Identifying and nurturing gifted children requires reliable and scientific methods. In the realm of children’s talent assessment, tests such as WISC (Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children) and CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test) are often considered the gold standard. These tools provide valuable insights into a child’s cognitive abilities, helping parents and educators craft tailored developmental plans. However, understanding the differences between these tests and their appropriate applications is essential for making informed decisions.
Understanding the WISC: The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children
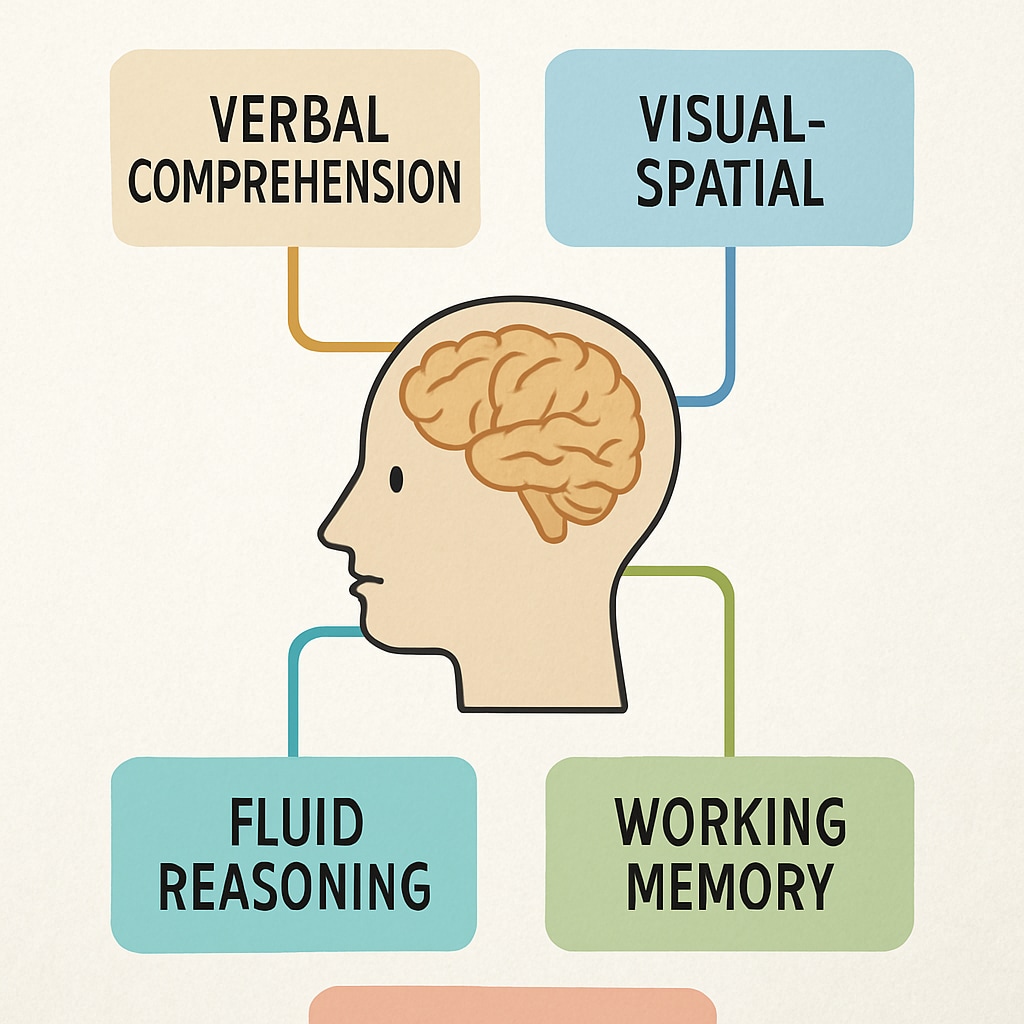
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, commonly referred to as WISC, is one of the most widely recognized intelligence tests globally. Designed to measure a child’s intellectual potential, WISC evaluates various cognitive functions across domains such as verbal comprehension, working memory, and processing speed. This multi-faceted approach not only identifies strengths but also highlights areas needing improvement.
WISC is particularly useful for diagnosing intellectual disabilities or identifying gifted children. Its highly detailed scoring system allows educators and psychologists to create customized support strategies. For example, a child excelling in verbal tasks but struggling with processing speed may benefit from interventions targeting time management and focus.
