Baccalauréat, preparation strategies, and time management are crucial elements for high school students navigating the challenging path towards college entrance exams. With the heavy academic burden of high school courses and the looming pressure of the baccalauréat, many students find themselves in a time management quagmire. This article aims to provide a systematic approach to help students prepare for the baccalauréat without sacrificing their current academic performance, thus making a smooth transition from “burning the midnight oil” to “smart studying.”
Understanding the Baccalauréat
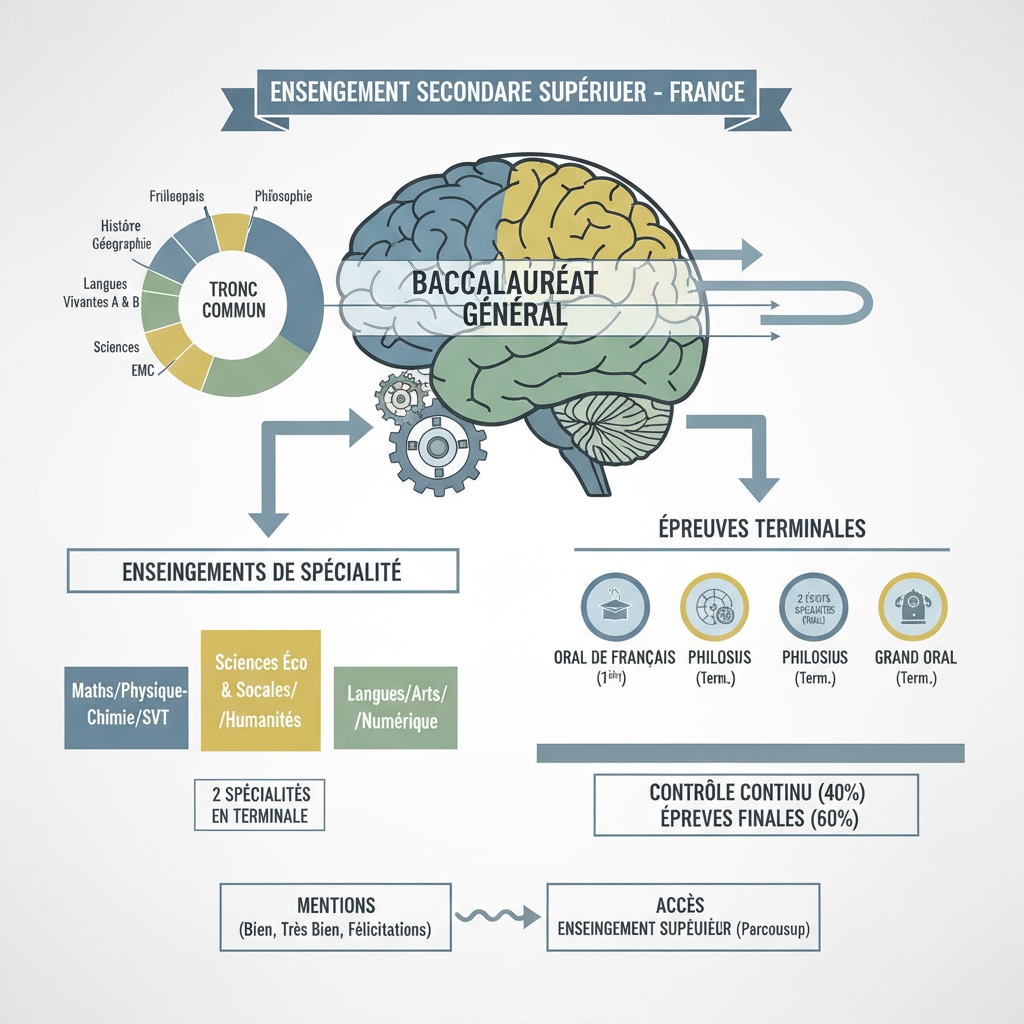
The baccalauréat is a significant milestone for high school students. It serves as a gateway to higher education. Before diving into preparation, it’s essential to understand its structure, subjects, and evaluation criteria. For example, different regions or educational systems may have variations in the baccalauréat requirements. Baccalaureate on Wikipedia provides detailed information about the baccalauréat in various countries.
Effective Time Management
Time management is the key to juggling high school coursework and baccalauréat preparation. First, create a detailed schedule. Allocate specific time slots for each subject, study sessions, and breaks. For instance, set aside an hour each day for baccalauréat-specific study. Additionally, make use of fragmented time, like the time between classes or during lunch breaks. Tools such as calendars or task management apps can be very helpful. Time Management on Britannica offers more insights into efficient time management techniques.

Another aspect is prioritization. Identify the most important tasks and subjects. If you’re struggling with a particular baccalauréat subject, prioritize it and allocate more study time. However, don’t neglect your regular high school courses as they also contribute to your overall academic development.
Readability guidance: Use short paragraphs and lists to summarize key points. Provide a list under each H2 when possible. Control the proportion of passive voice and long sentences. Incorporate transitional words like “however,” “therefore,” “in addition,” “for example,” and “as a result” throughout the article.


