The introduction of the UK’s age verification law has significantly impacted internet usage patterns, leading to a notable surge in VPN (Virtual Private Network) adoption. This legal requirement, aimed at protecting minors from accessing adult content, has raised concerns about privacy, enforcement, and the potential for unintended consequences. In this article, we explore the implications of the age verification law, the role of VPNs, and the broader conversation around digital privacy.
Understanding the UK’s Age Verification Law
The UK government implemented the age verification law as part of its effort to regulate online content and protect underage users from harmful material. The law requires websites hosting adult content to verify the age of their users, ensuring that only individuals aged 18 and above can access such material. Verification methods include providing official identification, such as a passport or driver’s license, or using third-party age verification services.
While the intention behind the legislation is commendable, critics argue that it introduces significant privacy risks. By forcing users to submit sensitive personal information, the law raises concerns about the secure storage of this data and the potential for misuse or breaches. Moreover, many users feel uncomfortable sharing such details with websites that may lack robust security measures.

VPNs: A Popular Workaround
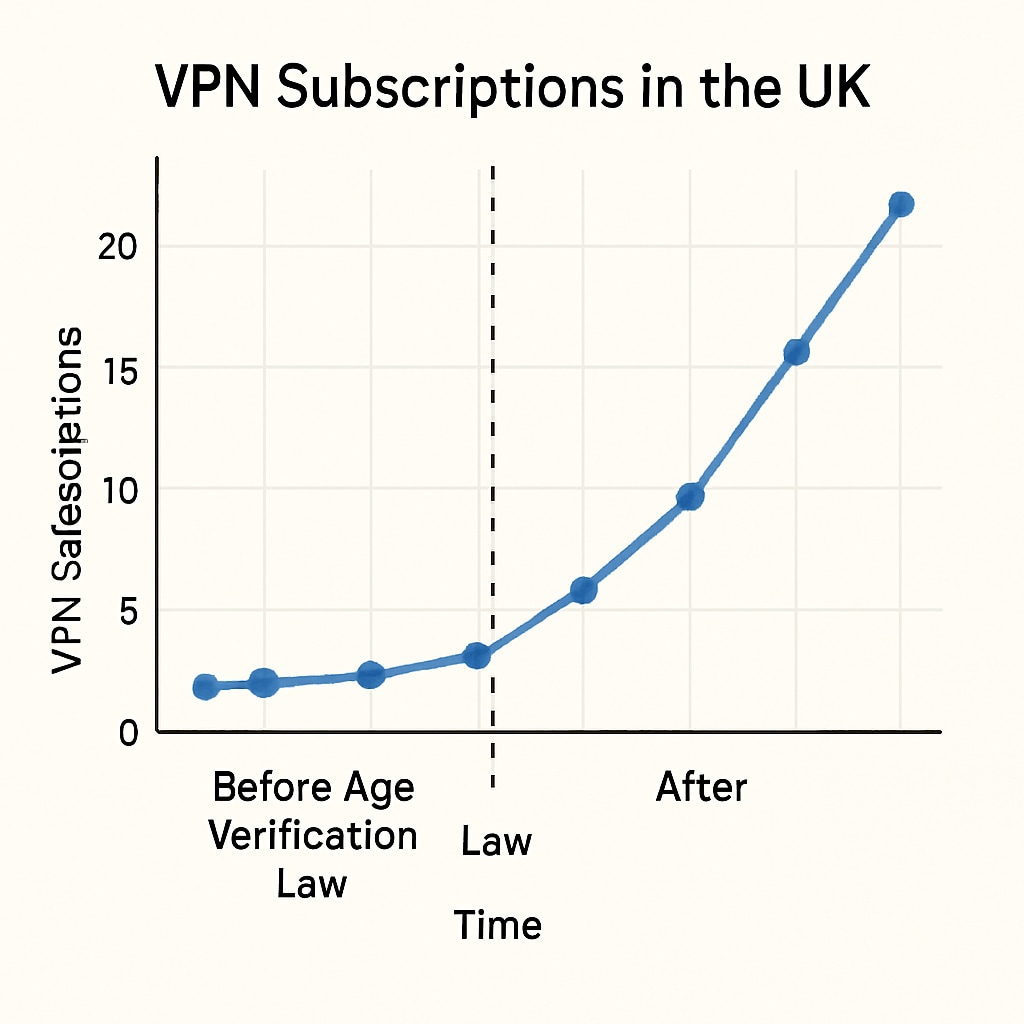
In response to the new legislation, many users have turned to VPNs as a means of circumventing the restrictions. A VPN allows users to mask their location by routing their internet traffic through servers in other countries. This effectively bypasses the age verification requirement, as the law only applies to users accessing content from within the UK.
The surge in VPN usage highlights a growing trend: individuals are increasingly prioritizing their privacy and seeking tools to evade intrusive regulations. VPN providers have reported a sharp increase in subscriptions since the law’s implementation, with many users citing concerns over data security and surveillance.
However, while VPNs offer a practical solution for bypassing age verification, their use raises ethical and legal questions. Is it appropriate to use such tools to circumvent a law designed to protect minors? And how can authorities adapt to a digital landscape where anonymity tools are readily available?
Broader Implications for Digital Privacy
The rise in VPN adoption due to the UK’s age verification law underscores a broader issue: the tension between regulation and privacy in the digital age. Governments worldwide are grappling with how to enforce laws online without infringing on individual rights. The UK’s approach has sparked debate over whether such measures strike the right balance or if they inadvertently drive citizens towards privacy-enhancing technologies.
For instance, critics of the law point out that it may disproportionately affect smaller websites that lack the resources to implement robust age verification systems. At the same time, larger platforms can afford to comply, potentially consolidating their market dominance. This raises questions about equity and fairness in internet regulation.
What Lies Ahead?
As the UK navigates the challenges of enforcing its age verification law, it is clear that the conversation around internet regulation is far from over. Policymakers must consider the unintended consequences of such measures, including their impact on privacy, free speech, and market competition.
Moreover, the surge in VPN usage serves as a reminder that users will always seek ways to maintain their digital autonomy. This trend highlights the need for a balanced approach to online regulation—one that protects vulnerable users without compromising the rights of the broader population.
In conclusion, the UK’s age verification law has ignited discussions about the intersection of technology, privacy, and regulation. As VPN usage continues to rise, it remains to be seen how governments and citizens will navigate these complex issues in the years to come.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs and frequent transitions ensure clarity. Lists and examples provide additional context. The article balances technical explanations with accessible language, making it suitable for a general audience.


