Artificial intelligence is transforming industries and reshaping the future, but integrating it into K12 education often faces challenges due to computational resource limitations. Designing artificial intelligence courses and student projects that demand minimal hardware is crucial to ensuring equitable access to AI education. This article outlines strategies to create engaging and resource-friendly AI projects for K12 students, breaking barriers and empowering exploration.
Why Computational Resource-Friendly AI Education Matters
Many schools, especially in underserved regions, lack access to high-end hardware required for running complex AI models. However, this limitation should not prevent students from diving into the world of artificial intelligence. By focusing on computationally lightweight tools and innovative teaching methods, educators can foster curiosity and creativity while bypassing the need for expensive infrastructure.
For example, tools like Scratch programming language or Google’s Teachable Machine offer simplified environments to introduce concepts like machine learning and pattern recognition. These platforms are browser-based and run on basic computers, making them ideal for resource-constrained settings.
Designing Projects for Limited Resources
To make AI education accessible, projects need to be designed with simplicity and scalability in mind. Here are a few examples:
- Data Labeling Activities: Students can manually label datasets, such as images or text, to learn about supervised learning without requiring model training.
- Pre-trained Models: Use pre-trained models to demonstrate AI concepts. For instance, students can explore image classification using lightweight APIs like TensorFlow Lite.
- Rule-Based AI: Introduce AI logic with rule-based systems, which require no machine learning but still demonstrate decision-making processes.
These projects not only reduce the computational burden but also emphasize foundational AI concepts, ensuring students grasp the basics before moving on to more complex tasks.
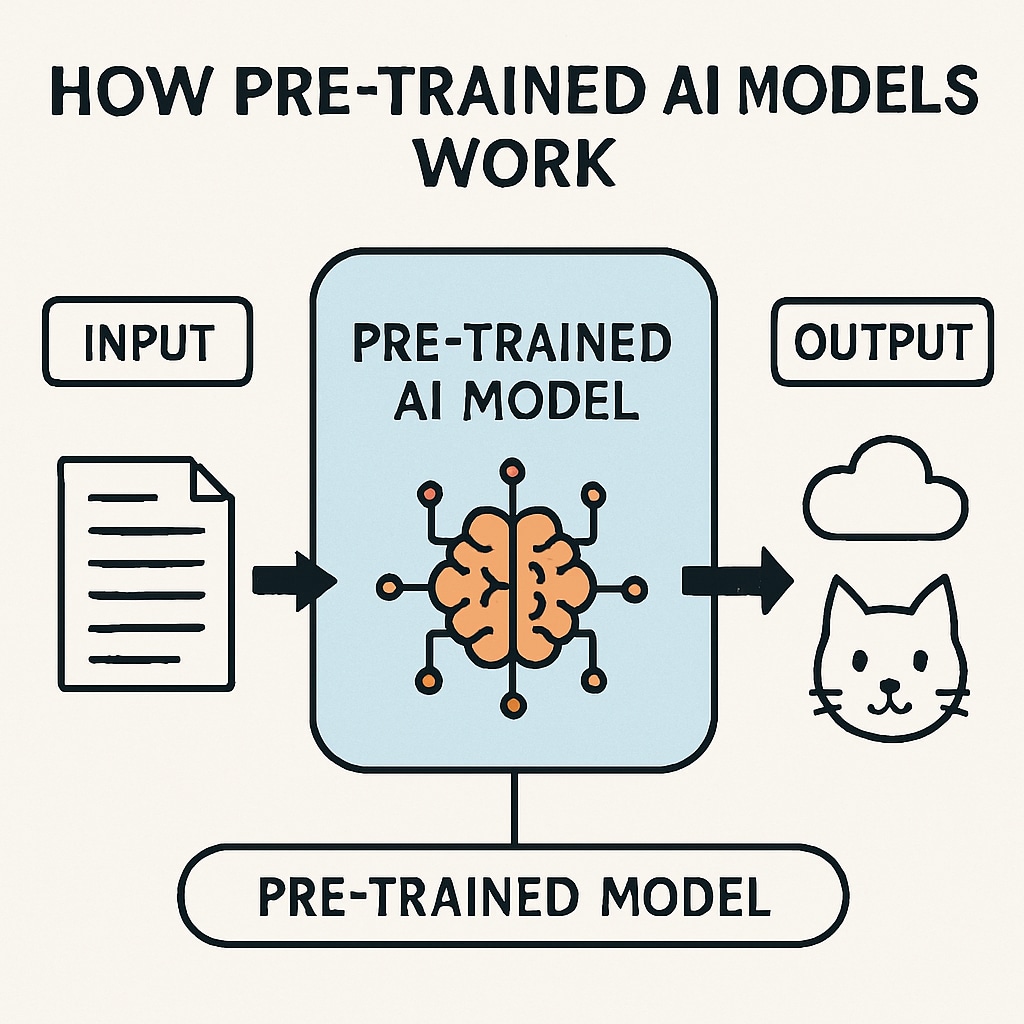
Teaching Methods That Encourage Exploration
Alongside resource-friendly projects, effective teaching methods are essential. Teachers can adopt a gradual learning path, starting with foundational concepts and building up to practical applications. Below are key strategies:
- Gamified Learning: Use AI-based games to teach principles like neural networks or decision trees in an engaging way.
- Collaborative Projects: Encourage teamwork on small-scale AI projects to foster problem-solving and critical thinking.
- Real-Life Applications: Relate AI concepts to everyday scenarios, such as chatbots or recommendation systems, to make learning tangible.
Moreover, educators can use visualization tools to simplify complex topics. For instance, platforms like Britannica’s AI resources provide accessible explanations of AI principles, helping students grasp abstract ideas visually.
Ensuring Equity in AI Education
Equitable AI education is not just about hardware; it’s about mindset. Schools can form partnerships with organizations that provide free or low-cost access to educational resources. For instance, initiatives like Code.org or AI4All offer materials tailored for K12 learning environments.
Additionally, students can leverage open datasets and free software to experiment with AI, leveling the playing field for those without access to expensive tools. By embracing these approaches, educators make AI education inclusive and inspire students to become innovators in the AI era.
In conclusion, creating computationally accessible artificial intelligence courses and student projects is critical to democratizing AI education in K12 schools. With thoughtful project designs, innovative teaching methods, and equitable access, we can empower every student to explore and innovate in the world of AI—regardless of their hardware limitations.


