For students aspiring to pursue a career in biostatistics, the choice between Calculus 2 and Linear Algebra is a critical step in their academic journey. These math courses lay the foundation for the statistical methods and models used in the field. But how do you determine which course is more relevant to your goals? In this article, we’ll explore the strengths of both courses, their applications in biostatistics, and factors to consider when making your decision.
Understanding the Role of Math in Biostatistics
Biostatistics is the application of statistical techniques to biological and health sciences. Mathematics serves as the backbone of this discipline, allowing researchers to analyze complex data and draw meaningful conclusions. While both Calculus 2 and Linear Algebra are valuable, their utility in biostatistics differs. Understanding how each course supports statistical methods can guide your decision.
Calculus 2: Strengths and Applications
Calculus 2 focuses on integral calculus, sequences, and series, which are essential for understanding continuous probability distributions and optimization problems. Key topics include:
- Integration techniques, which are useful for calculating probabilities and expectations in statistics.
- Infinite series, which play a role in approximating complex statistical formulas.
- Applications to physics and biology, providing context for real-world problems in biostatistics.
For example, modeling the spread of diseases often requires solving differential equations, a skill rooted in Calculus 2. As a result, students interested in epidemiology or dynamic systems may find this course particularly beneficial.
Linear Algebra: Practical Insights
Linear Algebra, on the other hand, is the study of vector spaces and linear transformations. Its applications in biostatistics are vast, particularly in data analysis and computational methods. Key topics include:
- Matrix operations, which are foundational for multivariate statistics and machine learning.
- Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, used in Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and other dimensionality reduction techniques.
- Systems of linear equations, critical for regression analysis and solving optimization problems.
Linear Algebra is indispensable for students planning to work with large datasets or advanced statistical models. For instance, genomic studies often rely on matrix operations to process high-dimensional data.
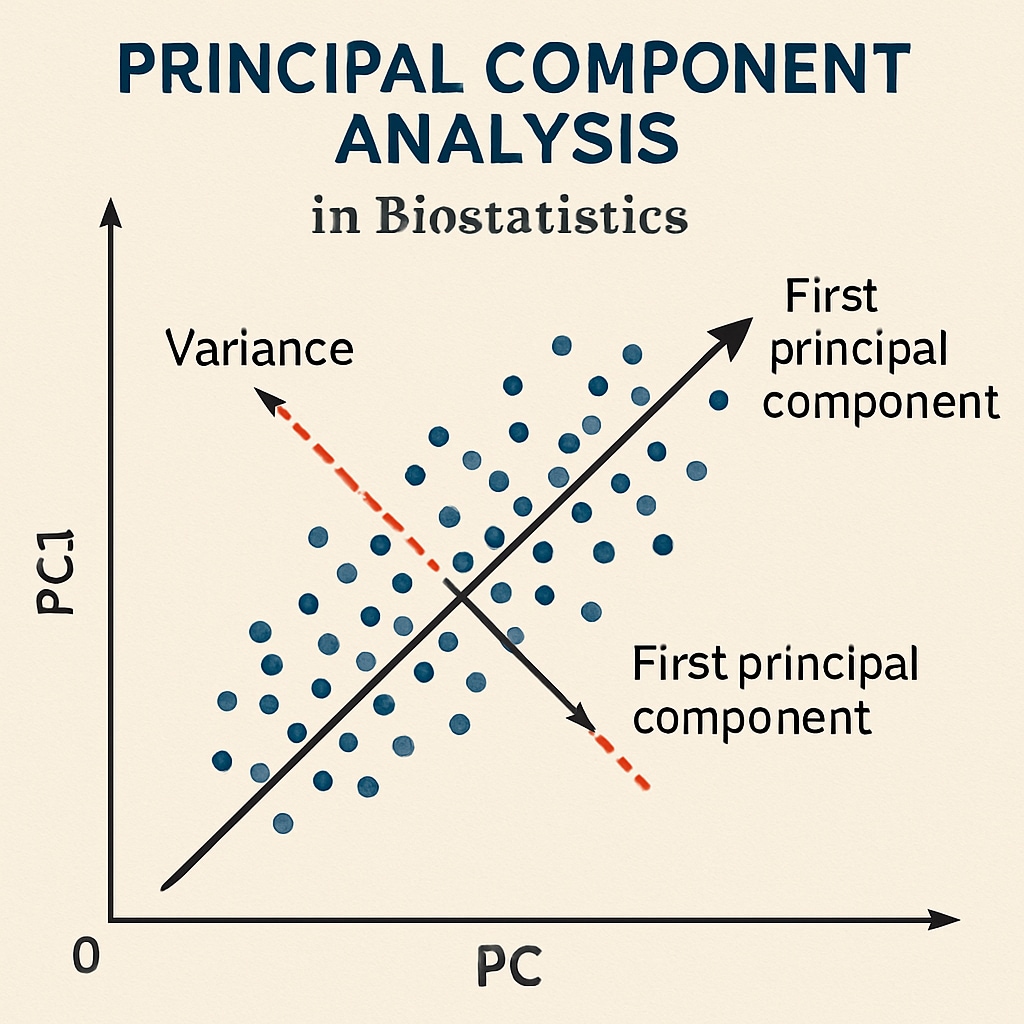
Factors to Consider When Choosing
To make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
- Career Goals: Are you more interested in theoretical modeling (favoring Calculus 2) or data analysis and computation (favoring Linear Algebra)?
- Course Availability: Evaluate the quality of instruction and resources for both courses at your institution.
- Future Coursework: Some graduate programs prioritize one course over the other. Check prerequisites and recommendations for your target programs.
In addition, seek advice from academic advisors or professors. Their insights can provide clarity based on your strengths and aspirations.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach
Ultimately, both Calculus 2 and Linear Algebra offer unique tools for biostatistics. If possible, taking both courses is ideal, as they complement each other and broaden your mathematical foundation. However, if you must choose, let your career goals and academic interests guide your decision. Remember, the skills you develop in these courses will serve as the building blocks for your success in biostatistics.
For further reading on the importance of math in biostatistics, check out Biostatistics on Wikipedia or explore advanced topics in Linear Algebra on Britannica.
Readability guidance: Use short paragraphs and lists to summarize key points. Balance technical details with practical advice, ensuring accessibility for a general audience.


