Student privacy, digital footprints, and facial recognition are becoming increasingly pressing issues as schools actively post students’ photos on social media and websites. In today’s digital age, every click and share can leave a lasting mark on a child’s digital identity.

The Privacy Risks of Sharing Student Photos
When schools share student photos without proper consent or consideration, they expose students to potential privacy risks. For example, personal information such as a student’s full name, location, or extracurricular activities can be linked to the photo. This information can be misused by malicious individuals. According to EPIC’s research on children’s privacy, kids are especially vulnerable in the digital world. In addition, photos can be shared beyond the school’s intended audience, reaching platforms where students may not want their images to be seen.
The Impact of Facial Recognition on Digital Footprints
Facial recognition technology is advancing rapidly, and it has a significant impact on students’ digital footprints. Once a student’s face is captured in a photo and uploaded online, it can be used for facial recognition algorithms. This means that their digital presence can be tracked and analyzed. As stated in Wikipedia’s entry on facial recognition technology, the technology has both positive and negative implications. If misused, it could lead to a student being identified in various situations, potentially affecting their future opportunities.
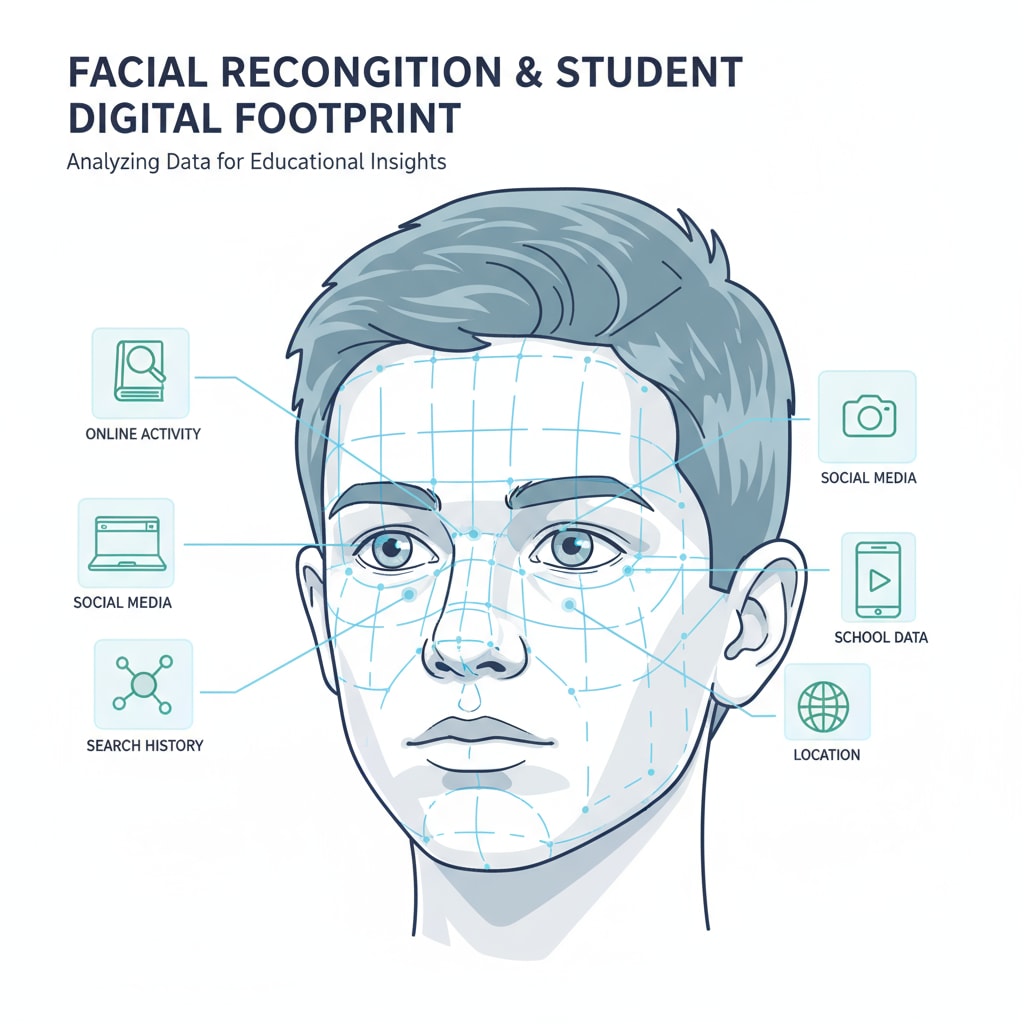
Educators need to be aware of these issues and take steps to balance the school’s need to promote activities and events with the protection of students’ privacy and digital futures. This could involve obtaining clear consent from students and parents, and implementing strict guidelines on photo sharing.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs to make the content easier to understand. Each H2 section provides a clear focus on different aspects related to student privacy and digital footprints. Transition words like “for example” and “in addition” are used to connect ideas smoothly. Passive语态 is minimized, and the language is kept at a level that is accessible to a wide audience.


