In the era of rapid technological advancement, AI writing tools have become increasingly popular in K12 education. The widespread use of these tools has brought new challenges for both students and teachers, especially when it comes to AI content detection. The question of whether manual input of AI-rewritten content can “fool” AI detectors, along with the impact of copy-pasting such content on detection results, has become a topic of great concern. AI detectors, manual input, and rewriting tools are now at the center of this educational debate.
The Rise of AI Writing Tools in K12 Education
AI writing tools have made significant inroads into K12 education. These tools can generate essays, reports, and other written works with remarkable speed and apparent quality. For example, platforms like GrammarlyGO and ChatGPT have features that allow users to input a topic, and within seconds, they receive a well-structured piece of writing. As a result, students may be tempted to use these tools to complete their assignments. However, this trend has raised serious questions about academic integrity. Teachers now have to be vigilant to ensure that the work submitted by students is original and not the product of AI writing tools. According to this report from EdSurge, many educational institutions are grappling with the issue of AI-generated content in student work.
The Mechanics of AI Detectors
AI detectors are designed to identify content that has been generated or heavily influenced by AI. These detectors use complex algorithms to analyze various aspects of the text, such as sentence structure, vocabulary usage, and writing style. For instance, they might look for patterns that are typical of AI-generated text, like overly formal language or a lack of natural flow. However, the effectiveness of these detectors can be influenced by different factors. Manual input of AI-rewritten content is one such factor that researchers and educators are closely examining. Some believe that manually typing out AI-generated text could potentially bypass the detection mechanisms of these tools. MIT Technology Review has reported on the limitations of AI detectors.
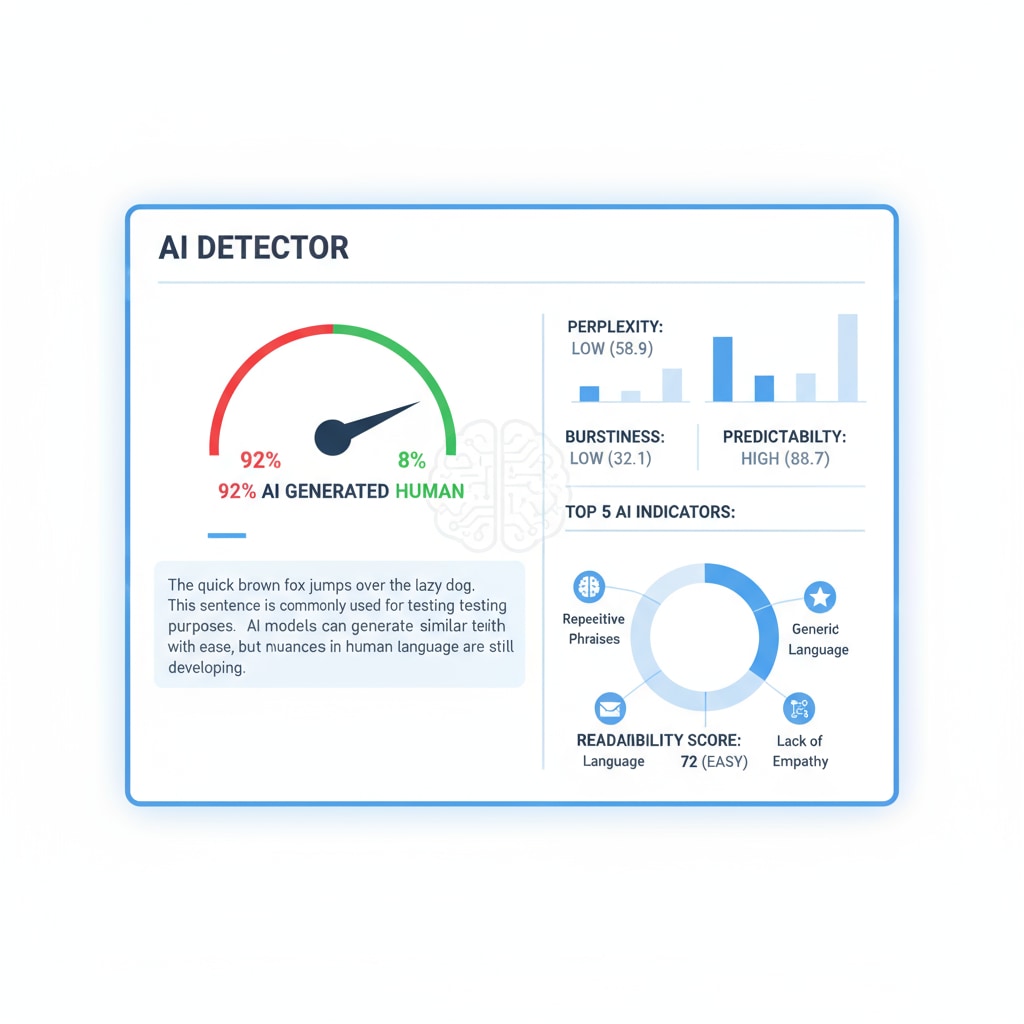
Manual Input vs. Copy-Pasting: Does It Make a Difference?
One of the key questions is whether manual input of AI-rewritten content can evade detection more effectively than simply copy-pasting it. Some students think that by typing out the AI-generated text themselves, they can make it seem more “human.” However, AI detectors are becoming more sophisticated. They can still detect signs of AI influence even in manually typed content. For example, the unique language patterns and logical structures that AI writing tools often produce can still be identified. In addition, the time taken to manually input a long piece of text might not match the normal writing speed of a student, which could also raise suspicions. On the other hand, copy-pasting is an obvious red flag for most AI detectors. The lack of any typing errors or the presence of formatting issues typical of copied text can easily lead to detection.
Readability guidance: This section clearly presents the comparison between manual input and copy-pasting in terms of AI detection. It uses short paragraphs and provides examples to make the points understandable. Transition words like “however,” “for example,” and “in addition” are used to enhance the flow.
The Impact on Educational Integrity and Assessment
The issue of AI content detection, especially in relation to manual input and copy-pasting of AI-rewritten content, has far-reaching implications for educational integrity. If students can successfully use AI writing tools and avoid detection, it undermines the fairness of the educational system. Teachers rely on assignments and assessments to gauge students’ learning progress and understanding. When AI-generated content is involved, these assessments become inaccurate. Moreover, it devalues the hard work of honest students. To maintain educational integrity, schools and educators need to develop better strategies for detecting AI-generated content and educating students about the importance of academic honesty.
Readability guidance: This part focuses on the consequences for educational integrity. It uses simple language and short sentences to convey the message. The transition word “moreover” is used to add another important point.
In conclusion, the relationship between AI detectors, manual input, and rewriting tools is complex. While manual input may seem like a potential way to avoid detection, AI detectors are evolving to be more effective. The widespread use of AI writing tools in K12 education demands that educators, students, and educational institutions work together to address the challenges of maintaining educational integrity and ensuring accurate assessment. As technology continues to develop, staying informed and adapting to these changes will be crucial for the future of education.


