In the realm of girls’ education, STEM teaching has long been marked by significant gender differences. The underrepresentation of girls in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields is a persistent issue that demands attention. This article aims to explore these differences and propose effective ways to bridge the gap.

The Gender Divide in STEM Learning
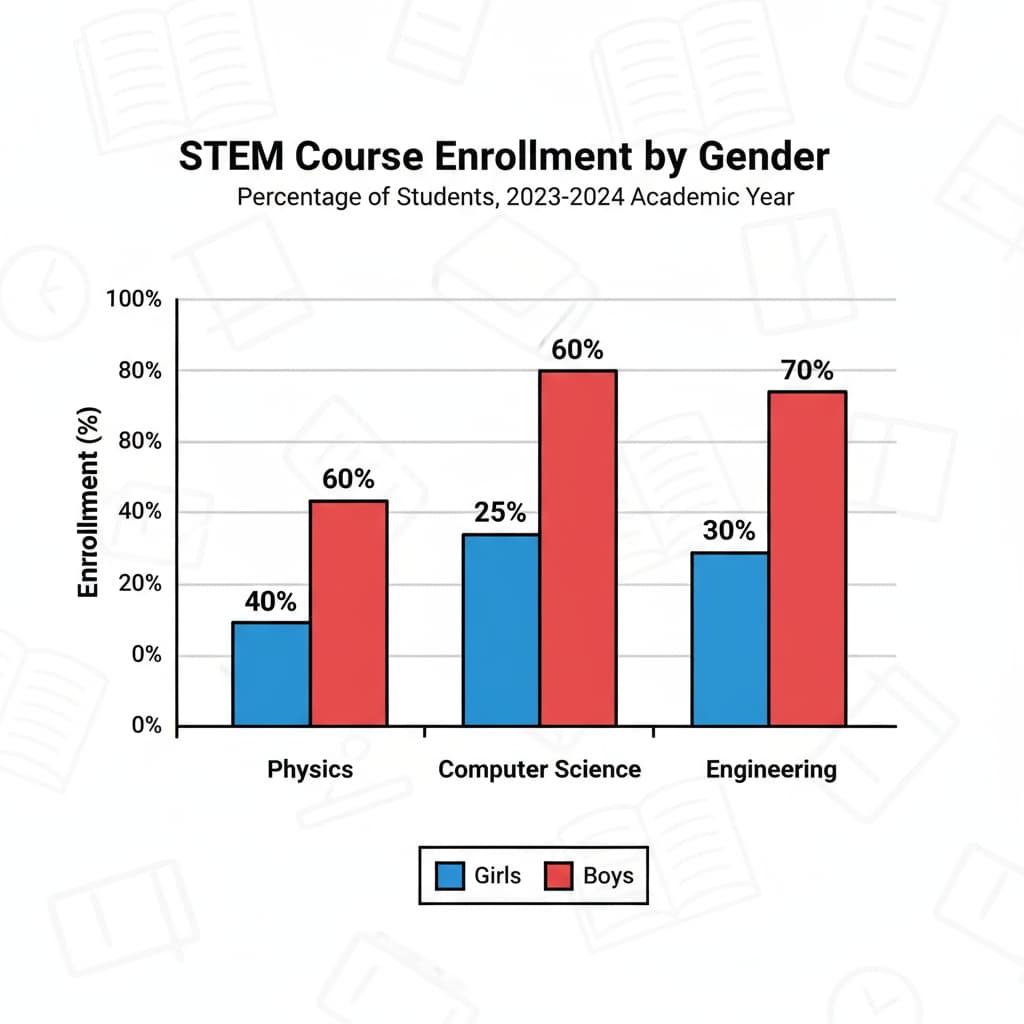
From an early age, girls often face barriers in STEM education. Research shows that stereotypes and biases play a major role. For example, society often associates STEM with masculinity, which can make girls feel less welcome in these fields. As a result, girls may be less likely to choose STEM courses in school. According to Gender inequality in education on Wikipedia, these stereotypes can limit girls’ access to quality STEM education resources.
Root Causes of Gender Disparities
The causes of gender differences in STEM education are multi – faceted. One key factor is the lack of female role models. When girls don’t see women succeeding in STEM, they may struggle to envision themselves in these careers. In addition, teaching methods that are not inclusive can also be a problem. Traditional teaching may not engage girls as effectively as it could. As per Education on Britannica, an understanding of these root causes is essential for developing solutions.
Another aspect is the lack of encouragement at home and school. Parents and teachers may unconsciously steer girls away from STEM, either through their words or actions. This lack of support can erode girls’ confidence in their STEM abilities.
Effective Teaching Strategies
To address the gender differences in STEM teaching, educators can adopt several strategies. First, integrating real – world examples into lessons can make STEM more relatable for girls. For instance, using examples of how STEM is used in fashion design or healthcare can pique their interest. Second, creating collaborative learning environments where girls can work with their peers can boost their confidence. Group projects allow them to share ideas and learn from each other.
Moreover, providing mentorship opportunities from female STEM professionals can be a game – changer. These role models can inspire girls and show them the possibilities in STEM. Educators can also use gender – inclusive teaching materials that feature diverse examples of successful women in STEM.
Creating an Inclusive Learning Environment
Beyond teaching strategies, creating an inclusive learning environment is crucial. Schools can organize STEM – focused events and clubs that are welcoming to girls. These activities can provide a safe space for girls to explore their interests. In addition, promoting a growth mindset in the classroom can help girls overcome self – doubt. By teaching them that intelligence can be developed through effort, girls are more likely to take on challenges in STEM.
Readability guidance: In this article, we’ve explored the gender differences in girls’ STEM education. We’ve looked at the root causes and provided practical strategies for educators. By implementing these ideas, we can work towards a more inclusive STEM learning environment for girls. Transition words like ‘however’, ‘therefore’, and ‘in addition’ have been used to enhance the flow. Short paragraphs and lists have been used to make the content more accessible.


