Student boredom, education environments, and international comparisons have become pressing topics in contemporary discussions about global education. Recent studies spanning countries like the UK, China, the US, and Senegal reveal a common and troubling phenomenon: students consistently report feeling disengaged and uninterested in classroom activities. This pervasive issue is an invisible barrier to effective learning, impacting academic outcomes, psychological well-being, and even future career aspirations. Understanding the causes, implications, and potential solutions to classroom boredom is essential for educators, policymakers, and parents alike.
Why Are Students Bored in Classrooms Worldwide?
Classroom boredom is not merely a localized problem; it is a global trend. Research suggests several recurring factors contributing to this disengagement:
- Standardized Curricula: Many countries prioritize standardized testing, which often leads to rigid and monotonous teaching methods that fail to spark creativity or curiosity.
- Lack of Relevance: Students frequently struggle to see how classroom lessons connect to real-world applications, making learning feel abstract and disconnected.
- Overloaded Schedules: In countries with competitive educational systems, students often face excessive workloads, leaving little room for exploratory or enjoyable learning.
- Teaching Methods: Traditional lecture-based approaches, rather than interactive or personalized methods, contribute significantly to student disengagement.

The Impact of Boredom on Student Outcomes
Boredom in the classroom is far from harmless. Its repercussions extend beyond immediate disengagement, affecting students’ academic performance, mental health, and future opportunities. For instance:
- Reduced Academic Achievement: Students who are disengaged tend to perform poorly on exams, as boredom undermines their ability to focus and retain information.
- Mental Health Challenges: Persistent boredom can lead to stress, anxiety, and even depression, particularly in high-pressure educational environments.
- Long-Term Skill Deficits: A lack of enthusiasm for learning during formative years can result in weaker critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are crucial for career success.
For example, a study published by Britannica indicates that student boredom significantly correlates with lower engagement levels in STEM subjects, which are critical for modern industries. Additionally, Wikipedia highlights that countries with higher student engagement scores tend to have better overall educational outcomes.
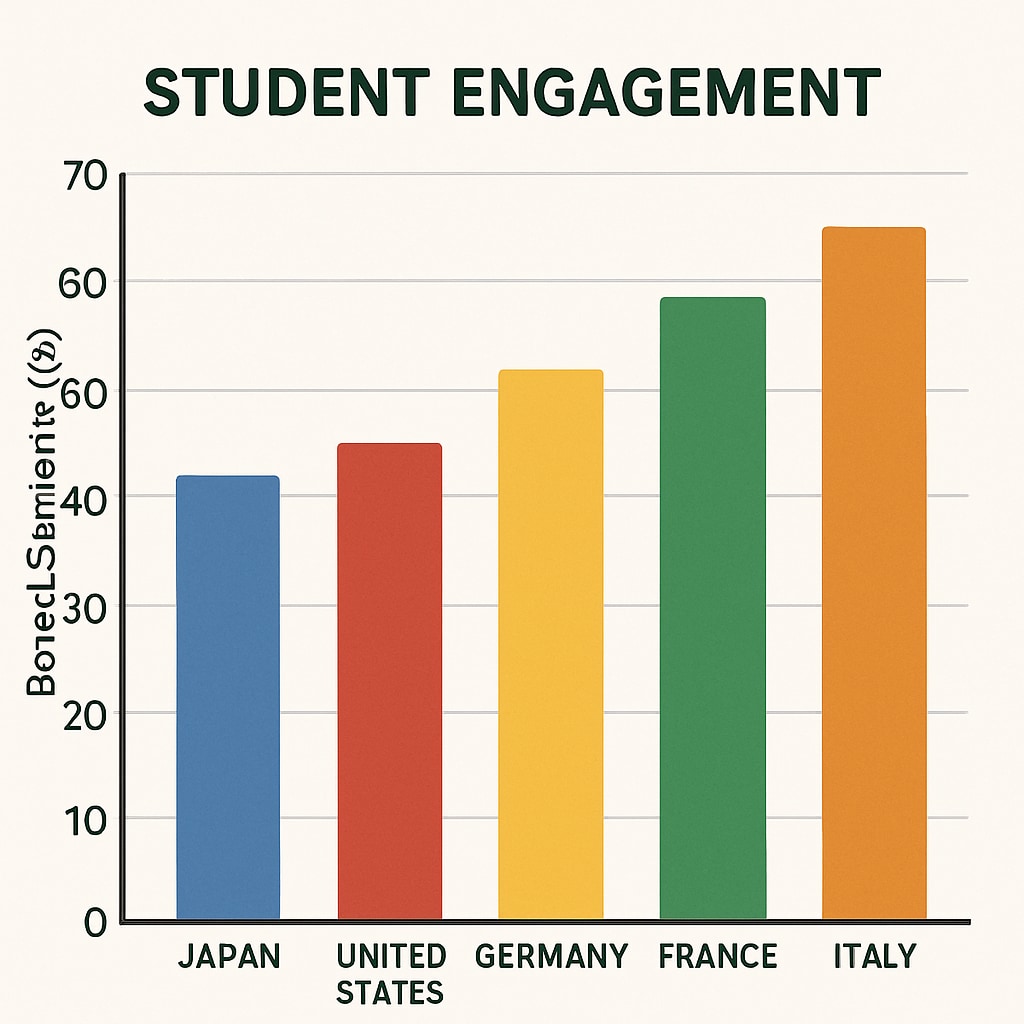
How Can Educators Combat Classroom Boredom?
Addressing student boredom requires a multifaceted approach involving curriculum redesign, innovative teaching strategies, and systemic changes to educational environments. Key solutions include:
- Interactive Learning: Incorporating hands-on activities, group projects, and real-world problem-solving exercises can make lessons more engaging.
- Personalized Education: Adaptive learning technologies allow teachers to tailor lessons to individual student interests and learning styles.
- Teacher Training: Providing educators with professional development opportunities to learn new teaching methods can enhance their ability to foster engagement.
- Curriculum Reform: Shifting focus from rote memorization to critical thinking and creativity will better align education with students’ aspirations and real-world needs.
In addition, fostering collaboration between schools, families, and communities can create a supportive environment that prioritizes student engagement. For example, inviting professionals from various industries to discuss the real-world relevance of classroom subjects can inspire curiosity and motivation.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Global Education
Student boredom in classrooms is a universal challenge that demands immediate attention. By understanding its causes, recognizing its impacts, and implementing innovative solutions, educators and policymakers can transform learning environments into spaces that inspire and engage students. The future of global education depends on addressing this silent epidemic, ensuring that every student has the opportunity to thrive both academically and personally.
As a result, tackling classroom boredom requires a collective effort. Governments, educators, and communities must work together to create educational environments where curiosity and enthusiasm flourish, preparing students for success in an ever-changing world.


