When embarking on a biostatistics journey, students often face the challenging decision of selecting the right mathematics course. Whether to choose Calculus 2 or Linear Algebra depends heavily on your academic goals and the demands of biostatistics as a discipline. Both courses provide unique tools and perspectives essential for mastering statistical techniques. This article examines the advantages of each, offering guidance for students striving to make an informed choice in their academic planning.
Understanding the Role of Mathematics in Biostatistics
Biostatistics relies heavily on mathematical principles to analyze and interpret biological data. A strong foundation in mathematics is not just beneficial but essential for success in this field. Students are often advised to focus on courses like Calculus 2 or Linear Algebra, as these subjects form the backbone of statistical methodologies.
For example, Calculus 2 dives into integral calculus and series, which are critical for understanding continuous probability distributions and optimization problems. On the other hand, Linear Algebra emphasizes vector spaces and matrix operations, which are foundational for multivariate statistics and data modeling. Both courses equip students with tools to handle the mathematical demands of biostatistics.
Calculus 2: Strengthening Analytical Foundations
Calculus 2 builds upon the basics of differential and integral calculus, focusing on advanced topics like infinite series, multivariable functions, and integration techniques. These concepts are directly applicable to biostatistics in areas such as:
- Continuous Probability Distributions: Understanding functions like the normal distribution requires knowledge of integration.
- Optimization Problems: Finding maximum likelihood estimates often involves advanced calculus techniques.
- Modeling Growth and Decay: Biological processes, such as population dynamics, are commonly modeled with calculus.
However, while Calculus 2 is undeniably valuable, its application in biostatistics is often indirect. Many statistical tools have integrated these calculations into software, reducing the need for manual computation. Nevertheless, a solid grasp of calculus concepts ensures a deeper understanding of statistical models.
Linear Algebra: The Language of Data and Models
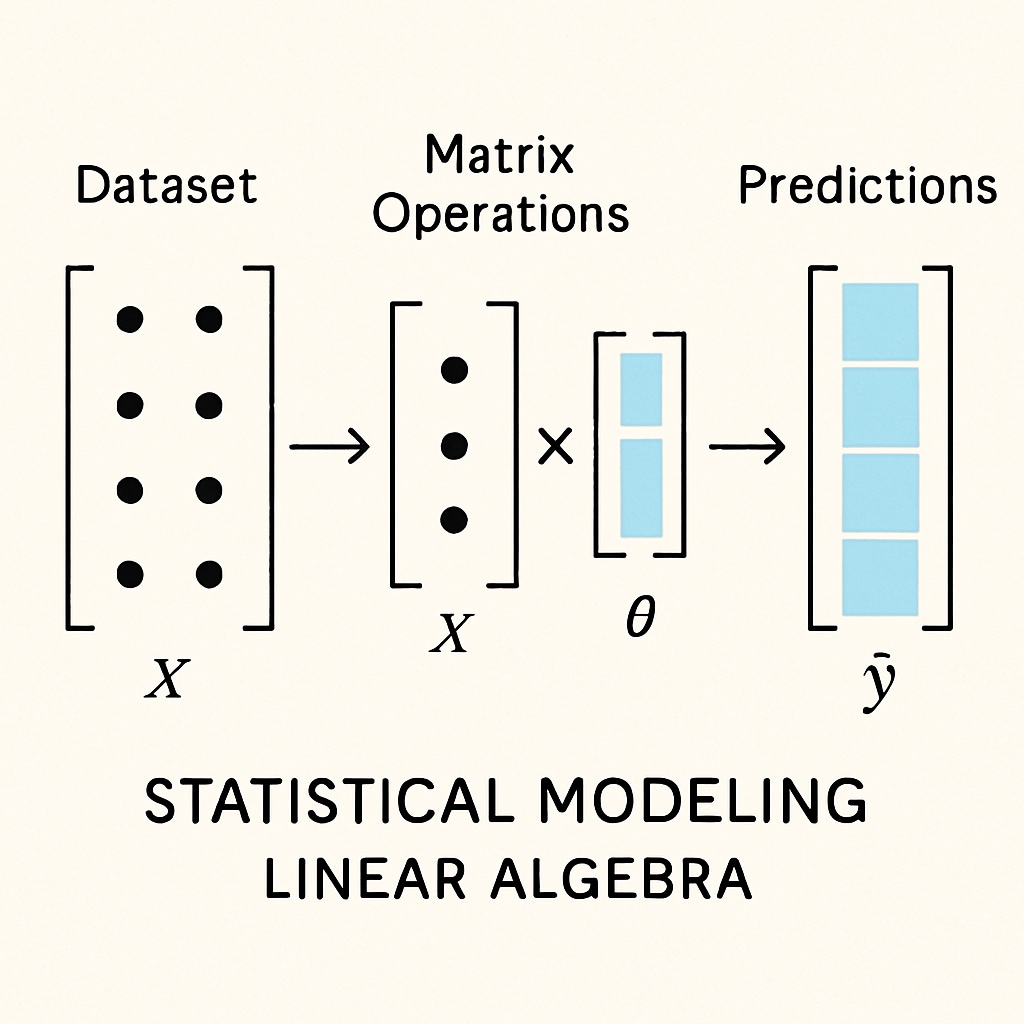
Linear Algebra, in contrast, is more focused on the structure and manipulation of data, making it incredibly relevant in modern biostatistics. Key concepts like matrix theory, eigenvalues, and vector spaces are instrumental for tasks such as:
- Multivariate Analysis: Techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) rely heavily on matrix operations.
- Data Transformation: Linear transformations are used to preprocess and normalize data in statistical modeling.
- Machine Learning Applications: Many algorithms, including regression and classification models, are built on linear algebra principles.
Unlike Calculus 2, Linear Algebra is directly applicable to computational statistics and data science. Its emphasis on matrices and vectors makes it a practical choice for students aiming to work with large datasets and perform advanced analyses using statistical software.
Choosing the Right Course: Key Considerations
Deciding between Calculus 2 and Linear Algebra involves assessing your career goals, academic interests, and the quality of instruction available. Here are some factors to help guide your decision:
- Relevance to Biostatistics: If your focus is on theoretical understanding, Calculus 2 may be the better choice. For applied data analysis, Linear Algebra is often more practical.
- Teaching Quality: The effectiveness of the course depends on the instructor and resources available. Research reviews or consult peers to determine the quality of each offering at your institution.
- Future Applications: Consider the mathematical tools required for your intended career path. Students interested in computational biology or data science may benefit more from Linear Algebra.
In some cases, students may find it beneficial to take both courses, as their combined knowledge significantly enhances statistical proficiency. However, if time or resources are limited, aligning the course selection with your specific interests remains crucial.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Mathematical Preparation
Ultimately, both Calculus 2 and Linear Algebra are invaluable for aspiring biostatisticians. While Calculus 2 enhances analytical foundations, Linear Algebra equips students with the tools to navigate complex data structures. Selecting the right course requires thoughtful consideration of your academic goals and career aspirations. By making an informed choice, you can build a strong mathematical foundation that supports your success in biostatistics.
For more detailed insights into these courses, refer to reputable online resources such as Calculus on Wikipedia and Linear Algebra on Wikipedia.