Exploring CogAT: Cognitive Abilities Test
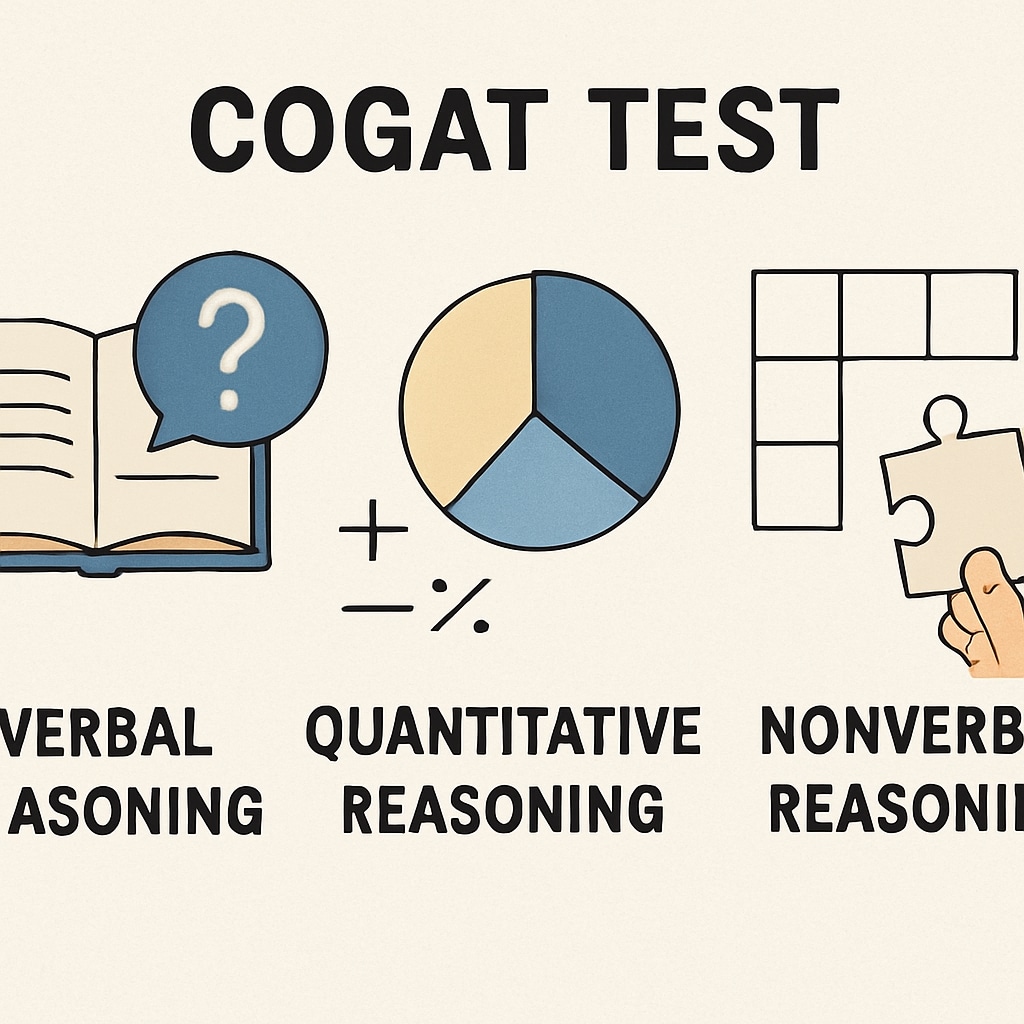
While WISC focuses on intellectual potential, CogAT takes a broader approach by assessing reasoning abilities across verbal, non-verbal, and quantitative domains. The Cognitive Abilities Test is often used in schools to screen for gifted programs due to its ability to measure a child’s problem-solving and critical-thinking skills.
CogAT is particularly advantageous for identifying students with unique learning profiles, such as those who excel in non-verbal reasoning but face challenges in linguistic tasks. This versatility makes CogAT suitable for diverse student populations, including non-native English speakers.
WISC vs. CogAT: Choosing the Right Tool
When it comes to selecting between WISC and CogAT, understanding the purpose of the assessment is crucial. Here are some key distinctions to consider:
- Purpose: WISC is ideal for diagnosing cognitive disabilities or identifying exceptional intellectual abilities, while CogAT is better suited for identifying strengths in reasoning and problem-solving.
- Structure: WISC provides a detailed breakdown of cognitive abilities, whereas CogAT evaluates reasoning skills across three broad domains.
- Application: WISC is typically administered in clinical settings by psychologists, while CogAT is commonly used in schools for group assessments.
Both tests are valuable tools, but their application should align with the specific goals of the assessment. Consulting with educational psychologists or school counselors can help determine the best approach for each child.
Beyond Testing: Fostering Holistic Development
While intelligence tests like WISC and CogAT offer critical insights, they represent only one piece of the puzzle in understanding a child’s potential. It is important to combine test results with observations of creativity, emotional intelligence, and even extracurricular interests. A holistic approach ensures that children are supported not just academically but also socially and emotionally.
For instance, a child who scores high on CogAT’s non-verbal reasoning section might excel in visual arts or engineering. Encouraging participation in related activities can help nurture their natural abilities. Similarly, children who perform well in verbal tasks on WISC may benefit from activities like debate clubs or creative writing workshops.
In addition, creating an environment that promotes curiosity and self-directed learning can significantly enhance a child’s development. Recognizing and celebrating their unique talents fosters confidence and a lifelong love for learning.
Conclusion: Empowering Gifted Children with the Right Tools
In conclusion, WISC and CogAT represent two of the most authoritative methods in children’s talent assessment. While WISC provides a detailed analysis of intellectual potential, CogAT offers a broader view of reasoning abilities. By understanding these tools and their applications, parents and educators can make informed decisions to help gifted children thrive.
More importantly, assessments should be complemented with opportunities for holistic growth. By fostering both cognitive and emotional development, we can empower children to reach their full potential, both in school and beyond.


