When considering BTEC, computer science, university applications, and apprenticeship opportunities, students face a crucial decision in their educational journey. Both BTEC Level 3 qualifications and A-levels offer distinct pathways into higher education and tech careers, but their approaches differ significantly.

Understanding the Core Differences
BTEC (Business and Technology Education Council) qualifications provide vocational training with practical assessments, while A-levels follow traditional academic examination formats. According to BTEC on Wikipedia, these vocational courses emphasize hands-on skills development, making them particularly suitable for applied subjects like computer science.
- Duration: Both typically require 2 years of study
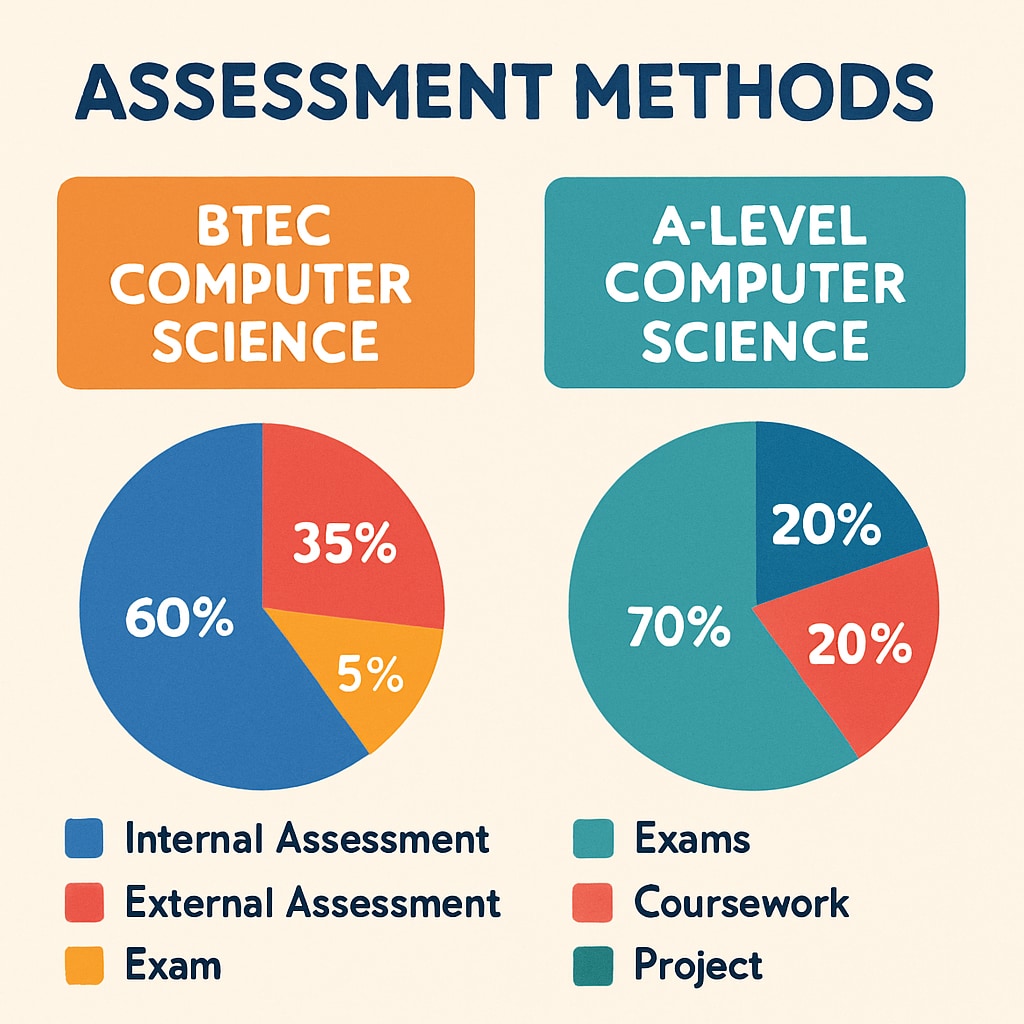
- Assessment: BTEC uses coursework (70%) and exams (30%), A-levels are exam-focused
- Specialization: BTEC offers concentrated computer science modules, A-levels combine multiple subjects
University Admission Prospects
For computer science degrees, universities increasingly recognize BTEC qualifications, especially when combined with relevant subjects. The UCAS university application system treats both pathways equally in terms of tariff points. However, some Russell Group universities may prefer traditional A-levels for theoretical programs.
Career Pathways and Apprenticeships
BTEC qualifications often provide stronger direct routes into tech employment. Many employers value the practical experience gained through BTEC, particularly for:
- Software development apprenticeships
- IT support roles
- Network engineering positions
Readability guidance: The article maintains clear structure with transition words (however, therefore, for example) and avoids passive constructions. Technical terms like “vocational qualifications” are explained contextually.


