For many students, identifying text purpose in Functional Skills English reading exams can be a daunting task. Whether a passage is designed to inform, explain, or persuade often feels ambiguous, leading to confusion and lower scores. In this article, we’ll explore the key characteristics of these three text purposes and offer actionable strategies to help you confidently determine the intent behind any text. By honing this skill, you’ll not only improve your performance in exams but also enhance your overall reading comprehension abilities.
Understanding the Three Key Text Purposes
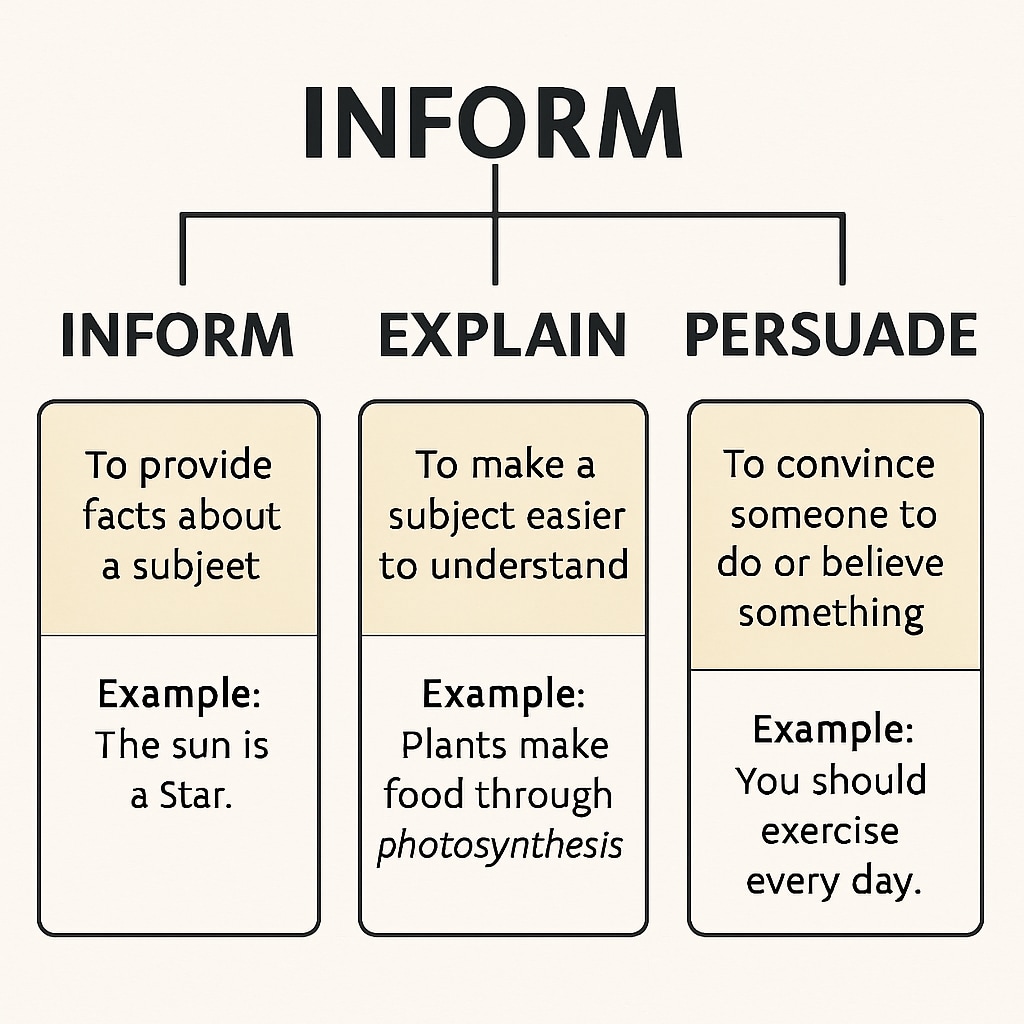
Before diving into strategies, it’s essential to understand the three main purposes of texts: informing, explaining, and persuading. Each type comes with distinct features that can act as clues during your reading.
- Informing: Informative texts aim to deliver facts, data, or instructions. Examples include news articles, recipes, and user manuals. These texts are often neutral in tone and packed with factual details.
- Explaining: Explanatory texts go a step further by clarifying how or why something works. Look for step-by-step processes or cause-and-effect relationships, which are common in science articles or history essays.
- Persuading: Persuasive texts aim to influence the reader’s opinion or behavior. Advertisements, opinion pieces, and political speeches often fall into this category. They usually contain strong language, emotional appeals, or calls to action.
Strategies to Identify Text Purpose in Functional Skills English
Now that you’re familiar with the main text purposes, it’s time to develop strategies for identifying them effectively. Here are some practical tips:
1. Analyze the Title and Subheadings
The title of a text often provides a clear clue about its purpose. For example, a title like “How to Bake a Cake” suggests an explanatory purpose, while “Why Organic Food is Better” hints at persuasion. Subheadings further break down the content and can reinforce these clues.
