The connection between K12 education and future opportunities in engineering design careers is both crucial and transformative. By tailoring educational frameworks to integrate STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math), foster design thinking, and establish diverse evaluation systems, students can be better prepared for academic and career success. This article examines how K12 education can support engineering design aspirations, evaluates degree paths, and highlights the importance of reforming existing systems.
The Role of K12 Education in Engineering Design Career Preparation
Engineering design careers often require professionals to combine technical expertise, creative problem-solving, and collaboration. However, many students lack exposure to these skills at an early stage. In the current K12 system, STEM subjects are frequently taught in isolation rather than as interconnected disciplines, leaving gaps in understanding how scientific principles apply to real-world design challenges.
For example, integrating hands-on projects, such as designing simple machines or coding basic applications, can help students apply theoretical concepts to practical scenarios. This approach nurtures curiosity and critical thinking, paving the way for future success in degree programs and professional roles.
Comparing Degree Paths: Which Route Offers the Best Value?
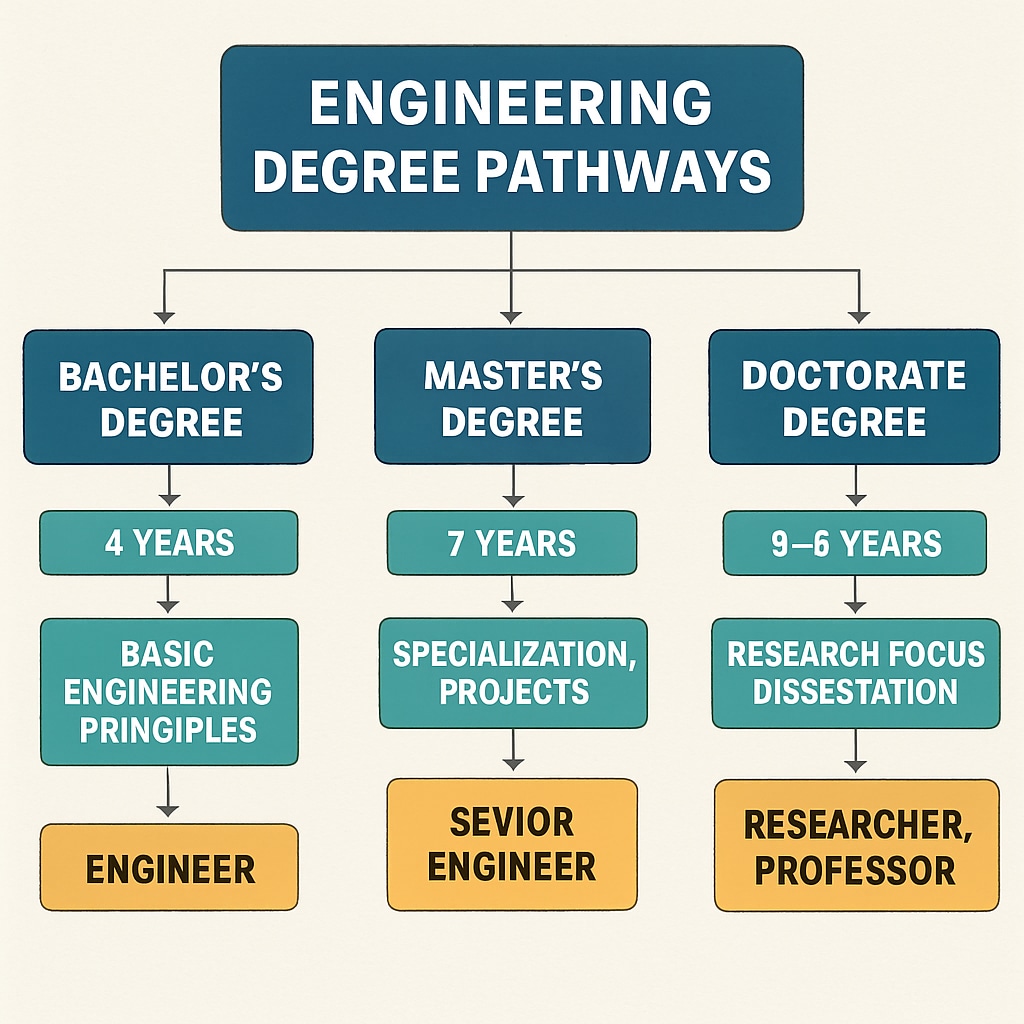
When students transition from K12 education to higher education, they face a variety of degree paths in engineering design. Common options include:
- Bachelor’s Degree in Engineering Design: Provides foundational knowledge and practical experience, often leading to entry-level roles in industries like architecture, product design, or systems engineering.
- Master’s Degree in Specialized Fields: Offers advanced training in areas such as sustainable design, industrial engineering, or robotics. Graduates often pursue leadership roles or research-oriented positions.
- Associate Degree or Technical Certifications: Focuses on practical skills and tools, ideal for roles like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) technicians or project coordinators.
Each path has distinct advantages depending on career goals. For instance, a bachelor’s degree is often essential for designing complex systems, while technical certifications may suffice for specialized roles. Students who are exposed to career exploration in K12 education can make informed decisions about which path aligns best with their interests and strengths.
Reforming K12 Education: Integration, Design Thinking, and Evaluation
To transform K12 education into a robust foundation for engineering design careers, three major reforms are essential:
- STEM Integration: Encourage interdisciplinary learning by connecting math and science to engineering and technology. For example, physics lessons can include projects to design bridges or test material strength.
- Design Thinking: Introduce problem-solving methodologies that emphasize empathy, ideation, and prototyping. Design thinking can help students approach challenges creatively and collaboratively.
- Evaluation Systems: Expand beyond traditional tests to include project-based assessments, portfolios, and peer reviews. These methods better reflect a student’s ability to apply knowledge in real-world contexts.
For educators, professional development in these areas is equally important. Training teachers to implement integrated STEM curricula and foster critical thinking skills ensures that reforms are effectively applied.
The Long-Term Impact of Early Preparation
Investing in K12 education reform creates ripple effects that extend beyond individual students. Communities benefit from a more skilled workforce capable of tackling complex engineering challenges, while industries gain innovative professionals who drive progress. Additionally, students who experience enriched education are more likely to pursue rewarding careers, contributing to social and economic growth.
Ultimately, the connection between K12 education and engineering design careers highlights the importance of equipping young learners with the tools they need to succeed. By prioritizing curriculum integration, design thinking, and diverse evaluations, educators can empower the next generation of innovators.
Readability guidance: This article uses concise paragraphs, lists, and logical transitions to ensure clarity. Reforms and pathways are explained with concrete examples to enhance understanding.


