When planning your future in Computer Science, understanding the differences between BTEC and A-level qualifications is crucial for university applications and career success. Both pathways offer unique advantages, but their suitability depends on your learning style and career goals. This article compares BTEC Computer Science and A-level qualifications to help you make an informed decision.
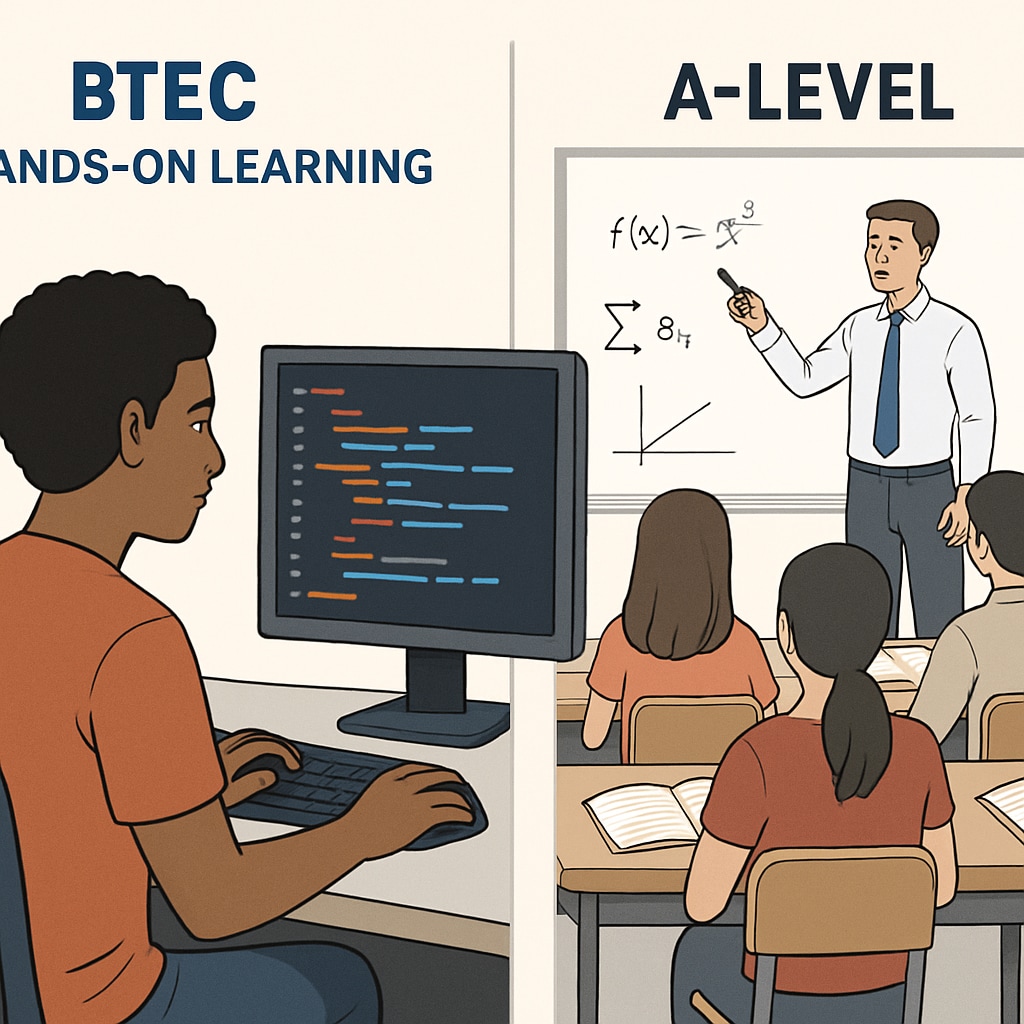
Understanding BTEC and A-level Qualifications
BTEC (Business and Technology Education Council) qualifications are vocational courses designed to provide hands-on experience in specific fields like Computer Science. In contrast, A-levels are academic qualifications that focus on theoretical knowledge and are widely recognized for university entry. According to UK government guidelines, BTECs emphasize practical skills, while A-levels prioritize academic rigor.
- BTEC Computer Science: Coursework-based with real-world projects
- A-level Computer Science: Exam-focused with theoretical depth
- Duration: Both typically take two years to complete
University Acceptance and Recognition
While A-levels have traditionally been the standard for university entry, many institutions now accept BTEC qualifications, especially for Computer Science degrees. However, some top universities may still prefer A-levels for highly competitive courses. The UCAS website provides detailed comparison tools to check specific university requirements.

Career Prospects in Computer Science
Both qualifications can lead to successful careers in tech, but they may open different doors:
- BTEC graduates: Often enter the workforce sooner with practical skills
- A-level graduates: Typically pursue higher education before employment
- Industry trends: Many employers value practical experience from BTEC
Readability guidance: Use short paragraphs with clear transitions like “however” and “therefore.” Keep sentences concise (12-16 words average) and prioritize active voice for better engagement.


