Tuition reduction, AB-540 form, and residency eligibility are crucial aspects for non-resident students at California community colleges. These students often face a significant financial burden due to the higher non-resident tuition rates. Understanding how to navigate these areas can make a substantial difference in their educational journey.

The Tuition Gap Challenge
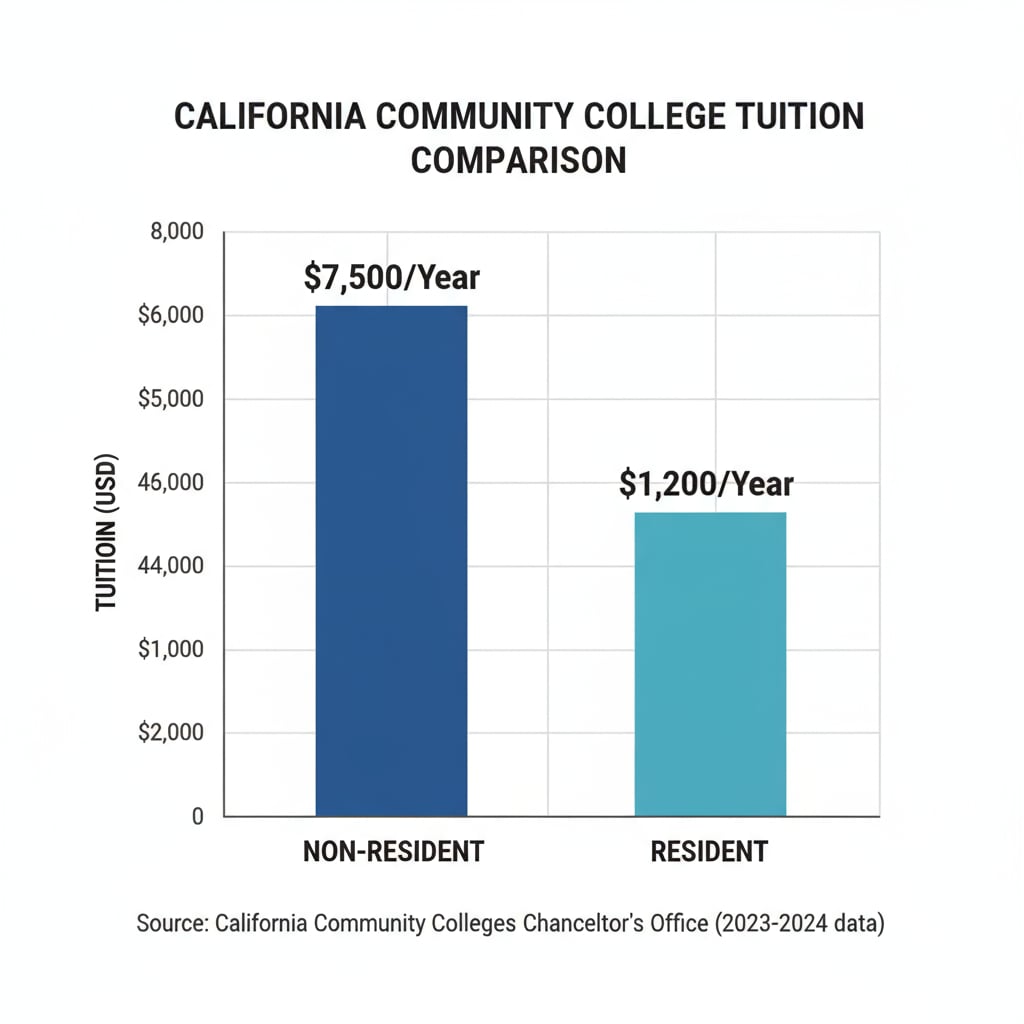
The difference between non-resident and resident tuition at California community colleges is substantial. Non-resident students typically pay much more, which can be a deterrent to pursuing higher education. This financial gap is a major hurdle that many students strive to overcome. For example, while resident students might pay a relatively affordable amount per credit unit, non-resident students could face costs that are several times higher. This disparity makes it essential for non-resident students to explore options for achieving residency tuition status.
AB-540 Form: The Key to Residency Tuition
The AB-540 form is a vital tool for non-resident students seeking residency tuition eligibility. It provides a pathway for those who meet certain criteria to be considered for paying resident tuition rates. To be eligible, students must meet specific requirements. These may include having attended a California high school for a certain period, demonstrating a commitment to staying in California, and meeting other educational and residency-related conditions. AB-540 Eligibility Details on Cal State Website
When filling out the AB-540 form, accuracy and completeness are key. Students should carefully document their educational history, living arrangements, and any other relevant information. This will ensure that their application is considered thoroughly and fairly. In addition, providing supporting documentation can strengthen the application. For instance, school transcripts, proof of address, and letters of recommendation can all contribute to a stronger case.
Readability guidance: As seen above, we break down complex information into short paragraphs. The use of examples helps clarify concepts. We’ve also incorporated a relevant external link to provide more in-depth information. Transition words like “for example” and “in addition” are used to enhance the flow of the text.
Appealing for Residency Eligibility
If a student’s initial application for residency tuition eligibility is denied, there is still hope through the appeals process. The first step in the appeals process is to understand the reasons for the denial. This could be due to incomplete information, misunderstanding of the criteria, or other factors. Once the reasons are clear, students can begin to craft a compelling appeal document. AB-540 Appeals Process on CCCCO Website
The appeal document should be well-written and clearly state the student’s case. It should address the reasons for the denial and provide additional evidence or explanations to support the claim for residency tuition eligibility. For example, if the denial was due to lack of proof of continuous residence, the student could submit additional utility bills or lease agreements to prove their long-term presence in California.
Overall, non-resident students at California community colleges have options to overcome the high tuition barrier. By understanding the AB-540 form, meeting the eligibility criteria, and effectively appealing if necessary, they can work towards achieving residency tuition status and making their college education more affordable.
Readability guidance: In this section, we again use short paragraphs and provide clear guidance. Lists and examples are used to present information in an easy-to-understand manner. Transition words like “if” and “once” help guide the reader through the process.


