Education funding is a crucial aspect of any educational system, and the Expanded Learning Opportunity Program (ELO-P) in California is a significant initiative in this regard. ELO-P is designed to provide students with more learning opportunities, aiming to bridge educational gaps and enhance overall student development.
The Promising Side of ELO-P
ELO-P has several notable advantages. Firstly, in terms of educational equity, it targets students from disadvantaged backgrounds. By providing additional resources and learning time, it helps level the playing field. For example, students who may not have access to quality after-school programs due to financial constraints can now benefit from ELO-P-funded activities. This initiative also focuses on enhancing students’ comprehensive skills. Through extended learning opportunities, students can engage in various enrichment activities such as art, music, and sports, which contribute to their well-rounded development. State Education Policy Guide on Edweek

The Hurdles Faced by ELO-P
However, ELO-P is not without its challenges. One of the major issues is the implementation barrier. Schools may struggle to effectively integrate the new program into their existing schedules and teaching models. In addition, resource distribution remains a problem. Some areas may receive more funding and resources than others, leading to an uneven implementation of the program. This can undermine the very goal of promoting educational equity that ELO-P aims to achieve. Addressing Inequities in Education Funding on Brookings
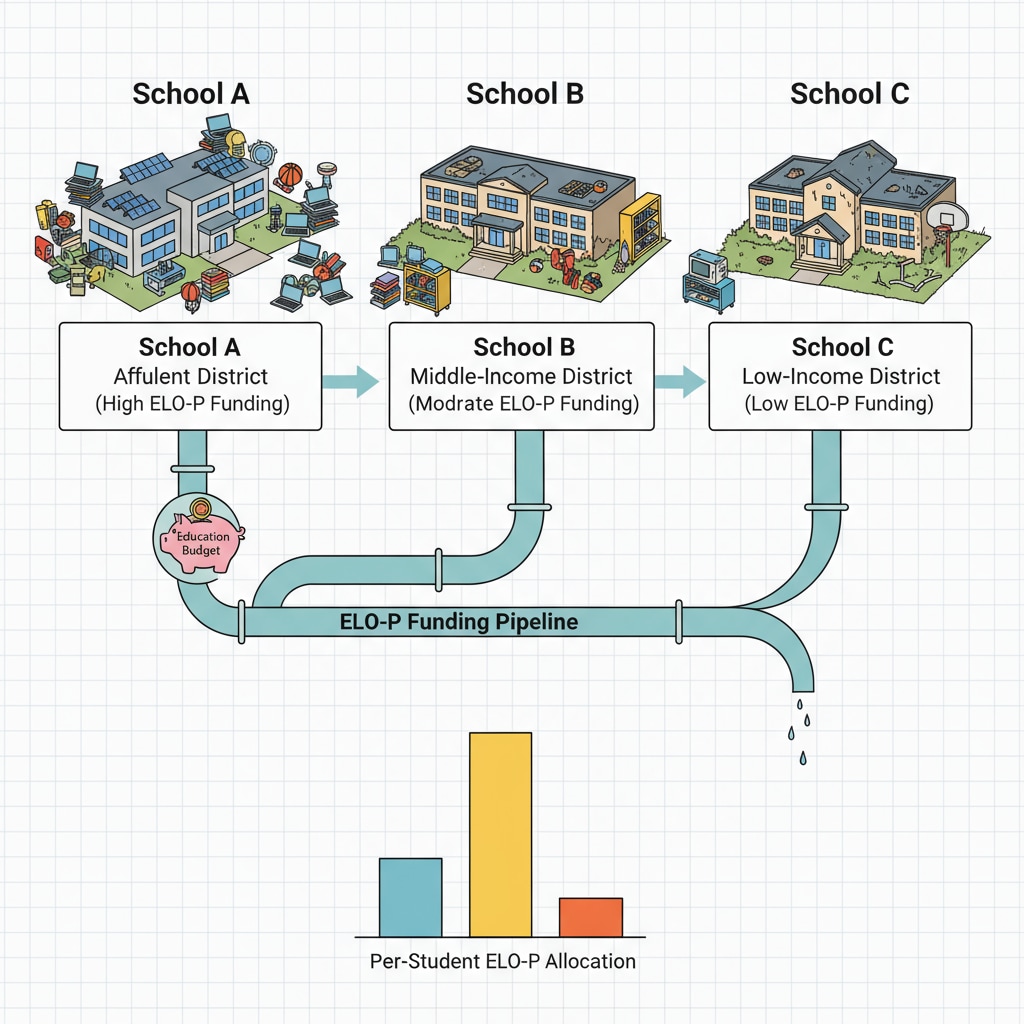
Evaluating the implementation effect of ELO-P is essential. By analyzing student performance data, feedback from teachers and students, and the overall impact on the educational environment, we can determine whether the program is achieving its intended goals. In conclusion, while ELO-P in California holds great promise in the realm of education funding and expanded learning opportunities, addressing its challenges is crucial for its long-term success and the betterment of students’ educational experiences.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs and lists to summarize key points. Each H2 section provides a list of relevant aspects. The proportion of passive voice and long sentences is controlled, and transition words are added throughout the text to enhance readability.


