The American high school geometry curriculum system, along with the development of geometric application programs, plays a crucial role in shaping students’ mathematical understanding. In this article, we will analyze the structure and teaching practices of this curriculum.
Understanding the American High School Geometry Curriculum Structure
The American high school geometry curriculum is designed to build students’ logical thinking and spatial awareness. It typically covers topics such as Euclidean geometry, coordinate geometry, and transformational geometry. For example, Euclidean geometry focuses on the study of points, lines, angles, and shapes. According to Wikipedia’s page on Geometry education in the United States, these concepts are gradually introduced and deepened over the course of the high school years. This structured approach helps students establish a solid foundation in geometric principles.
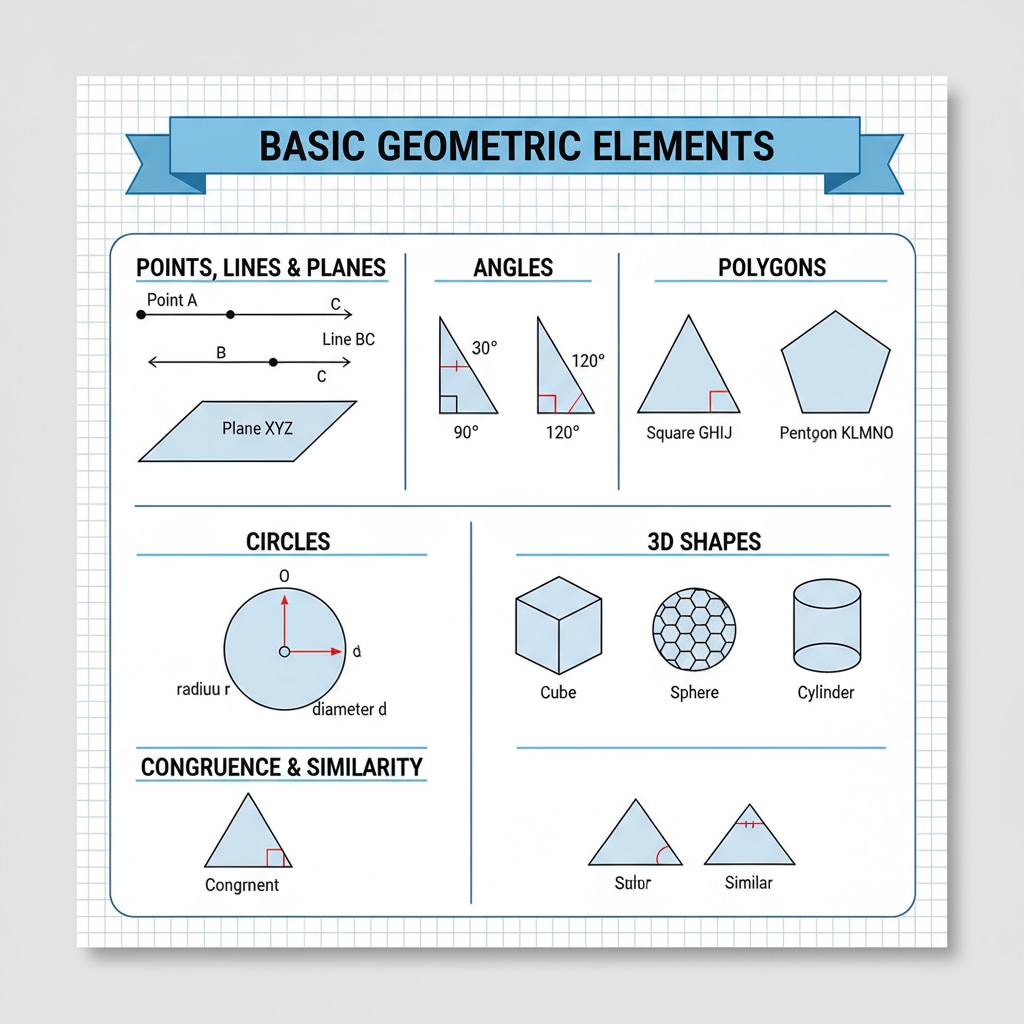
Teaching Practices in American High School Geometry
Teachers in American high schools adopt various teaching methods to engage students in geometry. They often use real-world examples to make abstract geometric concepts more relatable. For instance, using the architecture of buildings to explain concepts like symmetry and proportion. Additionally, hands-on activities and group work are encouraged. As stated on Britannica’s page on Geometry, this interactive approach helps students better understand and apply geometric knowledge. Through these practices, students not only learn the theoretical aspects but also develop practical skills.
In addition to traditional teaching methods, the digital age has brought new opportunities to American high school geometry education. The development of geometric application programs can enhance the learning experience. These apps can provide interactive visualizations, allowing students to explore geometric concepts in a more engaging way. As a result, students may find it easier to grasp complex ideas and improve their problem-solving abilities.
Readability guidance: By using short paragraphs and lists, we have summarized key points. Each H2 section has relevant content presented clearly. The passive语态 is kept to a minimum, and transition words like ‘for example’, ‘additionally’, and ‘as a result’ are used to make the flow smooth.


