For adults seeking further education, understanding the differences between high school diplomas obtained through various means such as GED, HiSet, and a traditional high school diploma is crucial. These options all play significant roles in the realm of adult education.
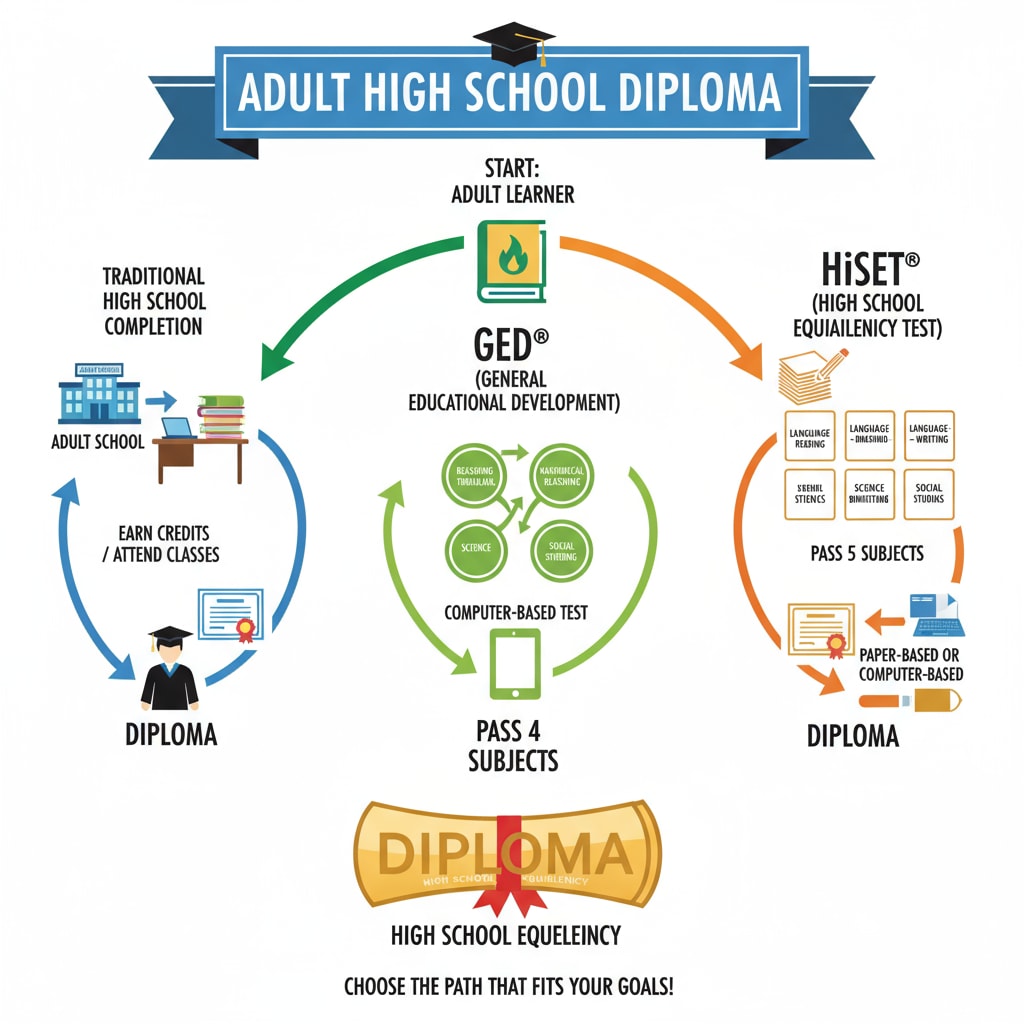
The Traditional High School Diploma
The traditional high school diploma is the most straightforward form. It is earned by attending a physical high school for a set number of years, usually four. Students take a comprehensive curriculum that includes core subjects like math, science, language arts, and social studies. This diploma is widely recognized by employers, colleges, and universities as a standard measure of high school completion. For example, when applying to a four-year university, a traditional high school diploma is often the preferred credential. High School Diploma on Wikipedia
GED: A Popular Equivalent Option
The General Educational Development (GED) test is a well-known alternative for adults. It assesses an individual’s knowledge in four main areas: language arts, mathematics, science, and social studies. Passing the GED exam is considered equivalent to having a high school diploma. Many adults choose the GED route because it offers flexibility. They can study at their own pace and take the exam when they feel ready. However, some institutions may view it slightly differently compared to a traditional diploma. General Educational Development on Britannica

In addition, certain career fields or higher education programs might have specific requirements regarding the type of diploma. While the GED is generally accepted, it’s important for adults to research in advance to ensure it meets their goals.
HiSet: Another Equivalent Diploma
The High School Equivalency Test (HiSet) is another option for adults looking to obtain an equivalent high school diploma. Similar to the GED, the HiSet measures proficiency in multiple subject areas. It provides an opportunity for individuals who didn’t complete high school to demonstrate their knowledge and skills. One advantage of the HiSet is that it may be more accessible in some regions or have different testing formats that suit certain learners better. However, like the GED, its acceptance can vary depending on the institution or employer.
Readability guidance: As we can see, each option has its own characteristics. The traditional diploma offers a more structured and widely recognized path. The GED and HiSet provide flexibility for adult learners but may face some differences in acceptance. By understanding these nuances, adults can make an informed decision about which route to take in their pursuit of a high school diploma.


