Career Technical Education (CTE) is revolutionizing the educational landscape by integrating traditional academic subjects with hands-on technical skills. Across school districts, educators are finding innovative ways to organize and implement CTE programs, fostering a holistic approach to student learning and development. This fusion of practical skills with foundational knowledge is not just reshaping K12 education but also preparing students for future success in a rapidly evolving workforce.
The Intersection of CTE and Traditional Academic Learning
CTE programs are designed to complement traditional academic subjects such as math, science, and language arts, by providing real-world applications. For example, a CTE course in engineering can integrate mathematical principles like geometry and algebra, while a culinary arts program might incorporate chemistry concepts related to food preparation. This interdisciplinary approach helps students see the relevance of academic knowledge in practical scenarios, boosting engagement and retention.
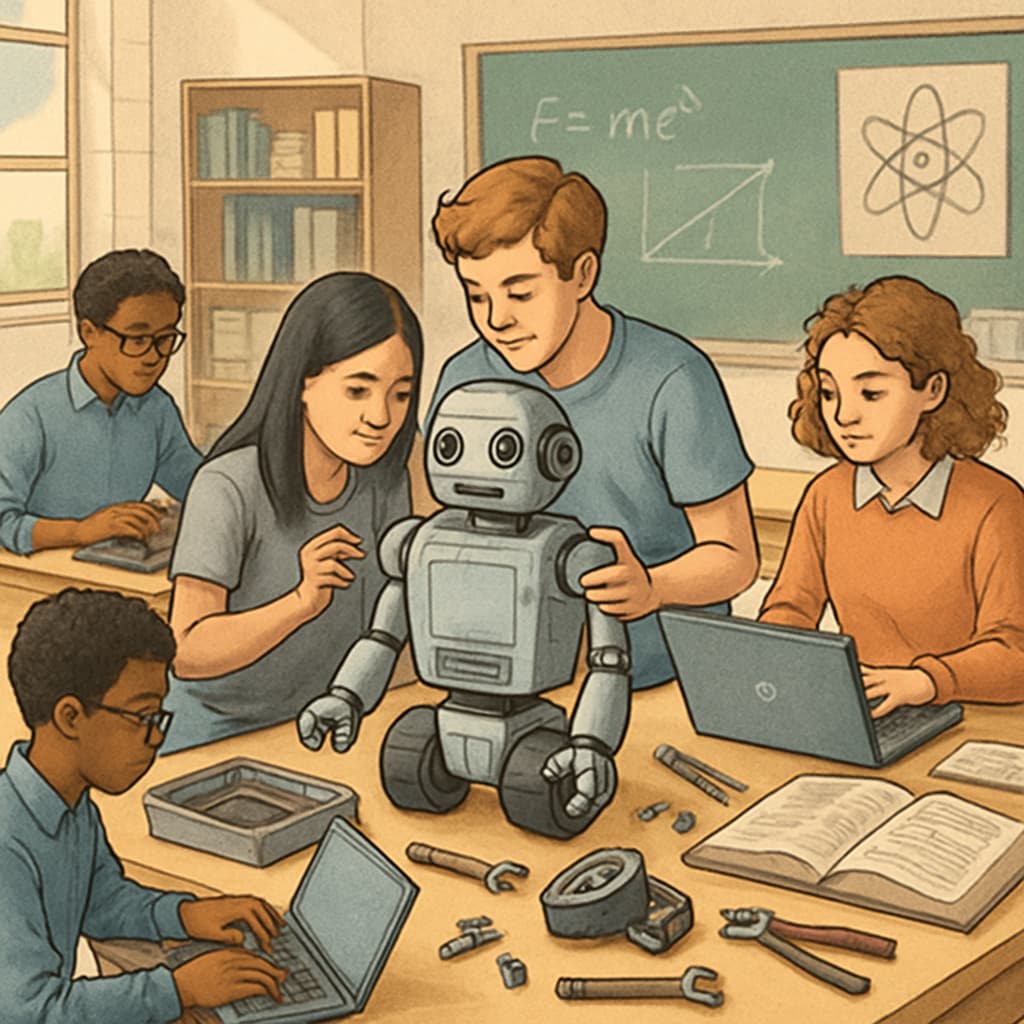
Research has shown that students enrolled in CTE programs often outperform their peers in traditional-only academic settings. According to a Britannica article on technical education, the hands-on nature of CTE fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential for academic and career success. Moreover, these programs promote collaboration, creativity, and communication—skills that are increasingly valued in modern workplaces.
Organizational Models for Implementing CTE in School Districts
School districts adopt various organizational structures to implement CTE programs effectively. Some districts integrate CTE courses directly into the standard curriculum, while others establish dedicated career academies or technical schools. These specialized institutions often provide students with access to industry-standard equipment and facilities, enhancing the quality of their learning experience.
In addition, partnerships with local businesses and community organizations are a cornerstone of successful CTE implementation. These collaborations allow schools to align their programs with regional workforce needs, ensuring students are equipped with relevant skills. For example, a district with a robust healthcare sector might offer CTE pathways in nursing or medical technology. For further insights, the Vocational Education page on Wikipedia provides an overview of how such programs can bridge the gap between education and employment.
Benefits for Students and Educators
CTE’s impact extends beyond academic achievement. Students who participate in these programs often report higher levels of confidence and motivation, as they can directly see the value of their education. Moreover, CTE prepares students for diverse career paths, whether they choose to enter the workforce immediately after high school or pursue higher education.
For educators, CTE offers an opportunity to innovate teaching methods and collaborate across disciplines. Teachers can work together to design projects that blend technical and academic skills, creating a dynamic and engaging classroom environment. This not only enhances student learning but also fosters professional growth among educators.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
While CTE programs have demonstrated significant benefits, challenges remain in ensuring equitable access across all school districts. Funding constraints, lack of qualified instructors, and limited facilities can hinder the expansion of these initiatives. However, increased awareness of CTE’s advantages is driving policy changes and investment at local, state, and national levels.
Moving forward, school districts must prioritize inclusivity and adaptability in their CTE offerings. This includes accommodating students with diverse needs and interests, as well as integrating emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and renewable energy into the curriculum. By addressing these challenges, educators can unlock the full potential of Career Technical Education.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs and lists summarize key points for clarity. Use of active voice and transition words ensures smooth flow. CTE’s interdisciplinary approach is highlighted, emphasizing its role in modern education.


