Special education, IEP, and comprehension difficulties are intertwined issues that special educators frequently encounter. Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) are crucial documents designed to meet the unique needs of students with disabilities. However, understanding these complex documents can pose significant challenges for educators.

The Complexity of IEP Documents
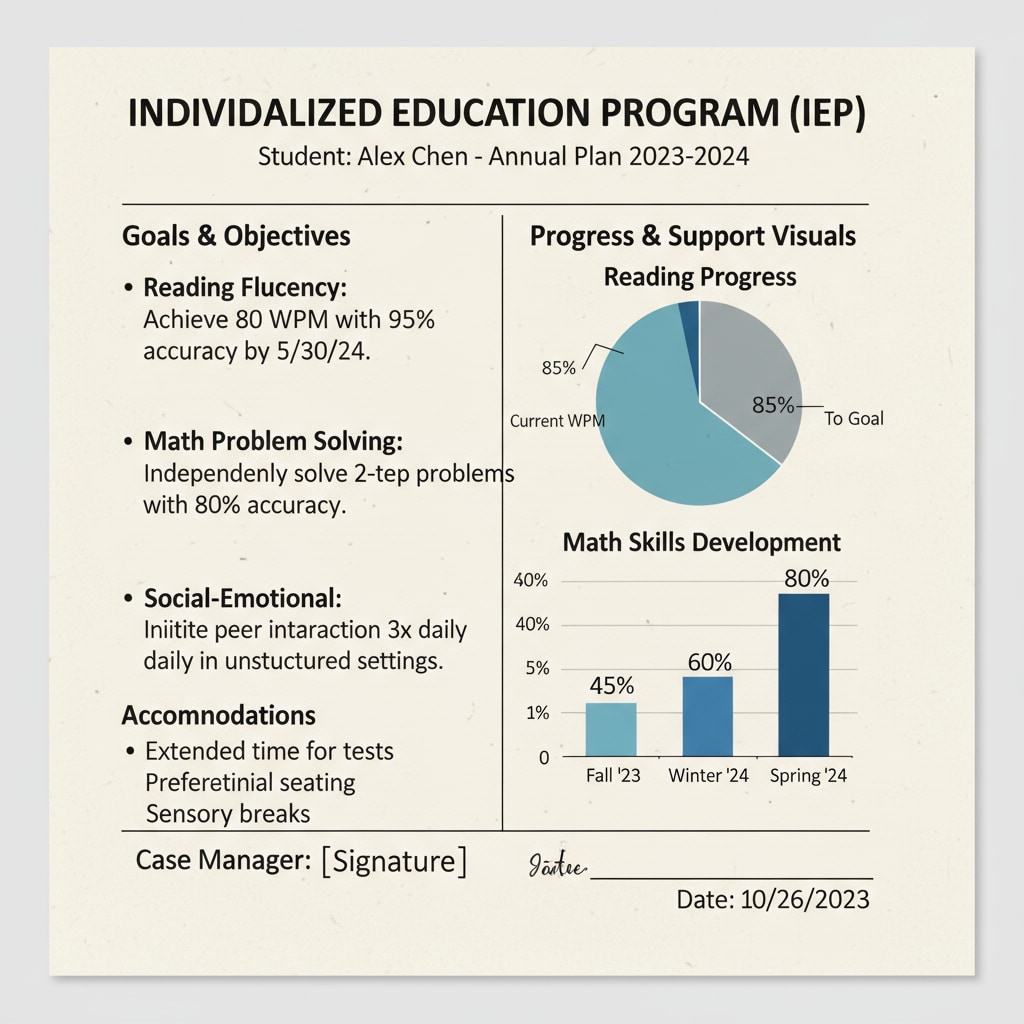
IEP documents are filled with a wealth of information, including a student’s present levels of academic achievement and functional performance, measurable annual goals, and the special education and related services to be provided. For example, they detail how a student with dyslexia will receive specialized reading instruction. This abundance of data can be overwhelming, making it difficult for educators to extract the most relevant details. According to Understood.org, the complexity of IEP language and the volume of information often contribute to comprehension issues.
Common Comprehension Hurdles
One major hurdle is the technical jargon used in IEPs. Terms like “least restrictive environment” and “response to intervention” may be unfamiliar to some educators. In addition, the legal and regulatory language can be dense and difficult to decipher. Another challenge is the individualized nature of each IEP. Since every student’s needs are different, the documents vary greatly, making it hard to develop a standard understanding approach. As a result, educators may struggle to accurately interpret the goals and services outlined.
Strategies for Overcoming Comprehension Difficulties
Professional development is key. Special educators should participate in workshops and training sessions focused on IEP interpretation. These can help them become more familiar with the jargon and the overall structure of the documents. Collaboration is also essential. Educators can work together to discuss and analyze IEPs, sharing insights and perspectives. For instance, a team of special educators can review an IEP together and break down its components. Moreover, using visual aids and summaries can simplify the information. By creating flowcharts or bullet-point summaries, educators can better understand the key points of an IEP. According to The National Center for Learning Disabilities, these strategies can enhance comprehension and improve service delivery for students with special needs.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs to present information clearly. Each section has a distinct focus, and lists could be further developed in future expansions. Passive语态 is minimized, and transition words like “however,” “in addition,” and “for example” are used to connect ideas smoothly.