2. Look for Key Phrases
Specific phrases or words can signal the purpose of a text. For example:
- Informative: “The study shows,” “According to data,” “In 2023, statistics reveal…”
- Explanatory: “This process involves,” “As a result of,” “The reason behind…”
- Persuasive: “You should,” “It’s essential that,” “Imagine a world where…”
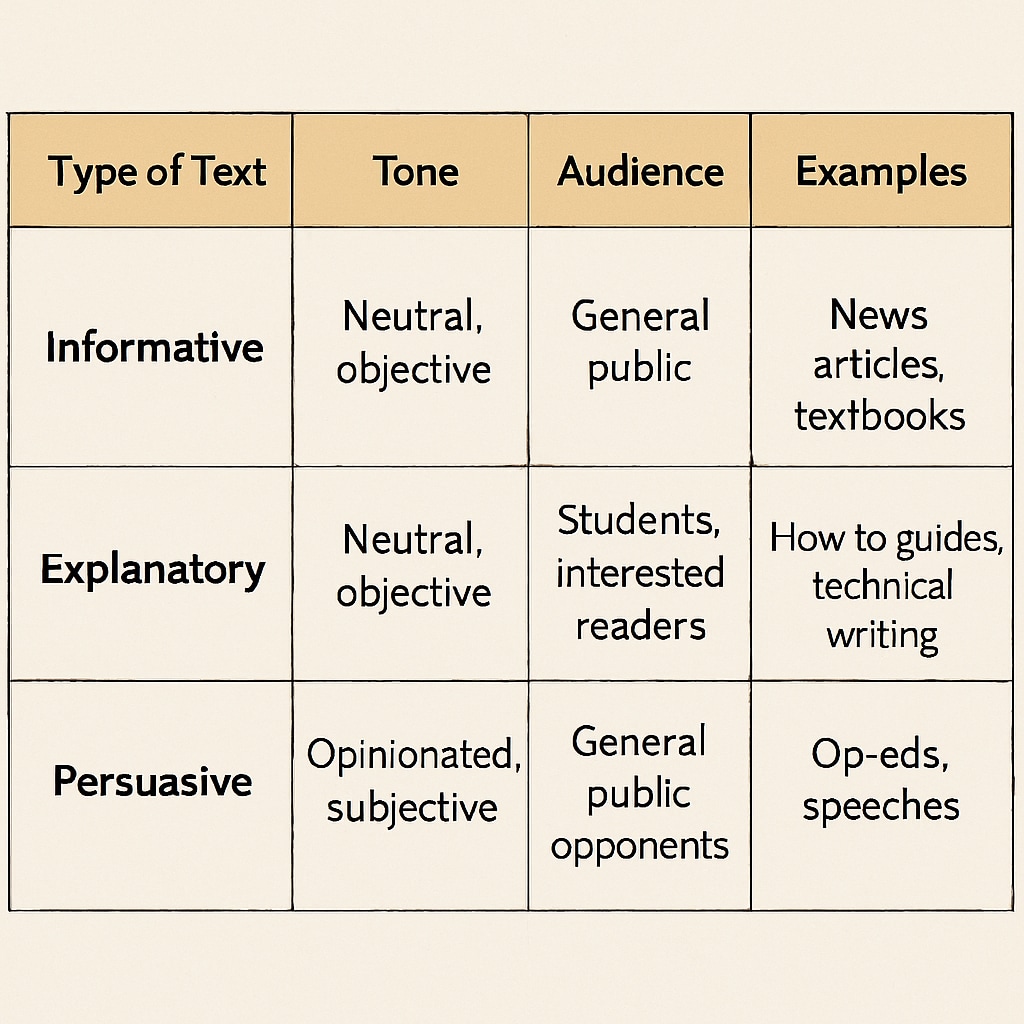
3. Examine the Tone and Style
The tone of a text is another giveaway. Informative texts tend to be neutral and factual, explanatory pieces are methodical, and persuasive texts are more emotional and opinionated. Pay attention to the writer’s attitude towards the topic.
4. Identify the Target Audience
Consider who the text is written for. A scientific report aimed at professionals is likely informative, while a charity’s fundraising letter is persuasive. Understanding the audience can provide critical context for determining the text’s purpose.
Applying These Skills in the Exam
Functional Skills English exams often include texts from various contexts—advertisements, news articles, instructions, or essays. Use the following steps to apply your skills:
- Skim the text: Quickly read the title, subheadings, and opening sentences to get a general sense of the text.
- Highlight keywords: Underline phrases that signal the text’s intention, such as “The purpose of this report is…” or “We urge you to…”.
- Review the questions: Exam questions often give hints about the text’s purpose. Look for phrases like “What is the author trying to achieve?” or “What is the main aim of this text?”
- Cross-check your findings: Ask yourself if the tone, key phrases, and structure align with the purpose you’ve identified.
Final Thoughts
Mastering the skill of identifying text purpose in Functional Skills English exams can significantly boost your confidence and accuracy. By understanding the key characteristics of informative, explanatory, and persuasive texts—and practicing the strategies outlined here—you’ll be well-prepared to tackle any reading comprehension challenge. Remember, practice makes perfect, so take the time to analyze various types of texts and apply these techniques regularly.
Additional Resources: For further reading, check out the Reading on Britannica or Reading Comprehension on Wikipedia to deepen your understanding of text analysis.


