show how time is affected by gravity. These visual aids can greatly enhance students’ understanding. General Relativity on Britannica

Furthermore, hands-on experiments can also be incorporated. For example, students can measure the time difference between two clocks, one at a lower altitude and one at a higher altitude. Although the difference is extremely small, it can still be a powerful way to demonstrate the concept. By engaging students in these activities, we can help them develop a deeper understanding of gravity, time warping, and relativity.
Readability guidance: We’ve used short paragraphs and examples to make the content accessible. The use of analogies and hands-on activities helps in better comprehension. Transition words like “for instance”, “in addition”, and “furthermore” are used to connect ideas smoothly.


