The issue of functional illiteracy, reading comprehension, and education crisis in the United States has drawn significant attention. Currently, a disturbing fact is that 54% of the US population has a reading comprehension level no higher than that of a fifth grader. This high rate of functional illiteracy is not just an educational concern but also has far-reaching implications for society.

The Alarming State of Functional Illiteracy
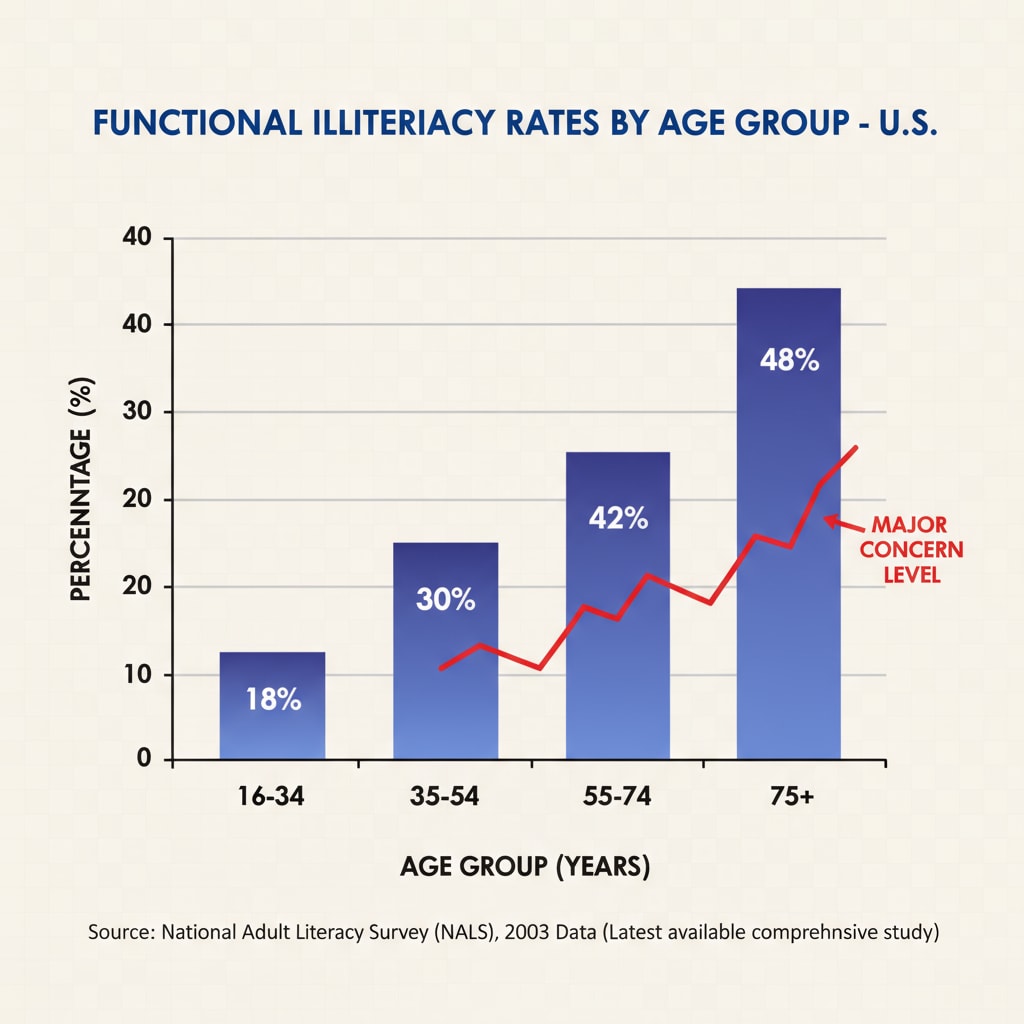
Functional illiteracy refers to the inability of individuals to use reading, writing, and computational skills effectively in their daily lives and at work (as defined by educational experts). In the US, this problem is widespread. A large number of people lack the necessary reading comprehension skills to understand complex texts, analyze information, and make informed decisions. This situation is not only a setback for personal development but also poses challenges to the overall progress of society. For example, it can limit career opportunities as many jobs require a certain level of reading and comprehension abilities. Functional illiteracy on Wikipedia
Causes of the Education Crisis
There are multiple factors contributing to this education crisis. One major cause is the uneven distribution of educational resources. In some areas, schools lack proper funding, experienced teachers, and up-to-date teaching materials. As a result, students do not receive a quality education that can help them develop strong reading comprehension skills. Another factor is the changing teaching methods. Some modern teaching approaches may not effectively focus on building a solid foundation in reading and language skills. Additionally, the influence of digital media and the internet has led to a decrease in traditional reading habits among students. Education problems on Britannica
The consequences of this high rate of functional illiteracy are significant. Socially, it can lead to a less informed citizenry, making it difficult for people to participate fully in democratic processes. Economically, it can slow down the development of the workforce as employees with poor reading skills may be less productive. Moreover, it can also contribute to social inequality as those with lower literacy levels often have fewer opportunities for advancement.
Readability guidance: By breaking down the content into shorter paragraphs and using lists where possible, we can improve readability. Each H2 section provides a focused discussion on different aspects of the issue. Transition words like ‘however’, ‘therefore’, and ‘in addition’ are used to connect ideas smoothly.


